Istinbat refers to the process of deriving legal rulings from primary Islamic sources such as the Quran and Sunnah through interpretation and reasoning. This methodology ensures that Sharia law remains applicable to contemporary issues by extracting relevant principles. Explore the rest of the article to understand how istinbat shapes Islamic jurisprudence and impacts your legal understanding.
Table of Comparison
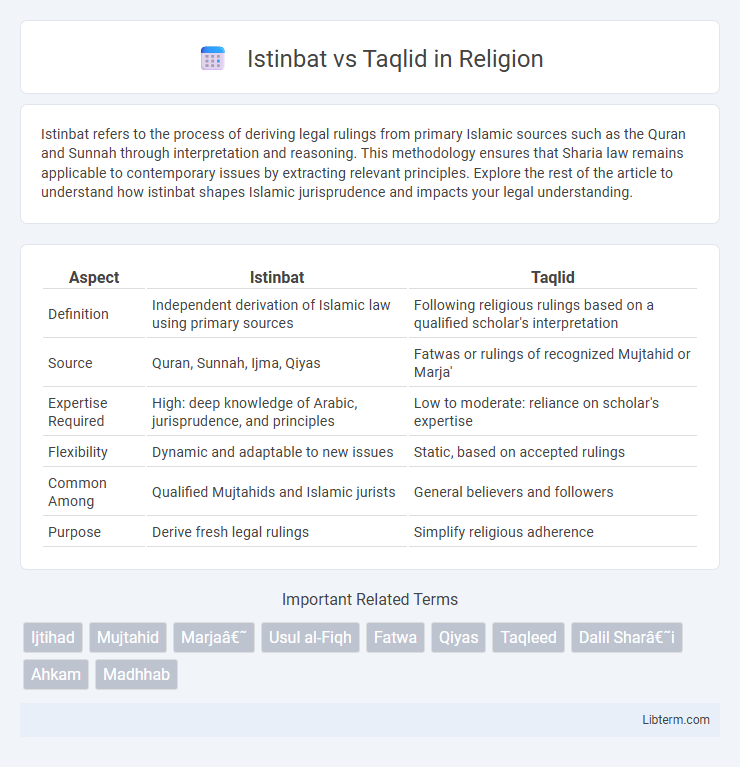
| Aspect | Istinbat | Taqlid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent derivation of Islamic law using primary sources | Following religious rulings based on a qualified scholar's interpretation |
| Source | Quran, Sunnah, Ijma, Qiyas | Fatwas or rulings of recognized Mujtahid or Marja' |
| Expertise Required | High: deep knowledge of Arabic, jurisprudence, and principles | Low to moderate: reliance on scholar's expertise |
| Flexibility | Dynamic and adaptable to new issues | Static, based on accepted rulings |
| Common Among | Qualified Mujtahids and Islamic jurists | General believers and followers |
| Purpose | Derive fresh legal rulings | Simplify religious adherence |
Introduction to Istinbat and Taqlid
Istinbat refers to the independent process of deducing Islamic legal rulings directly from primary sources such as the Quran and Sunnah, requiring deep knowledge of jurisprudence and principles. Taqlid involves following established legal opinions of qualified scholars without personally deriving rulings, emphasizing adherence to traditional interpretations. Understanding the distinction between Istinbat and Taqlid highlights the balance between informed personal reasoning and reliance on scholarly expertise in Islamic law.
Defining Istinbat in Islamic Jurisprudence
Istinbat in Islamic jurisprudence refers to the process of deriving legal rulings directly from primary sources such as the Qur'an and Sunnah, emphasizing independent reasoning and interpretation. This method contrasts with Taqlid, which relies on following established scholarly opinions without questioning their foundations. Istinbat requires deep knowledge of language, context, and principles of fiqh to ensure sound and authentic application of Sharia law.
