Seta is a multifunctional rarely overlooked natural fiber known for its softness, strength, and durability, making it ideal for textiles and luxury fabrics. Its unique properties enhance your clothing's comfort while providing excellent insulation and breathability. Explore the rest of the article to discover how seta can transform your wardrobe and lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
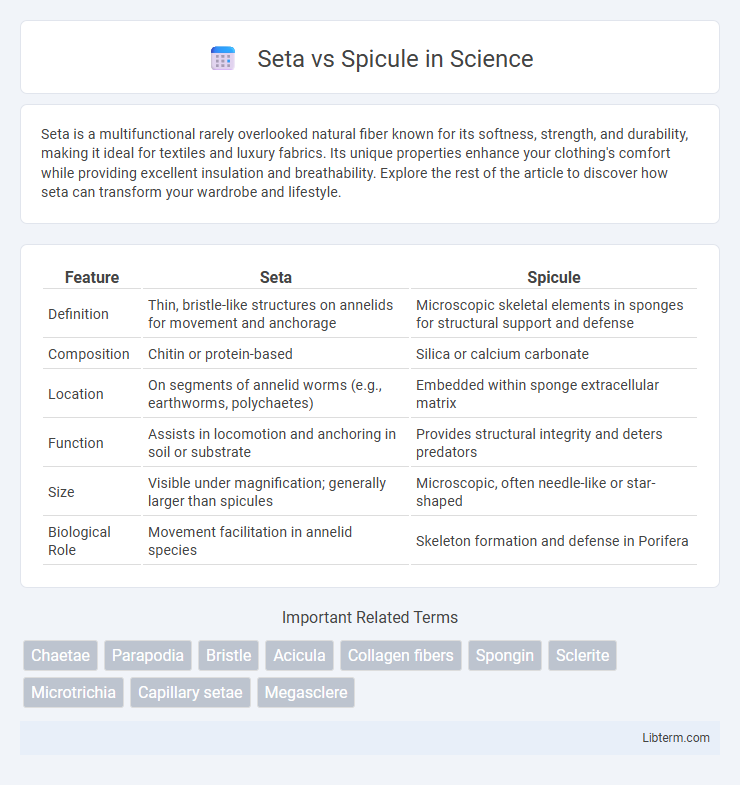
| Feature | Seta | Spicule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thin, bristle-like structures on annelids for movement and anchorage | Microscopic skeletal elements in sponges for structural support and defense |
| Composition | Chitin or protein-based | Silica or calcium carbonate |
| Location | On segments of annelid worms (e.g., earthworms, polychaetes) | Embedded within sponge extracellular matrix |
| Function | Assists in locomotion and anchoring in soil or substrate | Provides structural integrity and deters predators |
| Size | Visible under magnification; generally larger than spicules | Microscopic, often needle-like or star-shaped |
| Biological Role | Movement facilitation in annelid species | Skeleton formation and defense in Porifera |
Introduction to Seta and Spicule
Setae and spicules serve as structural components in various organisms, providing support and protection. Setae are bristle-like appendages found in annelids and some arthropods, composed primarily of chitin or keratin, aiding in locomotion and sensory functions. Spicules are rigid, mineralized elements found in sponges and some marine animals, made of silica or calcium carbonate, contributing to skeletal framework and defense mechanisms.
Definition and Basic Structure
Setae are hair-like bristles composed primarily of chitin found on the surface of various invertebrates, aiding in movement and sensory functions. Spicules are small, rigid structural elements made of silica or calcium carbonate that provide skeletal support in sponges and some marine organisms. While setae are flexible and involved in locomotion or sensing, spicules serve as a protective framework within the organism's body.
Biological Function of Seta
Setae function as hair-like structures on the surface of certain organisms, primarily aiding in locomotion, attachment, and sensory perception. They play a crucial role in providing grip and movement in annelids and arthropods by interacting with the environment, allowing organisms to anchor or crawl effectively. In contrast, spicules serve mainly as structural support within sponges, offering protection and maintaining shape rather than facilitating movement.
Biological Function of Spicule
Spicules play a critical biological role as structural elements in sponges, providing support and protection against predators through their rigid, needle-like composition made of silica or calcium carbonate. Unlike setae, which primarily aid in locomotion and sensory functions in annelids, spicules form the sponge's skeletal framework, facilitating water flow and nutrient exchange essential for filtering processes. The diverse shapes and sizes of spicules also contribute to species identification and adaptation to different aquatic environments.
Occurrence in Different Organisms
Setae commonly occur in annelids such as earthworms and polychaetes, serving as bristle-like structures that aid in locomotion and environmental interaction. Spicules are primarily found in sponges (Porifera), where they function as structural support and deterrents against predators through their rigid, needle-like forms. Both structures vary in composition, with setae typically composed of chitin or proteins, while spicules consist of silica or calcium carbonate, reflecting adaptations to their respective aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Structural Differences: Seta vs Spicule
Setae are rigid, bristle-like structures composed primarily of chitin, found on annelids such as earthworms and polychaetes, functioning in locomotion and anchorage. Spicules, on the other hand, are mineralized skeletal elements made of silica or calcium carbonate present in sponges, providing structural support and defense. While setae are flexible and externally located on segmented worms, spicules form an internal network contributing to sponge rigidity and protection.
Evolutionary Significance
Setae and spicules represent key evolutionary adaptations in diverse taxa, with setae primarily found in annelids and spicules in sponges, each contributing to organismal survival and ecological niche specialization. The development of setae in annelids enhances locomotion and substrate anchoring, promoting greater habitat exploitation and mobility, while spicules in sponges provide structural support and deterrence against predators, facilitating colonial stability and defense. These morphological features illustrate convergent evolutionary strategies for protection and environmental interaction, underscoring their significance in the diversification and success of respective phyla.
Role in Classification and Identification
Setae and spicules serve critical roles in the classification and identification of various organisms, especially invertebrates like annelids and sponges. Setae are bristle-like structures primarily used to differentiate species within segmented worms based on their shape, arrangement, and size. Spicules, composed of silica or calcium carbonate, provide a skeletal framework in sponges, with their unique morphologies serving as key taxonomic markers for species identification.
Applications in Research and Biotechnology
Setae and spicules serve distinct roles in research and biotechnology, with setae commonly applied in biomimetic studies for developing adhesive technologies due to their micro-structured surfaces inspired by gecko feet. Spicules, primarily studied in marine biology, are utilized as models in materials science to develop lightweight, strong composites and bioinspired structural materials. Both structures contribute to advancements in nanotechnology, tissue engineering, and the design of novel biomaterials through their unique morphological and mechanical properties.
Summary and Key Distinctions
Setae are thin, hair-like bristles found on the bodies of various invertebrates, primarily serving sensory or locomotion functions, whereas spicules are rigid, mineralized skeletal elements present in sponges, providing structural support and defense. Setae are composed mainly of chitin and vary in size and shape depending on their role, while spicules consist of silica or calcium carbonate with distinct geometric forms unique to sponge species. The key distinctions lie in their biological composition, function, and presence across different animal groups, with setae facilitating movement or sensory input, and spicules acting as a defensive and supportive framework in sponges.
Seta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com