Endometriosis is a chronic condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, causing pain and potential fertility issues. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options is crucial for managing your health and improving quality of life. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to recognize signs and find effective therapies for endometriosis.
Table of Comparison
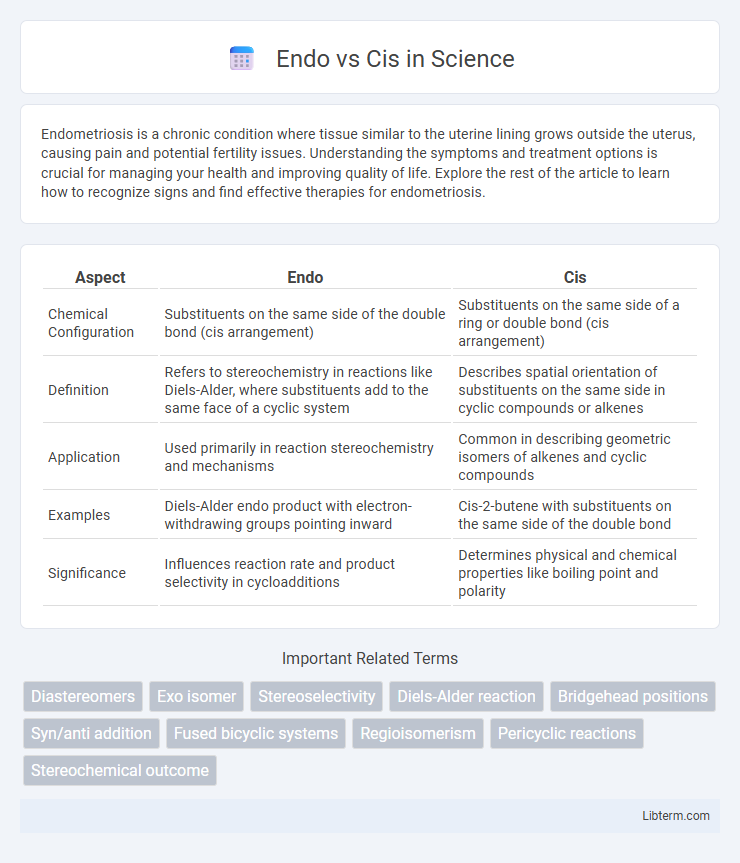
| Aspect | Endo | Cis |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Configuration | Substituents on the same side of the double bond (cis arrangement) | Substituents on the same side of a ring or double bond (cis arrangement) |
| Definition | Refers to stereochemistry in reactions like Diels-Alder, where substituents add to the same face of a cyclic system | Describes spatial orientation of substituents on the same side in cyclic compounds or alkenes |
| Application | Used primarily in reaction stereochemistry and mechanisms | Common in describing geometric isomers of alkenes and cyclic compounds |
| Examples | Diels-Alder endo product with electron-withdrawing groups pointing inward | Cis-2-butene with substituents on the same side of the double bond |
| Significance | Influences reaction rate and product selectivity in cycloadditions | Determines physical and chemical properties like boiling point and polarity |
Understanding Endo and Cis: Key Definitions
Endo and cis refer to specific stereochemical configurations in organic chemistry, describing the relative positions of substituents on cyclic compounds. Endo denotes substituents oriented toward the interior or underside of a ring system, while cis indicates substituents positioned on the same side of a double bond or ring. Understanding these definitions is crucial for interpreting molecular geometry and predicting reactivity in organic synthesis.
Historical Context of Endo and Cis
Endo and Cis are specialized terms with distinct historical roots in Japanese automotive culture, particularly within the drifting community. Endo refers to "end-over-end" car flips popularized by early street racers in the 1990s, while Cis, a less common term, is often associated with the "continuous inside drift style" emerging alongside Endo during the same period. The evolution of these styles paralleled Japan's underground racing scene development, influencing global drifting techniques and car customization trends.
Social and Cultural Implications
Endometriosis (Endo) and cisgender identities (Cis) bear distinct social and cultural implications, particularly in healthcare and community representation. Endometriosis, often misunderstood and underdiagnosed, highlights gaps in women's health and reinforces the need for increased medical awareness and advocacy. Cisgender individuals typically experience societal normativity, contrasting with the marginalized experiences faced by those navigating conditions like endometriosis or diverse gender identities, emphasizing the importance of inclusive dialogue and support systems.
Endo vs Cis: Identity Perspectives
Endo and Cis identities represent distinct experiences within gender and cultural contexts, with Endo referring to individuals of indigenous or native origin asserting traditional identities, while Cis denotes those whose gender identity aligns with their sex assigned at birth. The Endo perspective emphasizes cultural preservation and resistance against colonial legacies, contrasting with Cis experiences often centered on mainstream gender normativity. Understanding these identity frameworks highlights the interplay between cultural heritage and gender identity politics in diverse communities.
Common Misconceptions and Myths
Endometriosis (Endo) and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (Cis) are often confused due to similar symptom presentations, yet they represent distinct gynecological conditions with different pathologies. A common misconception is that Endo is related to cervical cancer or that Cis arises from endometrial tissue, whereas Endo involves ectopic endometrial tissue growth outside the uterus and Cis refers to precancerous changes in cervical cells. Clarifying these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient education.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Identity
Endo identities offer heightened privacy and anonymity through decentralized control but face challenges in widespread adoption due to complex user management and interoperability issues. Cis identities provide streamlined integration with existing centralized systems, facilitating easier regulatory compliance and user experience, yet they risk greater vulnerability to data breaches and limited user autonomy. Balancing security, control, and usability remains a central consideration when choosing between Endo and Cis identity frameworks.
Representation in Media and Popular Culture
Endometriosis (Endo) and cisgender identity (Cis) are depicted differently in media and popular culture, with Endo often underrepresented or portrayed inaccurately, leading to a lack of awareness about the chronic pain and infertility challenges faced by those with endometriosis. Media representation of cisgender individuals typically reinforces societal norms, marginalizing the visibility of gender-diverse experiences while influencing public perception and acceptance. Increasing accurate portrayals of Endo in popular culture can improve empathy and support for affected individuals, while broader representation of diverse gender identities promotes inclusivity and social understanding.
Community Experiences and Real Stories
Patients navigating gender identity often share profound community experiences highlighting the contrast between Endo and Cis identities, revealing unique challenges and support networks. Real stories emphasize how Endo individuals may face misunderstandings and require specialized medical care, while Cis people typically encounter societal acceptance aligned with their gender assigned at birth. These narratives deepen awareness of lived realities, fostering empathy and informed discussions within LGBTQ+ and healthcare communities.
Addressing Stigma and Discrimination
Endometriosis (Endo) and cisgender identity (Cis) face distinct but intersecting challenges regarding stigma and discrimination, impacting patient care and social acceptance. Endo patients often suffer from medical dismissal and misunderstanding due to the chronic pain invisibility, while individuals identifying as Cis generally benefit from societal norms but may lack awareness of gender diversity, perpetuating stigma against transgender and non-binary communities. Combating these issues requires targeted education, inclusive healthcare policies, and empathetic communication to reduce biases and improve outcomes for all affected groups.
Moving Toward Inclusivity and Respect
Endo and Cis identities highlight the importance of inclusivity and respect within gender and sexual orientation discussions. Embracing diverse experiences fosters understanding and combats prejudice by validating everyone's self-identification. Promoting empathy and open dialogue supports a culture where all individuals feel seen and respected.
Endo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com