Substance P is a neuropeptide involved in transmitting pain signals and regulating inflammatory responses in the nervous system. It plays a crucial role in conditions such as chronic pain, depression, and anxiety by affecting neurotransmitter release and receptor activity. Discover how understanding Substance P can enhance Your knowledge of pain management and therapeutic strategies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
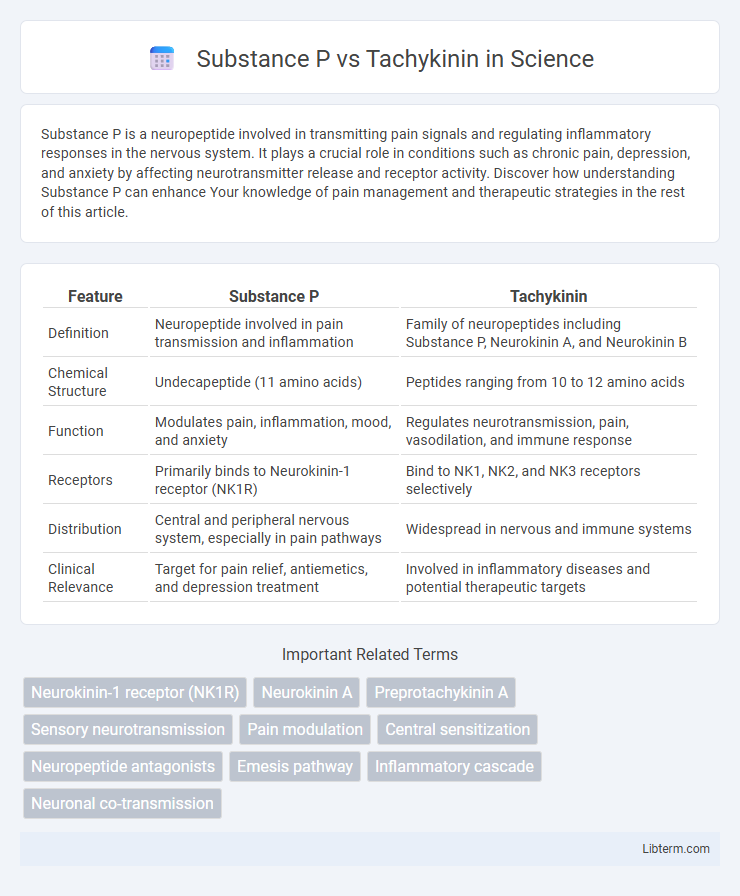
| Feature | Substance P | Tachykinin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Neuropeptide involved in pain transmission and inflammation | Family of neuropeptides including Substance P, Neurokinin A, and Neurokinin B |
| Chemical Structure | Undecapeptide (11 amino acids) | Peptides ranging from 10 to 12 amino acids |
| Function | Modulates pain, inflammation, mood, and anxiety | Regulates neurotransmission, pain, vasodilation, and immune response |
| Receptors | Primarily binds to Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) | Bind to NK1, NK2, and NK3 receptors selectively |
| Distribution | Central and peripheral nervous system, especially in pain pathways | Widespread in nervous and immune systems |
| Clinical Relevance | Target for pain relief, antiemetics, and depression treatment | Involved in inflammatory diseases and potential therapeutic targets |
Introduction to Substance P and Tachykinin
Substance P is a neuropeptide belonging to the tachykinin family, primarily involved in pain transmission and inflammatory responses. Tachykinins are a group of structurally related peptides that share a common carboxyl-terminal sequence, playing crucial roles in neurotransmission and smooth muscle contraction. Both Substance P and other tachykinins bind to neurokinin receptors, mediating physiological processes such as vasodilation and immune modulation.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Substance P and tachykinins share a conserved C-terminal sequence characterized by the amino acid motif Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, crucial for receptor binding and activation. Substance P, a specific tachykinin, consists of 11 amino acids with a sequence of Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, exhibiting unique N-terminal variations distinguishing it within the tachykinin family. Structural comparisons highlight that while all tachykinins possess the common C-terminal domain, differences in the N-terminal region, such as charged residues and peptide length, modulate their receptor selectivity and biological functions.
