Fatalism asserts that all events are predetermined and inevitable, leaving no room for free will or personal influence over outcomes. This philosophy challenges the notion of control, suggesting that Your choices may be mere illusions against an unchangeable fate. Explore the deeper implications of fatalism and how it shapes perspectives on life and destiny in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
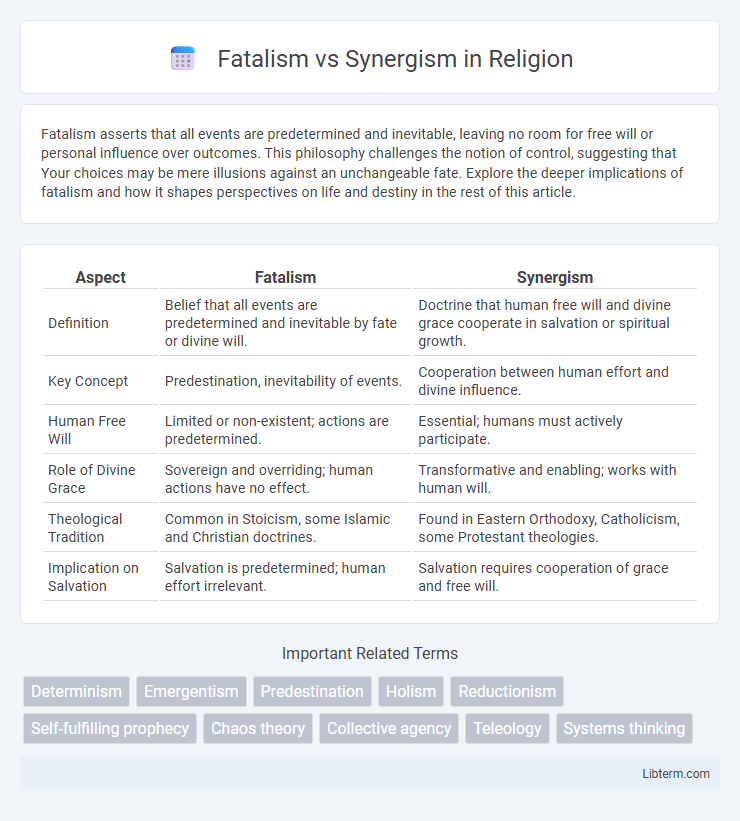
| Aspect | Fatalism | Synergism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that all events are predetermined and inevitable by fate or divine will. | Doctrine that human free will and divine grace cooperate in salvation or spiritual growth. |
| Key Concept | Predestination, inevitability of events. | Cooperation between human effort and divine influence. |
| Human Free Will | Limited or non-existent; actions are predetermined. | Essential; humans must actively participate. |
| Role of Divine Grace | Sovereign and overriding; human actions have no effect. | Transformative and enabling; works with human will. |
| Theological Tradition | Common in Stoicism, some Islamic and Christian doctrines. | Found in Eastern Orthodoxy, Catholicism, some Protestant theologies. |
| Implication on Salvation | Salvation is predetermined; human effort irrelevant. | Salvation requires cooperation of grace and free will. |
Understanding Fatalism: Definition and Core Beliefs
Fatalism is the philosophical doctrine asserting that all events are predetermined and inevitable, rendering human effort powerless to alter outcomes. Core beliefs in fatalism emphasize the inevitability of fate, suggesting that individual actions cannot change the course of events set by a higher power or destiny. This perspective contrasts sharply with synergism, which posits that human free will and divine influence work together to shape outcomes.
Synergism Explained: A Collaborative Worldview
Synergism emphasizes a collaborative worldview where individual efforts combine to produce outcomes greater than the sum of their parts, fostering cooperation and mutual enhancement. This perspective challenges fatalism by highlighting human agency, interaction, and the dynamic interplay of causes and effects in shaping events. Synergism promotes the understanding that collective actions and relationships are pivotal in influencing change and achieving shared goals.
Historical Roots: Origins of Fatalism and Synergism
Fatalism originates from ancient philosophical traditions like Stoicism and Hinduism, emphasizing predetermined destiny and inevitable outcomes. Synergism has roots in early Christian theology and Aristotelian philosophy, highlighting cooperative interaction between divine grace and human free will. Both concepts historically address the balance between destiny and agency in human life and salvation.
Psychological Impacts: How Worldviews Shape Behavior
Fatalism often leads to feelings of helplessness and resignation, as individuals perceive their actions as powerless against predetermined outcomes, negatively affecting motivation and mental health. Synergism fosters a sense of agency and collaboration, promoting proactive behavior and resilience by emphasizing the combined effects of individual effort and external factors. These contrasting worldviews significantly influence stress management, decision-making, and overall psychological well-being.
Fatalism in Religion and Philosophy
Fatalism in religion and philosophy asserts that all events are predetermined and inevitable, often attributing this inevitability to divine will or cosmic order. This worldview minimizes human free will, suggesting that individual actions cannot alter destined outcomes, which is evident in doctrines like predestination in Christianity or the concept of karma in certain interpretations of Hinduism and Buddhism. The belief in fatalism influences ethical and existential perspectives by emphasizing acceptance of fate rather than personal agency in shaping life's course.
Synergism in Science and Society
Synergism in science emphasizes the cooperative interaction of elements or agents to produce a combined effect greater than the sum of their separate effects, often observed in fields like biology, chemistry, and social systems. It explains phenomena such as ecosystem interdependence, collaborative innovation, and social cohesion, highlighting how collective effort drives complex problem-solving and advancement. Societal synergism fosters inclusive cooperation, leveraging diverse talents and perspectives to achieve sustainable development and improved community resilience.
Comparing Outcomes: Fate Versus Cooperation
Fatalism suggests outcomes are predetermined and inevitable, implying limited human influence on events, whereas synergism emphasizes cooperative interaction to achieve results greater than individual efforts alone. In fatalism, success or failure is attributed to destiny, reducing motivation to change circumstances; synergism fosters proactive collaboration, enhancing problem-solving and innovation. Comparative studies show synergistic approaches yield higher adaptability and improved outcomes across social, organizational, and ecological systems compared to fatalistic acceptance.
Modern Applications: Fatalism vs Synergism Today
Fatalism in modern applications often appears in deterministic frameworks such as predictive analytics and automated decision making, where outcomes are viewed as inevitable based on data patterns. Synergism, by contrast, emphasizes collaborative efforts and interconnected systems, powering innovations in team-based problem solving, adaptive technologies, and complex system modeling. The contrast between fatalism and synergism highlights divergent approaches in fields like artificial intelligence and organizational management, influencing both strategic planning and technological development.
Critiques and Controversies Surrounding Both Views
Critiques of Fatalism emphasize its deterministic nature, arguing it negates human free will and moral responsibility, leading to passive resignation in decision-making. Synergism faces controversy for suggesting a cooperative interaction between divine grace and human free will, which some view as diminishing divine sovereignty or introducing ambiguity in salvation. Both views spark ongoing debate within theological and philosophical circles regarding the balance between predestination and human agency.
Choosing a Path: Implications for Personal and Collective Growth
Choosing between fatalism and synergism profoundly impacts personal and collective growth by shaping beliefs about control and responsibility. Fatalism, which asserts that outcomes are predetermined, often leads to passivity and limits proactive change, whereas synergism emphasizes collaboration and the dynamic interaction of forces, fostering empowerment and innovation. Embracing synergism encourages individuals and communities to actively co-create their futures, driving sustainable development and adaptive resilience.
Fatalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com