Aqidah refers to the core beliefs and creed that form the foundation of Islamic faith, encompassing concepts such as the oneness of God, prophethood, and the afterlife. Understanding Aqidah is essential for strengthening Your spiritual commitment and guiding your daily practices. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your knowledge of Aqidah and its significance in Islam.
Table of Comparison
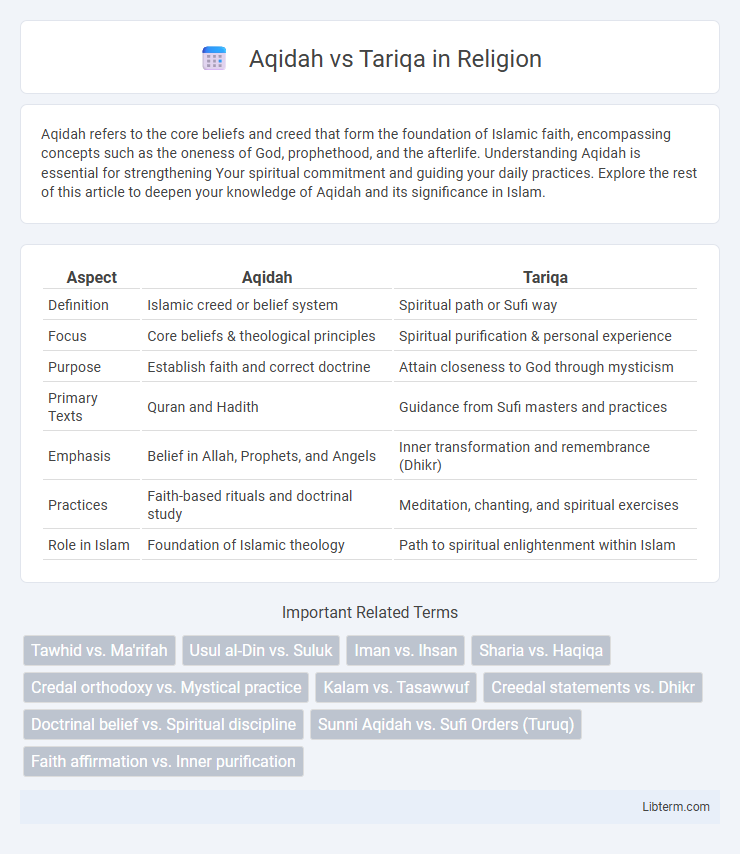
| Aspect | Aqidah | Tariqa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Islamic creed or belief system | Spiritual path or Sufi way |
| Focus | Core beliefs & theological principles | Spiritual purification & personal experience |
| Purpose | Establish faith and correct doctrine | Attain closeness to God through mysticism |
| Primary Texts | Quran and Hadith | Guidance from Sufi masters and practices |
| Emphasis | Belief in Allah, Prophets, and Angels | Inner transformation and remembrance (Dhikr) |
| Practices | Faith-based rituals and doctrinal study | Meditation, chanting, and spiritual exercises |
| Role in Islam | Foundation of Islamic theology | Path to spiritual enlightenment within Islam |
Understanding Aqidah: Core Islamic Beliefs
Aqidah represents the foundational Islamic beliefs that define a Muslim's faith, including the oneness of Allah, prophethood of Muhammad, and the afterlife, serving as the essential framework for spiritual understanding. Tariqa, by contrast, refers to Sufi paths or spiritual methods aimed at deepening personal experience and connection with these core beliefs through practices like dhikr and meditation. Understanding Aqidah ensures a correct theological basis, while Tariqa emphasizes inner purification and experiential knowledge of Islamic truths.
What is Tariqa? Exploring Sufi Spiritual Paths
Tariqa in Sufism refers to the spiritual path or method pursued by seekers to attain closeness to Allah through inner purification and mystical practice. It encompasses disciplined rituals, meditation, and guidance under a spiritual master (Shaykh) to transcend the ego and experience divine realities. Each Tariqa represents a distinct Sufi order emphasizing particular spiritual techniques aligned with Islamic teachings and the foundational beliefs encapsulated in Aqidah.
