Atheism represents the absence of belief in deities, focusing on empirical evidence and reason rather than faith. It challenges traditional religious doctrines by promoting skepticism and critical thinking about metaphysical claims. Discover how atheism shapes worldviews and impacts personal and societal values in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
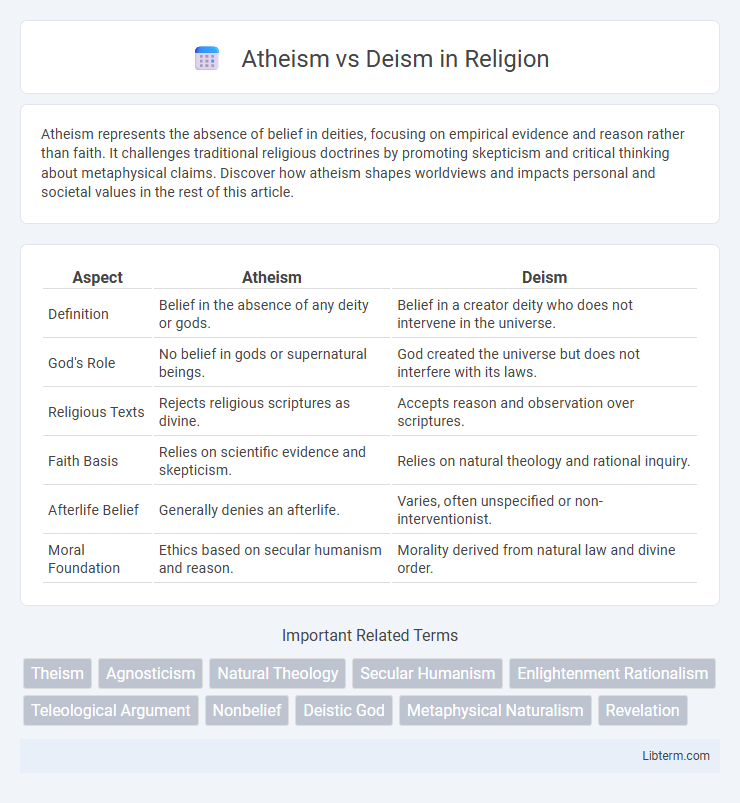
| Aspect | Atheism | Deism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in the absence of any deity or gods. | Belief in a creator deity who does not intervene in the universe. |
| God's Role | No belief in gods or supernatural beings. | God created the universe but does not interfere with its laws. |
| Religious Texts | Rejects religious scriptures as divine. | Accepts reason and observation over scriptures. |
| Faith Basis | Relies on scientific evidence and skepticism. | Relies on natural theology and rational inquiry. |
| Afterlife Belief | Generally denies an afterlife. | Varies, often unspecified or non-interventionist. |
| Moral Foundation | Ethics based on secular humanism and reason. | Morality derived from natural law and divine order. |
Defining Atheism: Core Concepts and Beliefs
Atheism is defined by the absence of belief in deities, rejecting the existence of gods due to lack of empirical evidence and rational justification. Core concepts include naturalism, skepticism, and reliance on scientific inquiry, emphasizing human reason over supernatural explanations. Atheists often advocate for secular ethics and reject religious dogma, focusing on observable reality and critical thinking.
Understanding Deism: Key Principles and Philosophies
Deism centers on the belief in a rational creator who designed the universe but does not intervene in its operations, emphasizing reason and observation over revelation or religious dogma. Key principles include the rejection of supernatural events, scriptures, and organized religion, advocating instead for a natural theology based on the laws of nature as evidence of a divine architect. Deist philosophy underscores human reason as the primary means to understand the creator, promoting ethical living grounded in natural law rather than faith or clerical authority.
Historical Evolution: Atheism and Deism Through Time
Atheism and Deism have distinct historical trajectories reflecting evolving human understanding of divinity and existence. Atheism, notably gaining prominence during the Enlightenment, challenges theistic claims by rejecting belief in deities based on empirical skepticism and scientific inquiry. Deism emerged in the 17th and 18th centuries, advocating a rational belief in a creator who does not intervene in the universe, influenced by the rise of natural philosophy and critiques of organized religion.
Foundational Arguments: Existence of God vs. Rejection
Atheism fundamentally rejects the existence of God, citing the lack of empirical evidence and inconsistencies in religious doctrines as primary arguments. Deism, conversely, asserts the existence of a non-interventionist Creator based on natural theology and the complexity of the universe, emphasizing reason and observation over revelation. Both positions engage deeply with metaphysical inquiries, but atheism denies supernatural claims outright while deism accepts a singular divine origin without endorsing organized religion.
The Role of Reason: Logic and Evidence in Belief Systems
Atheism relies heavily on empirical evidence and logical reasoning to reject the existence of deities, emphasizing skepticism and scientific inquiry as foundations for belief. Deism posits a Creator known through reason and observation of the natural world, rejecting revealed religion but accepting a divine origin based on rational deduction. Both belief systems prioritize logic and evidence but diverge in their conclusions regarding the existence and nature of a higher power.
Moral Frameworks: Ethics Without Divinity
Atheism bases its moral framework on secular ethics, relying on reason, empathy, and societal well-being without invoking divine authority. Deism, while rejecting revealed religion, often acknowledges a Creator whose role does not extend to prescribing moral laws, leaving ethical principles to human discernment and natural law. Both perspectives emphasize human responsibility in constructing moral values independent of supernatural mandates.
Science, Nature, and the Universe: Contrasting Worldviews
Atheism rejects belief in deities, emphasizing empirical evidence and scientific methods to explain the universe and natural phenomena. Deism posits a non-interventionist creator who set the universe in motion, aligning with observations of natural laws but denying supernatural interference. Both perspectives seek to understand existence through reason, yet atheism relies solely on observable data, while deism invokes a prime mover consistent with the cosmos' order.
Influential Thinkers: Prominent Atheists and Deists
Prominent atheists such as Richard Dawkins and Christopher Hitchens have significantly shaped the discourse on secularism and scientific skepticism, emphasizing empirical evidence and rejecting supernatural beliefs. Influential deists like Thomas Paine and Voltaire advocated for a rational belief in a creator based on reason and natural laws, distancing themselves from organized religion and dogma. Both groups have deeply impacted philosophical debates on faith, reason, and the nature of divinity.
Societal Impact: Religion, Secularism, and Public Life
Atheism promotes secularism by advocating for the separation of religion from public institutions, influencing policies that emphasize scientific reasoning and human rights. Deism, while acknowledging a creator, supports a naturalistic understanding of the universe that fosters tolerance but often coexists with religious traditions in public life. Both perspectives challenge orthodox religious authority, shaping societal debates on morality, education, and the role of religion in governance.
Contemporary Debates: Atheism vs. Deism Today
Contemporary debates between atheism and deism revolve around the existence and nature of a deity, with atheists rejecting belief in any god while deists accept an impersonal creator without religious dogma. Atheism emphasizes empirical evidence and scientific reasoning, whereas deism relies on rational inference and natural theology to argue for a non-interventionist divine force. These debates often highlight differing approaches to faith, reason, and the role of spirituality in modern secular societies.
Atheism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com