Sadducees were a Jewish sect during the Second Temple period, known for their strict adherence to the written Torah and rejection of oral traditions held by the Pharisees. They held significant religious and political influence, often associated with the priestly class and the Temple in Jerusalem. Discover how the beliefs and historical impact of the Sadducees shaped ancient Judaism and influenced later religious developments in the article below.
Table of Comparison
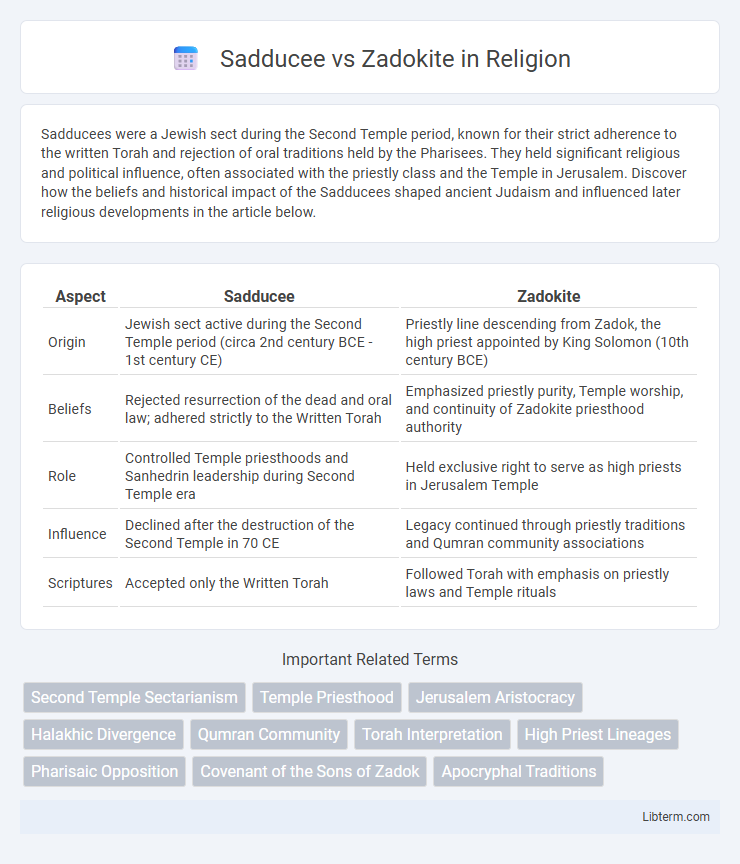
| Aspect | Sadducee | Zadokite |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Jewish sect active during the Second Temple period (circa 2nd century BCE - 1st century CE) | Priestly line descending from Zadok, the high priest appointed by King Solomon (10th century BCE) |
| Beliefs | Rejected resurrection of the dead and oral law; adhered strictly to the Written Torah | Emphasized priestly purity, Temple worship, and continuity of Zadokite priesthood authority |
| Role | Controlled Temple priesthoods and Sanhedrin leadership during Second Temple era | Held exclusive right to serve as high priests in Jerusalem Temple |
| Influence | Declined after the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE | Legacy continued through priestly traditions and Qumran community associations |
| Scriptures | Accepted only the Written Torah | Followed Torah with emphasis on priestly laws and Temple rituals |
Origins of the Sadducees and Zadokites
The Sadducees originated as a Jewish sect during the Second Temple period, primarily composed of the priestly aristocracy and associated with the Temple in Jerusalem. The Zadokites trace their lineage to Zadok, the high priest appointed by King Solomon, and represented a hereditary priestly family that claimed legitimate religious authority during the First Temple era. The Sadducees likely emerged from or were influenced by the Zadokite priesthood, emphasizing strict adherence to the written Torah and Temple rituals.
Historical Context and Development
The Sadducees, a Jewish sect prominent during the Second Temple period, largely comprised the priestly aristocracy and aligned closely with the Temple's rituals and political authority. The Zadokites, descended from Zadok the high priest, represent a priestly lineage that maintained strict adherence to Temple service and purity laws, claiming legitimacy through genealogical continuity. Historical records suggest the Sadducees' theological positions, especially their denial of resurrection and prophecy, contrasted with the Pharisees, while the Zadokites served as the orthodox priestly faction endorsing the Temple's central role in Jewish worship.
