Alchemy, the ancient practice combining science, philosophy, and mysticism, sought to transform base metals into gold and discover the elixir of life. This enigmatic art laid the groundwork for modern chemistry while influencing spiritual and intellectual thought throughout history. Dive into the rest of this article to uncover alchemy's profound impact on your understanding of both science and symbolism.
Table of Comparison
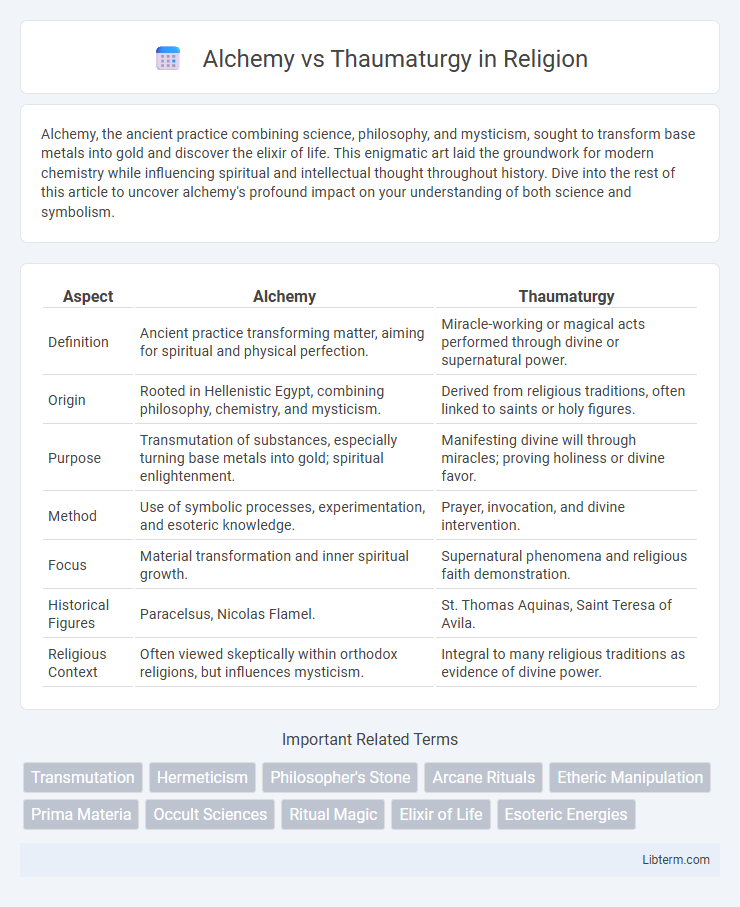
| Aspect | Alchemy | Thaumaturgy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ancient practice transforming matter, aiming for spiritual and physical perfection. | Miracle-working or magical acts performed through divine or supernatural power. |
| Origin | Rooted in Hellenistic Egypt, combining philosophy, chemistry, and mysticism. | Derived from religious traditions, often linked to saints or holy figures. |
| Purpose | Transmutation of substances, especially turning base metals into gold; spiritual enlightenment. | Manifesting divine will through miracles; proving holiness or divine favor. |
| Method | Use of symbolic processes, experimentation, and esoteric knowledge. | Prayer, invocation, and divine intervention. |
| Focus | Material transformation and inner spiritual growth. | Supernatural phenomena and religious faith demonstration. |
| Historical Figures | Paracelsus, Nicolas Flamel. | St. Thomas Aquinas, Saint Teresa of Avila. |
| Religious Context | Often viewed skeptically within orthodox religions, but influences mysticism. | Integral to many religious traditions as evidence of divine power. |
Introduction to Alchemy and Thaumaturgy
Alchemy is an ancient practice centered on transforming matter, often seeking to transmute base metals into noble ones like gold or create elixirs for immortality, using a blend of mystical philosophy and early chemistry. Thaumaturgy, by contrast, involves the performance of miracles or magical feats through supernatural power, often linked to ritualistic or divine sources rather than physical processes. Both disciplines explore the manipulation of natural laws but differ in methods and goals, with alchemy rooted in material transformation and thaumaturgy in spiritual or mystical influence.