Understanding the Concept of Taqlid
Taqlid, in Islamic jurisprudence, refers to the practice of following the legal opinions of a qualified scholar without independently deriving rulings from the primary sources, the Quran and Sunnah. Understanding Taqlid involves recognizing its role in providing Muslim laypersons access to established jurisprudential interpretations while maintaining religious coherence and unity. Istinbat, by contrast, denotes the process of independent legal reasoning, where scholars extract rulings through ijtihad, emphasizing a direct engagement with foundational texts over imitation.
Historical Development of Istinbat and Taqlid
The historical development of Istinbat, the process of deriving Islamic legal rulings through independent reasoning, traces back to the early Islamic period where scholars employed Quran, Hadith, Ijma, and Qiyas to address new issues. Taqlid, referring to the adherence to established legal precedents without independent reasoning, gained prominence as legal schools (Madhabs) solidified between the 8th and 10th centuries, providing structured guidance for believers. Over time, debates between proponents of Istinbat and Taqlid reflected broader tensions between innovation in jurisprudence and preservation of traditional interpretations within Islamic law.
Key Differences Between Istinbat and Taqlid
Istinbat involves deriving Islamic rulings directly from primary sources like the Quran and Sunnah through critical reasoning by qualified scholars, emphasizing ijtihad (independent judgment). Taqlid refers to following established legal opinions and verdicts of recognized scholars without independently examining the evidence, prioritizing conformity to tradition for laypersons. The key difference lies in the level of intellectual autonomy: Istinbat demands active legal reasoning, while Taqlid requires acceptance of precedent to ensure consistency and accessibility in Islamic jurisprudence.
The Role of Mujtahid in Istinbat
The role of a Mujtahid in Istinbat is central, as they exercise independent reasoning (ijtihad) to derive legal rulings directly from primary Islamic sources such as the Quran and Sunnah. Mujtahids assess complex jurisprudential issues, ensuring that rulings adapt to new circumstances without blindly adhering to precedent. In contrast, Taqlid involves following established interpretations by qualified scholars, limiting the dynamic legal evolution fostered by the Mujtahid's analytical expertise.
The Importance of Taqlid for Laypersons
Taqlid serves as a critical framework for laypersons by allowing adherence to established Islamic rulings without requiring direct engagement in complex jurisprudential reasoning, thereby ensuring religious compliance and unity. It bridges the gap between intricate Istinbat processes, which involve independent legal deduction by qualified scholars, and the practical needs of everyday believers. Reliance on Taqlid minimizes errors stemming from inadequate knowledge, safeguarding individual faith within Shariah guidelines.
Benefits and Challenges of Istinbat
Istinbat involves deriving legal rulings directly from Quran and Hadith, enabling flexible, context-specific interpretations critical for addressing new issues in Islamic law. This method promotes intellectual engagement and adaptability, fostering a deeper understanding of Sharia and encouraging jurisprudential innovation but requires advanced knowledge and rigorous methodology to avoid misinterpretation. The challenges of Istinbat include the risk of subjective errors and the demand for specialized scholars well-versed in Arabic, jurisprudence, and the principles of Islamic law, limiting its accessibility compared to Taqlid, which relies on established rulings.
Contemporary Debates on Istinbat vs Taqlid
Contemporary debates on Istinbat versus Taqlid center on the balance between independent jurisprudential reasoning and adherence to established legal opinions. Istinbat empowers scholars to derive rulings directly from primary sources like the Qur'an and Sunnah, promoting dynamic adaptability in Islamic law. Taqlid emphasizes conformity to classical interpretations, raising concerns about stagnation but ensuring consistency and communal unity among followers.
Conclusion: Balancing Istinbat and Taqlid in Modern Times
Balancing Istinbat and Taqlid in modern Islamic jurisprudence requires integrating independent legal reasoning with adherence to established scholarly opinions for practical guidance. Istinbat enables dynamic adaptation of Sharia to contemporary issues through direct analysis of sources, while Taqlid provides continuity and stability by following qualified jurists. Effective Islamic legal practice today hinges on a pragmatic synthesis that respects tradition while embracing contextual ijtihad.
Istinbat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com