Cathodes are essential components in electronic devices, serving as the negative electrode where electrons are emitted or received in processes like electrolysis and electron tubes. Their performance directly impacts the efficiency and longevity of batteries, vacuum tubes, and other semiconductor devices. Explore the article to discover how cathode materials and designs enhance your technology's functionality.
Table of Comparison
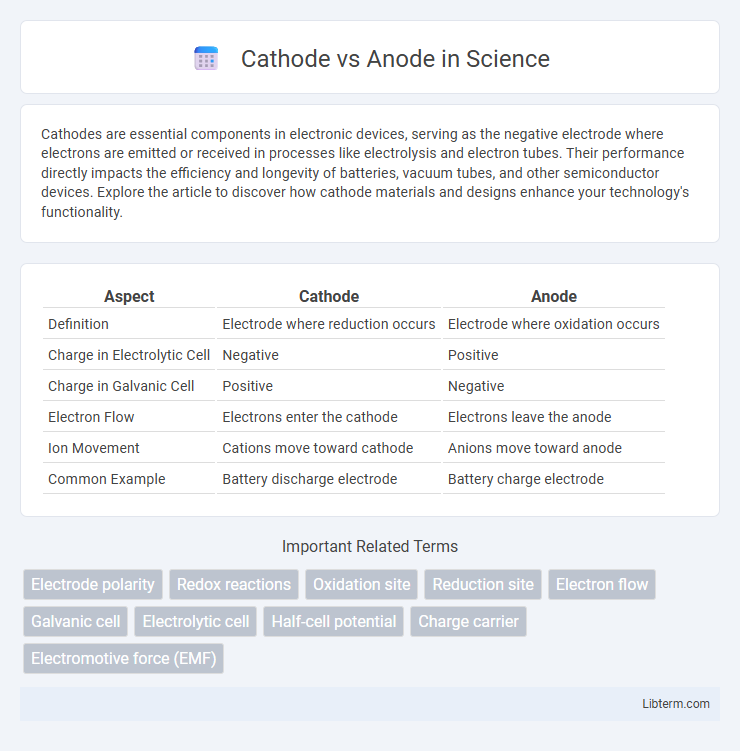
| Aspect | Cathode | Anode |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electrode where reduction occurs | Electrode where oxidation occurs |
| Charge in Electrolytic Cell | Negative | Positive |
| Charge in Galvanic Cell | Positive | Negative |
| Electron Flow | Electrons enter the cathode | Electrons leave the anode |
| Ion Movement | Cations move toward cathode | Anions move toward anode |
| Common Example | Battery discharge electrode | Battery charge electrode |
Introduction to Cathode and Anode
The cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs, attracting cations during electrochemical reactions, while the anode is the site of oxidation, releasing electrons and attracting anions. In batteries and electrolytic cells, the cathode serves as the positive terminal in galvanic cells and the negative terminal in electrolytic cells, contrasting with the anode's opposing polarity. Understanding the distinct roles of cathodes and anodes is crucial for designing efficient energy storage and conversion systems.
Definition of Cathode
The cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs in an electrochemical cell, characterized by the gain of electrons during the chemical reaction. In galvanic cells, the cathode is the positive terminal attracting cations, whereas in electrolytic cells, it serves as the negative terminal. Understanding the distinct role of the cathode is essential for optimizing battery design, electroplating processes, and various electrochemical applications.
Definition of Anode
The anode is the electrode where oxidation occurs, releasing electrons into an external circuit. In electrolytic cells, the anode is positively charged, attracting anions, while in galvanic cells, it is negatively charged as it supplies electrons. This electrode plays a crucial role in electrochemical reactions by facilitating electron flow and enabling energy conversion.
Key Differences Between Cathode and Anode
The cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs, attracting cations, while the anode is the electrode where oxidation takes place, attracting anions. In galvanic cells, the cathode is positive and the anode negative, whereas in electrolytic cells, the cathode is negative and the anode positive. Electron flow moves from anode to cathode, defining their roles in electrochemical reactions and energy conversion processes.
Function in Electrochemical Cells
The cathode functions as the site of reduction where electrons are gained during electrochemical reactions, while the anode serves as the site of oxidation where electrons are lost. In galvanic cells, the cathode is the positive electrode attracting cations, and the anode is the negative electrode releasing electrons. During electrolysis, these roles reverse with the cathode being negative and the anode positive, facilitating targeted electron flow essential for chemical transformations.
Role in Batteries
The cathode in batteries serves as the positive electrode where reduction reactions occur, enabling electrons to flow into the external circuit during discharge. The anode functions as the negative electrode, undergoing oxidation reactions that release electrons to power devices. Together, the cathode and anode drive the electrochemical processes essential for energy storage and delivery in rechargeable and primary batteries.
Importance in Electrolysis
In electrolysis, the cathode serves as the electrode where reduction occurs, attracting cations to gain electrons, while the anode is the site of oxidation, where anions lose electrons. This differentiation is crucial for driving the redox reactions that enable the decomposition of compounds and the extraction of elements. Understanding the distinct roles of cathode and anode ensures efficient design and operation of electrolysis cells in industrial applications such as metal plating, refining, and water splitting.
Applications in Various Industries
Cathodes and anodes play crucial roles in industries such as electronics, healthcare, and energy storage, where cathodes commonly serve as the positive electrodes in batteries, facilitating electron flow to generate power, while anodes act as negative electrodes, enabling ion exchange and oxidation processes. In metal plating and electrolysis, anodes release metal ions into solutions for coating or purification, whereas cathodes attract these ions to form uniform deposits. The semiconductor industry utilizes cathodes and anodes in devices like diodes and LEDs, optimizing electrical conductivity and efficiency based on electrode material properties.
Common Misconceptions
A common misconception is that the cathode is always positive and the anode always negative; in reality, their charges depend on the device type and reaction direction. In galvanic cells, the cathode is positive and the anode negative, while in electrolytic cells, the cathode is negative and the anode positive. Another frequent error is assuming oxidation occurs at the cathode and reduction at the anode, whereas oxidation always happens at the anode and reduction at the cathode.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Cathode and Anode
Choosing between cathode and anode depends on the specific electrochemical application, as the cathode functions as the site of reduction, attracting cations, while the anode serves as the oxidation site, attracting anions. In battery design, cathodes typically determine energy density and voltage, whereas anodes influence cycle life and stability. Optimal selection requires balancing factors like material properties, operational environment, and desired electrical performance.
Cathode Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com