Biosynthesis and Distribution
Substance P, a member of the tachykinin peptide family, is synthesized through the cleavage of the preprotachykinin A gene product, primarily in sensory neurons of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Tachykinins, including neurokinin A and B, share a common biosynthetic pathway involving post-translational modifications and proteolytic processing of preprotachykinins A and B. Their distribution spans wide neural circuits, with Substance P prominently localized in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord regions associated with pain transmission, while other tachykinins exhibit distinct but overlapping patterns in the brain and gastrointestinal tract.
Receptor Binding and Mechanisms
Substance P is a neuropeptide belonging to the tachykinin family, characterized by its high affinity for the neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor, which it activates to modulate pain transmission and inflammatory responses. Tachykinins, including substance P, neurokinin A, and neurokinin B, bind selectively to NK1, NK2, and NK3 receptors, respectively, initiating G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades that influence smooth muscle contraction, vasodilation, and neurotransmitter release. The differential receptor binding profiles and downstream intracellular mechanisms of tachykinins determine their distinct physiological and pathological roles in nociception, neurogenic inflammation, and gastrointestinal motility.
Physiological Roles in the Nervous System
Substance P, a neuropeptide belonging to the tachykinin family, primarily modulates pain perception and inflammatory responses in the nervous system. Tachykinins, including Substance P, neurokinin A, and neurokinin B, regulate neurotransmission, smooth muscle contraction, and vasodilation across central and peripheral nervous pathways. Their interaction with neurokinin receptors (NK1, NK2, NK3) underpins critical physiological processes such as nociception, stress response, and neurogenic inflammation.
Involvement in Pain and Inflammation
Substance P, a key neuropeptide within the tachykinin family, plays a critical role in mediating pain perception and promoting inflammatory responses through its action on neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptors. Tachykinins, including neurokinin A and B alongside Substance P, collectively contribute to neurogenic inflammation by inducing vasodilation, plasma extravasation, and leukocyte recruitment at injury sites. The selective binding of Substance P to NK1 receptors distinguishes its potent involvement in transmitting nociceptive signals and amplifying inflammatory cascades, making it a primary target for pain and inflammation modulation therapies.
Clinical Significance and Pathological Roles
Substance P, a neuropeptide belonging to the tachykinin family, plays a critical role in transmitting pain signals and modulating inflammatory responses, making it a significant target in clinical pain management and inflammatory disease therapies. Tachykinins, including Substance P, neurokinin A, and neurokinin B, are involved in various pathological processes such as neurogenic inflammation, asthma, and psychiatric disorders by interacting with neurokinin receptors (NK1, NK2, NK3). The heightened expression of Substance P and other tachykinins in pathological tissues correlates with conditions like chronic pain syndromes, respiratory diseases, and cancer progression, thus emphasizing their importance in developing receptor antagonists for therapeutic interventions.
Therapeutic Potential and Drug Development
Substance P, a prominent neuropeptide within the tachykinin family, plays a critical role in pain transmission and inflammatory responses, making it a key target for therapeutic interventions in conditions like chronic pain, depression, and inflammatory diseases. Tachykinin receptor antagonists, particularly NK1 receptor blockers, have shown significant promise in drug development by effectively modulating Substance P-mediated signaling pathways, leading to advancements in treatments for chemotherapy-induced nausea and psychiatric disorders. Ongoing research emphasizes optimizing receptor selectivity and bioavailability to enhance the clinical efficacy and safety profiles of tachykinin-based therapeutics.
Recent Research and Emerging Trends
Recent research highlights that Substance P, a key neuropeptide in the tachykinin family, plays a crucial role in pain modulation, inflammation, and neuroimmune interactions. Emerging trends focus on its receptor, neurokinin-1 (NK1R), as a therapeutic target for conditions like chronic pain, depression, and cancer. Advanced studies utilize novel antagonists and gene editing to modulate tachykinin signaling pathways, aiming to improve specificity and minimize side effects.
Future Directions and Challenges
Future research on Substance P and tachykinins is poised to enhance understanding of their roles in neuroinflammation and chronic pain pathways, driving development of targeted therapeutics with improved selectivity and efficacy. Advances in receptor subtype characterization and signaling mechanisms offer potential for novel drug designs that minimize side effects commonly associated with current tachykinin receptor antagonists. Challenges remain in translating preclinical findings to clinical success due to complex receptor interactions and compensatory biological pathways influencing therapeutic outcomes.
Substance P Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com