Genealogical Claims and Priesthood Lineage
Sadducees traced their priesthood lineage directly to Zadok, the high priest during King Solomon's reign, asserting their genealogical legitimacy through this prestigious ancestry to maintain temple authority. Their claim emphasized an unbroken hereditary line from Zadok, differentiating them from other priestly groups such as the Pharisees, who focused on legalistic adherence rather than lineage. The Zadokite priesthood, therefore, symbolized strict genealogical purity, reinforcing their exclusive right to perform temple sacrifices and rituals in ancient Jerusalem.
Religious Beliefs and Doctrinal Differences
Sadducees, a priestly sect in ancient Judaism, rejected beliefs in the resurrection, angels, and spirits, emphasizing the written Torah exclusively and denying oral traditions upheld by other groups. Zadokites, linked to the priestly lineage of Zadok, upheld strict Temple rituals and maintained closer adherence to priestly purity laws, aligning more closely with traditional priesthood responsibilities. The doctrinal divide hinges on Sadducees' literal scriptural interpretation versus Zadokites' emphasis on priestly legitimacy and ritual precision within Temple worship.
Scriptural Authority: Torah vs. Broader Texts
Sadducees recognized only the Torah as the authoritative scriptural text, rejecting later writings such as the Prophets and Writings accepted by other Jewish groups. Zadokites, aligned with priestly traditions, embraced broader scriptural texts including the Torah and prophetic writings, reflecting a more expansive scriptural authority. This divergence impacted their theological interpretations and ritual practices within Second Temple Judaism.
Temple Practices and Ritual Purity
Sadducees, often associated with the priestly aristocracy, maintained strict Temple practices centered on the written Torah and emphasized ritual purity based on established priestly laws. Zadokites, descendants of Priest Zadok, were a specific priestly lineage who played a key role in Temple worship, emphasizing strict adherence to purity regulations and maintaining the sanctity of Temple rituals. The Zadokite priests held exclusive rights to perform certain sacred rites, reinforcing their authority in maintaining Temple purity and ritual correctness.
Political Influence and Social Status
Sadducees, primarily composed of the priestly aristocracy and wealthy elites in Second Temple Judaism, wielded significant political influence by collaborating with the Roman authorities to maintain the status quo and control the Sanhedrin, the highest Jewish council. Zadokites, descendants of Zadok, were a prestigious priestly lineage with religious authority centered around temple rituals but held more limited direct political power compared to Sadducees. The social status of Sadducees was elevated through their elite connections and governance roles, whereas Zadokites were highly respected for their sacred purity and liturgical duties within the temple hierarchy.
Relations with Other Jewish Sects
The Sadducees, a priestly aristocracy closely linked to the Temple in Jerusalem, often clashed with the Pharisees over interpretations of Jewish Law and beliefs in the afterlife, favoring a strict Torah-only approach. Zadokites, descendants of Zadok the high priest, maintained religious authority through their hereditary priesthood and had significant influence on the Temple practices, often aligning more with Sadducean priorities in ritual purity and temple service. Relations with other Jewish sects such as the Essenes were typically distant or adversarial due to differing views on law, purity, and messianic expectations.
Legacy and Impact on Judaism
The Sadducees, a priestly sect associated with the Jerusalem Temple, heavily influenced Jewish religious practices during the Second Temple period but lost prominence after the Temple's destruction, sharply curtailing their legacy. The Zadokites, descendants of Zadok, the high priest during King David's era, shaped the priestly hierarchy and temple rituals with enduring authority recognized in later Jewish traditions. Their impact is evident in the continued emphasis on priestly lineage and ceremonial purity central to modern rabbinic Judaism's historical foundation.
Key Differences Summarized
Sadducees were a Jewish sect during the Second Temple period known for their aristocratic priestly class, rejection of oral Torah, and denial of the resurrection, while Zadokites were priestly descendants of Zadok, emphasizing strict temple ritual purity and legitimacy of priesthood lineage. Sadducees often aligned with the Temple's priestly elite and aristocracy, whereas Zadokites focused on maintaining Zadok's priesthood standards and were influential in establishing the legitimacy of High Priests. The main doctrinal divide lies in Sadducees' scriptural strictness to the written Torah versus Zadokites' role in upholding priestly purity and temple traditions.
Sadducee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com