Sunni Islam represents the largest branch of Islam, emphasizing the importance of following the Sunnah, or traditions, of the Prophet Muhammad. It is characterized by its adherence to the first four caliphs as rightful successors and its focus on consensus within the Muslim community. Discover how Sunni Islam shapes the beliefs and practices of millions worldwide by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
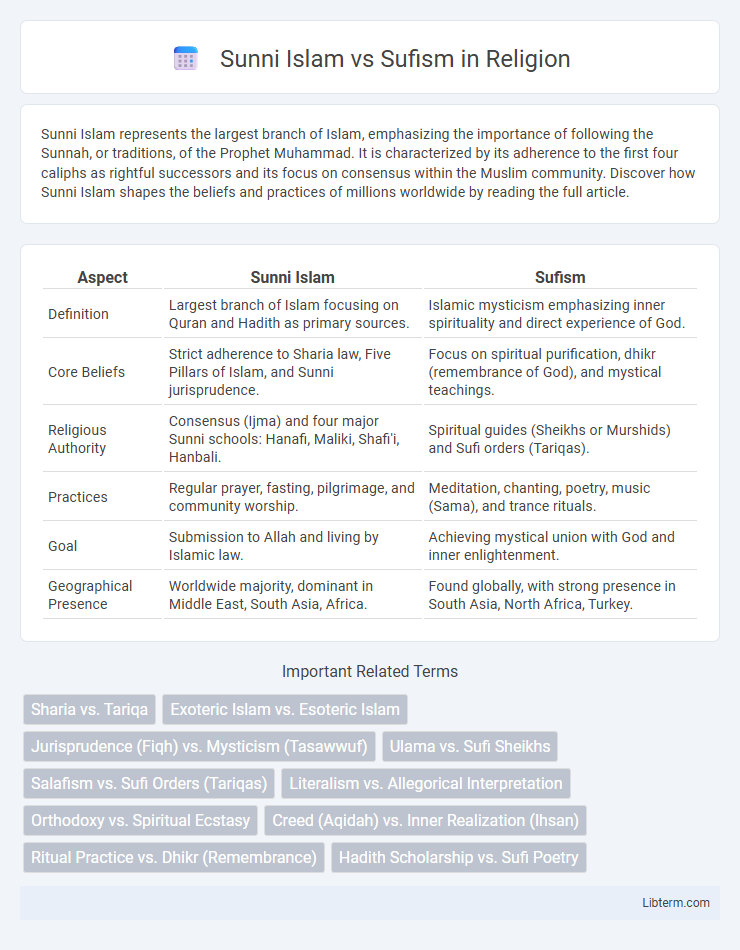
| Aspect | Sunni Islam | Sufism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Largest branch of Islam focusing on Quran and Hadith as primary sources. | Islamic mysticism emphasizing inner spirituality and direct experience of God. |
| Core Beliefs | Strict adherence to Sharia law, Five Pillars of Islam, and Sunni jurisprudence. | Focus on spiritual purification, dhikr (remembrance of God), and mystical teachings. |
| Religious Authority | Consensus (Ijma) and four major Sunni schools: Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i, Hanbali. | Spiritual guides (Sheikhs or Murshids) and Sufi orders (Tariqas). |
| Practices | Regular prayer, fasting, pilgrimage, and community worship. | Meditation, chanting, poetry, music (Sama), and trance rituals. |
| Goal | Submission to Allah and living by Islamic law. | Achieving mystical union with God and inner enlightenment. |
| Geographical Presence | Worldwide majority, dominant in Middle East, South Asia, Africa. | Found globally, with strong presence in South Asia, North Africa, Turkey. |
Introduction to Sunni Islam and Sufism
Sunni Islam represents the largest branch of Islam, emphasizing adherence to the Quran, Hadith, and the consensus of the Muslim community (ijma) as guiding principles. Sufism, often described as Islamic mysticism, focuses on the inner, spiritual dimension of Islam through practices like dhikr (remembrance of God) and the pursuit of direct personal experience with the divine. While Sunni Islam centers on legalistic and theological frameworks, Sufism prioritizes personal purification and spiritual connection, often coexisting within Sunni communities.
Historical Origins and Development
Sunni Islam, originating in the 7th century following Prophet Muhammad's death, emphasizes adherence to the Quran and Hadith as interpreted by the consensus of the Muslim community (Ummah) and the four major Sunni schools of jurisprudence. Sufism emerged as a mystical dimension within Islam during the 8th and 9th centuries, emphasizing inner spirituality, personal connection with God, and practices such as dhikr (remembrance). Historically, Sufism developed alongside Sunni Islam, influencing its devotional life while maintaining adherence to Sunni orthodoxy, but distinct in its focus on esoteric knowledge and spiritual experience.
