Ontogeny explores the development of an individual organism from fertilization to maturity, revealing key insights into genetic expression and cellular differentiation. Understanding ontogeny helps uncover how complex structures and functions arise throughout growth and development. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how ontogeny shapes your biological identity.
Table of Comparison
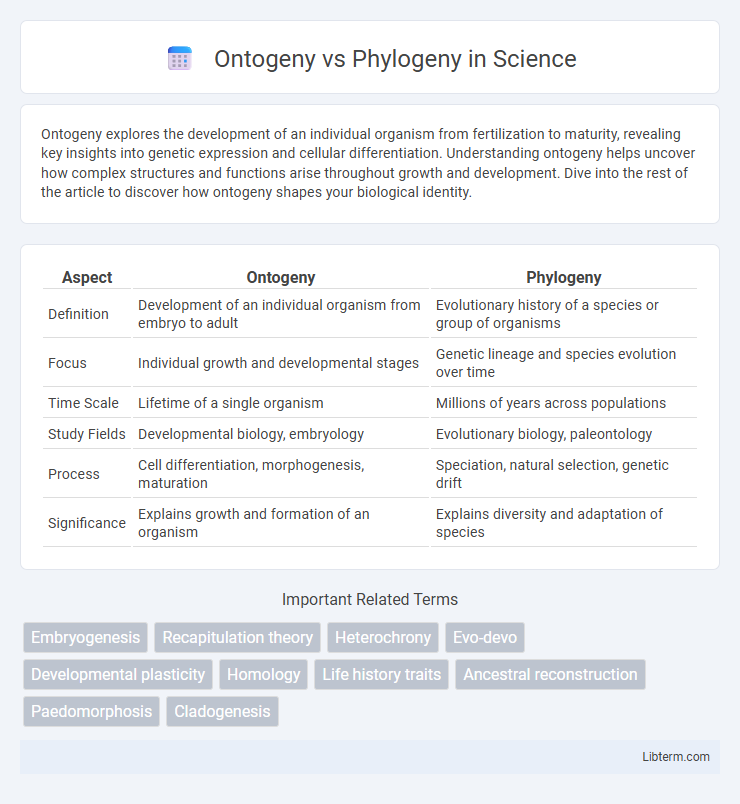
| Aspect | Ontogeny | Phylogeny |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development of an individual organism from embryo to adult | Evolutionary history of a species or group of organisms |
| Focus | Individual growth and developmental stages | Genetic lineage and species evolution over time |
| Time Scale | Lifetime of a single organism | Millions of years across populations |
| Study Fields | Developmental biology, embryology | Evolutionary biology, paleontology |
| Process | Cell differentiation, morphogenesis, maturation | Speciation, natural selection, genetic drift |
| Significance | Explains growth and formation of an organism | Explains diversity and adaptation of species |
Introduction to Ontogeny and Phylogeny
Ontogeny refers to the development of an individual organism from fertilization to maturity, encompassing all physical and behavioral changes throughout its life cycle. Phylogeny describes the evolutionary history and relationships among species, illustrating how organisms are related through common ancestry. Understanding ontogeny and phylogeny provides insights into the biological development and evolutionary processes that shape biodiversity.
Defining Ontogeny: The Developmental Perspective
Ontogeny refers to the developmental process by which an individual organism grows and differentiates from a single cell into its mature form, encompassing stages such as embryogenesis, growth, and aging. This perspective highlights the biological and genetic mechanisms driving cellular differentiation, tissue formation, and phenotypic changes throughout the organism's lifespan. Ontogeny provides crucial insights into developmental biology, revealing how genetic information and environmental factors interact to shape morphology and function.
Understanding Phylogeny: The Evolutionary Perspective
Phylogeny represents the evolutionary history and relationships among species, tracing lineage diversification through genetic and morphological data. This perspective helps reconstruct ancestral connections and species divergence over millions of years, providing insights into how traits and organisms evolved. Analyzing phylogenetic trees reveals patterns of common descent, adaptive radiation, and speciation, critical for understanding biodiversity and evolutionary processes.
Key Differences Between Ontogeny and Phylogeny
Ontogeny refers to the development of an individual organism from fertilization to maturity, highlighting processes such as cell differentiation, growth, and morphological changes. Phylogeny, on the other hand, describes the evolutionary history and relationships among species over geological time, emphasizing lineage divergence and speciation events. Key differences include ontogeny's focus on individual development stages versus phylogeny's broader perspective on species evolution and ancestral traits.
Historical Context: Haeckel’s Theory and Beyond
Ernst Haeckel's theory of ontogeny recapitulating phylogeny posited that an organism's development (ontogeny) mirrors its species' evolutionary history (phylogeny), influencing 19th-century evolutionary biology. This concept, although foundational, faced criticism for oversimplification and was revised with advances in embryology and genetics highlighting more complex developmental mechanisms. Modern evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) integrates molecular data, showcasing how genetic regulation shapes ontogeny without strict recapitulation of phylogenetic stages.
The Role of Ontogeny in Modern Biology
Ontogeny, the development of an individual organism from embryo to adult, plays a crucial role in modern biology by providing insights into evolutionary processes and species adaptation. It helps elucidate how genetic and environmental factors shape phenotypic traits across life stages, enhancing understanding of developmental biology and evolutionary mechanisms. Research in ontogeny contributes to advancements in fields like evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo), medicine, and conservation biology by linking developmental pathways to phylogenetic history.
Phylogenetic Approaches in Evolutionary Research
Phylogenetic approaches in evolutionary research analyze the evolutionary relationships among species by constructing trees based on genetic, morphological, and molecular data to trace lineage divergence and common ancestry. These methods enhance understanding of evolutionary patterns and processes by integrating comparative data across taxa, allowing inference of ancestral traits and evolutionary pathways. Modern techniques such as molecular phylogenetics and computational algorithms provide high-resolution insights into speciation events and adaptive evolution.
How Ontogeny and Phylogeny Interact
Ontogeny, the development of an individual organism from embryo to adult, interacts with phylogeny, the evolutionary history of a species, by reflecting ancestral traits in developmental stages. This relationship is demonstrated by the concept of recapitulation, where ontogenetic development can mirror phylogenetic changes, indicating that evolutionary adaptations influence developmental processes. Molecular genetics further reveals how gene expression during ontogeny is shaped by phylogenetic history, linking developmental biology with evolutionary patterns.
Applications in Developmental and Evolutionary Biology
Ontogeny, the development of an individual organism from embryo to adult, provides critical insights into gene expression patterns and morphological changes that inform evolutionary biology. Phylogeny, the evolutionary history and relationships among species, aids in reconstructing lineage diversification and ancestral traits through comparative genomics and paleontological data. Integrating ontogenetic and phylogenetic analyses enhances understanding of developmental constraints, evolutionary novelties, and the mechanisms driving biodiversity.
Future Directions in Ontogeny and Phylogeny Studies
Future directions in ontogeny and phylogeny studies emphasize integrative approaches combining genomics, developmental biology, and computational modeling to unravel complex evolutionary mechanisms. Advances in single-cell sequencing and CRISPR gene editing enable detailed analysis of developmental pathways and evolutionary divergences at unprecedented resolution. Increasing collaboration across disciplines aims to refine evolutionary developmental theories, enhancing understanding of phenotypic plasticity and species adaptation over time.
Ontogeny Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com