Historical Origins of Alchemy
Alchemy, originating in Hellenistic Egypt around the 3rd century BCE, combines elements of ancient Greek philosophy, Egyptian metallurgy, and early chemistry. Its foundational texts, such as the Emerald Tablet attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, reflect a synthesis of mystical and proto-scientific traditions aimed at transmutation and the philosopher's stone. Medieval Islamic scholars preserved and expanded alchemical knowledge, which later influenced European Renaissance alchemy and laid the groundwork for modern chemistry.
The Roots of Thaumaturgy
Thaumaturgy originates from ancient mystical traditions emphasizing the manipulation of supernatural forces through ritualistic practices and esoteric knowledge. Its roots lie in early religious ceremonies, where practitioners invoked divine powers to produce miraculous effects, distinguishing it from alchemy's empirical and transformation-focused methodology. While alchemy centers on material transmutation, thaumaturgy embodies the spiritual and magical invocation of unseen energies to alter reality.
Philosophical Foundations Compared
Alchemy is grounded in the Hermetic principle of transformation, emphasizing the unity between the material and spiritual worlds and the transmutation of base metals into noble substances as a metaphor for inner enlightenment. Thaumaturgy is based on the belief in supernatural intervention through divine or mystical forces, prioritizing miraculous acts and the manipulation of spiritual energy to achieve tangible effects. While alchemy integrates metaphysical concepts with physical processes, thaumaturgy relies more heavily on faith and ritual as pathways to manifest extraordinary phenomena.
Methods and Practices in Alchemy
Alchemy relies on the transformation of base materials through processes such as calcination, dissolution, and coagulation, aiming to purify substances or create the philosopher's stone. Its methods involve extensive use of distillation, fermentation, and sublimation techniques to manipulate elemental properties. Practitioners meticulously combine symbolic correspondences with practical experimentation to achieve both material and spiritual transmutations.
Rituals and Techniques in Thaumaturgy
Thaumaturgy relies heavily on precise rituals and techniques that manipulate magical energy through gestures, incantations, and symbolic components to achieve specific effects. These rituals often involve invoking supernatural forces or commanding elemental powers, distinguishing them from Alchemy's focus on material transmutation and potion crafting. Mastery in Thaumaturgy requires understanding complex ceremonial frameworks and the alignment of metaphysical elements to harness otherworldly phenomena effectively.
Goals and Purposes: Transformation vs. Miracle
Alchemy centers on the transformation of materials, aiming to convert base metals into noble ones, discover the elixir of life, and unlock the secrets of creation through scientific experimentation and symbolic processes. Thaumaturgy focuses on performing miracles or supernatural feats by invoking divine or mystical powers to alter reality, heal, or influence events beyond natural laws. The fundamental goal of alchemy lies in achieving physical and spiritual transmutation, while thaumaturgy seeks to manifest extraordinary effects as an expression of divine intervention or magical prowess.
Key Figures and Influential Texts
Alchemy prominently features figures such as Paracelsus, credited with integrating medical knowledge and chemical processes, and Nicolas Flamel, renowned for his purported discovery of the Philosopher's Stone. Influential alchemical texts include the "Emerald Tablet," a foundational Hermetic document, and "Theatrum Chemicum," an extensive compilation of alchemical writings. Thaumaturgy centers on practitioners like John Dee, an advisor to Queen Elizabeth I who combined occult knowledge with mathematics, and Aleister Crowley, a modern occultist emphasizing ritual magic; key texts include Dee's "Monas Hieroglyphica" and Crowley's "Magick in Theory and Practice.
Modern Interpretations and Applications
Modern interpretations of alchemy emphasize its symbolic and psychological dimensions, often linked to personal transformation and spiritual growth, whereas contemporary thaumaturgy is commonly associated with practical magic and ritualistic practices aimed at tangible results. In scientific communities, alchemy is studied as a historical precursor to chemistry, with applications in art restoration and herbal medicine, while thaumaturgy finds relevance in modern occultism and popular culture through its portrayal in fantasy literature and media. Both disciplines continue to influence new age spirituality and alternative healing systems by integrating ancient principles with modern therapeutic techniques.
Alchemy vs. Thaumaturgy: Core Differences and Similarities
Alchemy involves the transformation of materials and the creation of potions through scientific principles combined with magical elements, emphasizing substance manipulation and experimentation. Thaumaturgy centers on performing miracles or supernatural feats using direct magical energy, focusing on instantaneous effects and ritualized spellcasting. Both practices harness magical forces but differ primarily in methodology, with alchemy relying on material properties and thaumaturgy relying on pure arcane power.
Alchemy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com