Core Beliefs and Doctrines
Sunni Islam centers on strict adherence to the Quran and Hadith, emphasizing the Five Pillars as essential practices, with a strong focus on Sharia law and the consensus of the Muslim community (ijma). Sufism, often considered the mystical dimension of Islam, prioritizes inner spirituality, direct personal experience of God (Ihsan), and practices such as dhikr (remembrance of God) to attain divine love and deeper truth. While Sunni doctrine stresses external compliance and communal orthodoxy, Sufism promotes inward transformation and the esoteric interpretation of Islamic teachings.
Key Practices and Rituals
Sunni Islam emphasizes the Five Pillars, including Shahada (faith declaration), Salah (daily prayers), Zakat (almsgiving), Sawm (fasting during Ramadan), and Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca), as foundational practices for all adherents. Sufism, a mystical dimension within Islam, focuses on Dhikr (remembrance of God through repetitive prayer), Sama (spiritual music and dance), and spiritual mentorship under a Sufi Sheikh to attain inner purification and divine love. Both traditions engage in Salah and Quranic recitation, but Sufism incorporates additional esoteric rituals aimed at direct experiential knowledge of God.
Major Figures and Scholars
Sunni Islam is anchored by key figures such as Imam Abu Hanifa, Imam Malik, Imam Shafi'i, and Imam Ahmad ibn Hanbal, who established the four major Sunni madhabs (legal schools) shaping orthodox Islamic jurisprudence. Sufism is deeply influenced by scholars and mystics like Jalal al-Din Rumi, Al-Ghazali, Ibn Arabi, and Rabia al-Adawiyya, whose teachings emphasize the inward, spiritual dimensions of Islam and personal experience of the divine. The distinction between the two lies in Sunni Islam's focus on legalistic adherence and communal practice, while Sufism prioritizes mystical knowledge and esoteric wisdom.
Approaches to Spirituality and Mysticism
Sunni Islam emphasizes adherence to the Quran and Hadith with a focus on Sharia law and communal worship, promoting spirituality through defined rituals and religious obligations. Sufism, regarded as the mystical dimension of Islam, prioritizes inner purification, direct personal experience of the divine, and practices like dhikr (remembrance of God) and meditation. This approach to spirituality in Sufism seeks an intense, intimate connection with God beyond formal legalism, exploring metaphysical concepts and transcendental realities.
Attitudes Toward Law and Theology
Sunni Islam emphasizes strict adherence to Sharia law derived from the Quran and Hadith, with a focus on the consensus (ijma) of scholars and established jurisprudence (fiqh). In contrast, Sufism prioritizes inner spirituality and personal experience of the divine, often interpreting law and theology through mystical practices and allegorical meanings. While Sunni theology upholds orthodox creeds, Sufism integrates esoteric interpretations that sometimes challenge rigid legalism in favor of spiritual freedom.
Social and Cultural Influences
Sunni Islam, representing the largest Muslim sect, emphasizes adherence to Sharia law and traditional jurisprudence, shaping social structures through established religious institutions like mosques and madrasas. Sufism, as a mystical dimension of Islam, has profoundly influenced cultural expressions via poetry, music, and rituals, fostering spiritual inclusivity and communal bonding across diverse societies. Both traditions contribute to social cohesion but differ in practice, with Sunni Islam focusing on orthodoxy and Sufism on personal spiritual experience and devotion.
Areas of Convergence and Divergence
Sunni Islam and Sufism converge in their foundational belief in the core tenets of Islam, including the Quran, Sunnah, and the Five Pillars. Divergence arises as Sunni Islam emphasizes strict adherence to Sharia law and jurisprudence, whereas Sufism focuses on the inner spiritual journey and direct experience of God through mysticism and practices like dhikr (remembrance). Both traditions contribute to the richness of Islamic thought by balancing external ritual observance with internal spiritual growth.
Contemporary Perspectives and Challenges
Sunni Islam, characterized by its adherence to the Quran and Hadith within a jurisprudential framework, faces challenges balancing traditional religious law with modern societal issues like human rights and secular governance. Sufism, emphasizing mystical experience and spiritual connection to God, encounters skepticism and opposition from some Sunni orthodox groups who view its practices as deviations. Both streams navigate pressures of globalization, political tensions, and efforts to preserve religious identity while adapting to contemporary cultural pluralism.
Sunni Islam Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com