Historical Development of Aqidah and Tariqa
Aqidah, the foundation of Islamic creed, developed early in Islamic history through scholarly efforts to define core beliefs such as Tawhid (monotheism) and Prophethood, solidifying during the Abbasid era with works like Al-Aqeedah Al-Tahawiyyah. Tariqa, representing the spiritual path or Sufi orders, emerged later during the 9th and 10th centuries as mystics like Al-Junayd and Al-Ghazali institutionalized practices emphasizing inner purification and divine closeness. The historical evolution of Aqidah focused on doctrinal clarity and orthodoxy, while Tariqa prioritized experiential spirituality and devotional disciplines within Islamic tradition.
Key Differences Between Aqidah and Tariqa
Aqidah represents the core Islamic beliefs and creed encompassing fundamental theological concepts like Tawhid (the oneness of God), prophethood, and the afterlife. Tariqa refers to the spiritual path or method within Sufism aimed at achieving mystical closeness to God through practices such as dhikr (remembrance) and meditation. The key difference lies in Aqidah being the foundation of Islamic faith while Tariqa focuses on experiential inner purification and spiritual development.
The Role of Aqidah in Islamic Spirituality
Aqidah, the core Islamic creed encompassing beliefs about God, prophethood, and the afterlife, forms the foundational framework for Muslim spirituality and guides ethical conduct. It establishes the correct understanding of Tawhid (oneness of God) and acts as the reference point for evaluating spiritual experiences within Tariqa, the mystical path of Sufism. By affirming Aqidah, seekers ensure their Tariqa practices align with orthodox Islamic theology, preserving spiritual authenticity and preventing deviation.
How Tariqa Complements Islamic Faith
Tariqa, representing the spiritual path within Sufism, serves as a practical extension of Aqidah, the core Islamic creed that defines fundamental beliefs about God, prophecy, and the afterlife. While Aqidah establishes the essential theological framework, Tariqa provides a methodical approach to experiencing and internalizing these beliefs through rituals, meditation, and ethical discipline. This complementary relationship deepens a Muslim's connection to faith by transforming abstract doctrines into lived spiritual realities, fostering personal purification and divine closeness.
Misconceptions About Aqidah and Tariqa
Misconceptions about Aqidah and Tariqa often stem from confusing Aqidah, the foundational Islamic creed defining core beliefs, with Tariqa, which represents the spiritual path or method of Sufi practice. Aqidah establishes essential tenets like monotheism and prophecy, while Tariqa focuses on personal spiritual growth and inner purification through specific rituals and guidance under a spiritual master. Understanding their distinct roles helps clarify that Aqidah is about doctrinal certainty, whereas Tariqa is about experiential spirituality within Islamic tradition.
Influence of Sufism on Islamic Thought
The distinction between Aqidah (Islamic creed) and Tariqa (Sufi spiritual path) highlights the profound influence of Sufism on Islamic thought by integrating mystical experience with orthodox belief. Sufism's Tariqa emphasizes inner purification and divine love, enriching Aqidah with experiential knowledge of God beyond legalistic interpretations. This integration shaped key theological concepts and fostered a dynamic spiritual discourse within Sunni and Shia traditions, impacting Islamic philosophy, ethics, and jurisprudence.
Common Figures in Aqidah and Tariqa Traditions
Aqidah revolves around foundational Islamic beliefs exemplified by scholars like Imam Abu Hanifa and Imam Al-Ghazali, who shaped creed and theology, while Tariqa emphasizes spiritual path and mysticism represented by figures such as Jalaluddin Rumi and Ibn Arabi. Both traditions share key personalities like Al-Ghazali, bridging theological doctrine and Sufi practice through their works on faith and inner purification. These figures collectively influence the understanding and practice of Islam's core beliefs and spiritual disciplines.
Choosing Between Aqidah and Tariqa: Harmonizing Belief and Practice
Choosing between Aqidah and Tariqa requires understanding that Aqidah represents the fundamental Islamic creed, encompassing core beliefs about God, prophets, and the afterlife, while Tariqa refers to the spiritual path or Sufi order emphasizing personal purification and mystical experience. Harmonizing belief and practice involves integrating Aqidah's doctrinal clarity with Tariqa's experiential spiritual development to achieve a balanced Islamic life. Prioritizing sound Aqidah safeguards faith's authenticity, whereas Tariqa offers methods to embody those beliefs through disciplined spiritual practices.
Aqidah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com