A guru is a revered spiritual teacher or guide who imparts wisdom and knowledge to help individuals achieve personal growth and enlightenment. Their teachings often transcend religious boundaries, offering insights that nurture your inner journey and foster self-awareness. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a guru's guidance can transform your life.
Table of Comparison
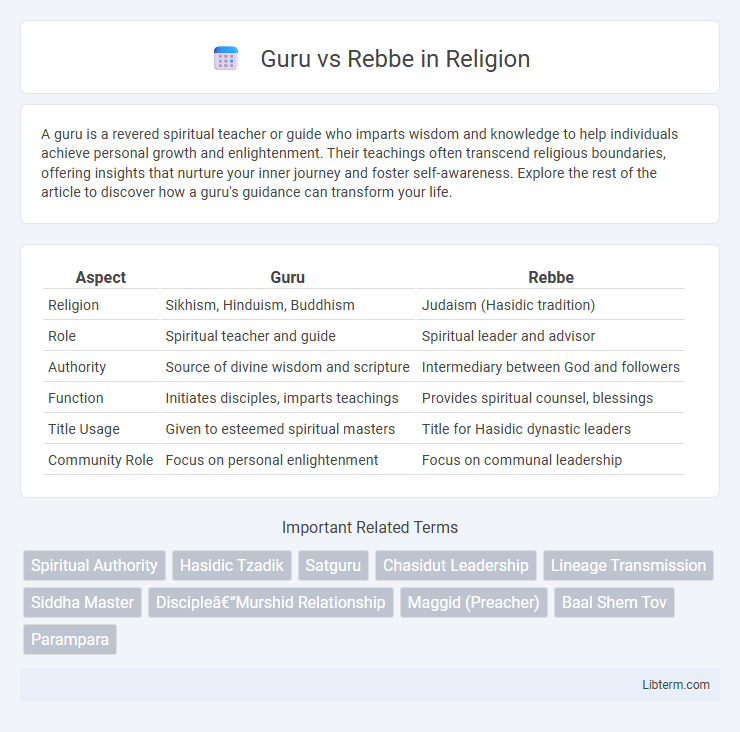
| Aspect | Guru | Rebbe |
|---|---|---|
| Religion | Sikhism, Hinduism, Buddhism | Judaism (Hasidic tradition) |
| Role | Spiritual teacher and guide | Spiritual leader and advisor |
| Authority | Source of divine wisdom and scripture | Intermediary between God and followers |
| Function | Initiates disciples, imparts teachings | Provides spiritual counsel, blessings |
| Title Usage | Given to esteemed spiritual masters | Title for Hasidic dynastic leaders |
| Community Role | Focus on personal enlightenment | Focus on communal leadership |
Understanding the Terms: Guru and Rebbe
The term "Guru" in Indian traditions refers to a spiritual teacher or guide who imparts wisdom and enlightenment, often embodying divine qualities for disciples. In Jewish culture, a "Rebbe" denotes a Hasidic leader combining roles as a teacher, spiritual guide, and community authority, emphasizing personalized mentorship. Both terms signify respected figures central to their respective faiths, playing crucial roles in transmitting spiritual knowledge and fostering community identity.
Historical Origins and Cultural Context
The terms "Guru" and "Rebbe" both signify spiritual leaders but originate from distinct cultural and historical backgrounds, with "Guru" rooted in ancient Indian traditions, particularly Hinduism and Sikhism, where they are revered as teachers and guides imparting wisdom and enlightenment. "Rebbe," on the other hand, stems from Jewish Hasidic tradition, especially within Eastern Europe, serving as a spiritual advisor, teacher, and communal leader guiding followers in religious and ethical matters. These roles reflect the unique religious developments and cultural contexts of South Asia and Eastern European Jewry, highlighting their respective influences on spiritual leadership and community life.
Spiritual Lineage and Authority
A Guru in Hinduism holds spiritual authority derived from an unbroken lineage tracing back to divine sources, emphasizing personal transmission of wisdom and initiation (diksha). A Rebbe in Judaism serves as a spiritual leader within the Hasidic tradition, embodying authority through hereditary succession and deep communal ties that reinforce spiritual guidance and covenantal leadership. Both figures sustain their communities by maintaining authentic connections to their spiritual ancestry, ensuring continuity of religious teachings and practices.
Roles in Community Life
A Guru serves as a spiritual guide and teacher in Indian traditions, offering wisdom, meditation techniques, and life guidance to disciples. A Rebbe, in Jewish Hasidic communities, functions as both a spiritual leader and a communal authority, providing religious instruction, personal advice, and fostering communal unity. Both roles establish deep personal connections and influence followers' spiritual and daily lives within their respective cultures.
Methods of Teaching and Guidance
Gurus often employ personalized mentorship integrating spiritual practices, meditation, and direct transmission of wisdom to guide disciples toward self-realization. Rebbes emphasize communal learning through rigorous study of sacred texts, halachic discourse, and fostering a collective spiritual connection within the Hasidic community. Both roles prioritize transformative guidance but differ in their methods: individualized experiential teaching by Gurus versus text-centered, community-focused pedagogy by Rebbes.
Relationship with Disciples and Followers
A Guru cultivates a personal, mentor-like bond with disciples, guiding spiritual growth through direct teachings and individual attention. A Rebbe acts as both a spiritual leader and a communal figure, fostering a deep, familial connection with followers within the Hasidic tradition. The Guru's relationship emphasizes personal transformation, while the Rebbe's role integrates guidance with communal responsibility and collective identity.
Philosophical Differences and Core Beliefs
Gurus in Hinduism emphasize self-realization and the transmission of spiritual knowledge to guide disciples toward moksha, highlighting an individualized path to enlightenment. Rebbe in Judaism serves as both a spiritual leader and community guide, focusing on adherence to Jewish law (Halacha) and collective religious practice through Hasidic teachings. The core philosophical difference lies in the Guru's focus on personal spiritual liberation versus the Rebbe's emphasis on communal religious life and covenantal faithfulness.
Ritual Practices and Traditions
Guru and Rebbe hold central roles in Sikhism and Hasidic Judaism, respectively, with distinct ritual practices and traditions. Gurus in Sikhism are venerated through rituals such as reading from the Guru Granth Sahib, participating in kirtan (devotional singing), and observing traditions like the langar communal meal, which emphasizes equality. Rebbes guide Hasidic communities through customs including teaching Torah, leading prayer services, granting blessings, and celebrating events like the tish gatherings, which reinforce spiritual connection and communal bonds.
Modern-Day Influence and Representation
Modern-day gurus in Hinduism often serve as spiritual guides, emphasizing personal enlightenment and meditation practices, with a widespread presence through digital platforms and global spiritual communities. Rebbes in Hasidic Judaism act as both religious leaders and community authorities, maintaining traditional roles while adapting to contemporary issues through communal counseling and educational leadership. Both figures significantly influence their followers' religious identities and daily practices, reflecting evolving interpretations of spirituality in modern contexts.
Choosing a Spiritual Guide: Guru or Rebbe?
Choosing a spiritual guide involves understanding the distinct roles of a Guru in Hindu and Sikh traditions versus a Rebbe in Hasidic Judaism. A Guru provides personalized teachings and initiations, often emphasizing meditation, self-realization, and a direct connection with the divine, while a Rebbe serves as a communal leader and Torah scholar guiding followers through Jewish law and mystical insights. Evaluating one's spiritual goals, cultural background, and preferred practices is essential when deciding between the transformative guidance of a Guru or the profound wisdom of a Rebbe.
Guru Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com