Trans rights are fundamental human rights that ensure equality, dignity, and protection for transgender individuals. Understanding these rights helps combat discrimination and promotes inclusivity in all areas of society. Discover how protecting trans rights impacts your community by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
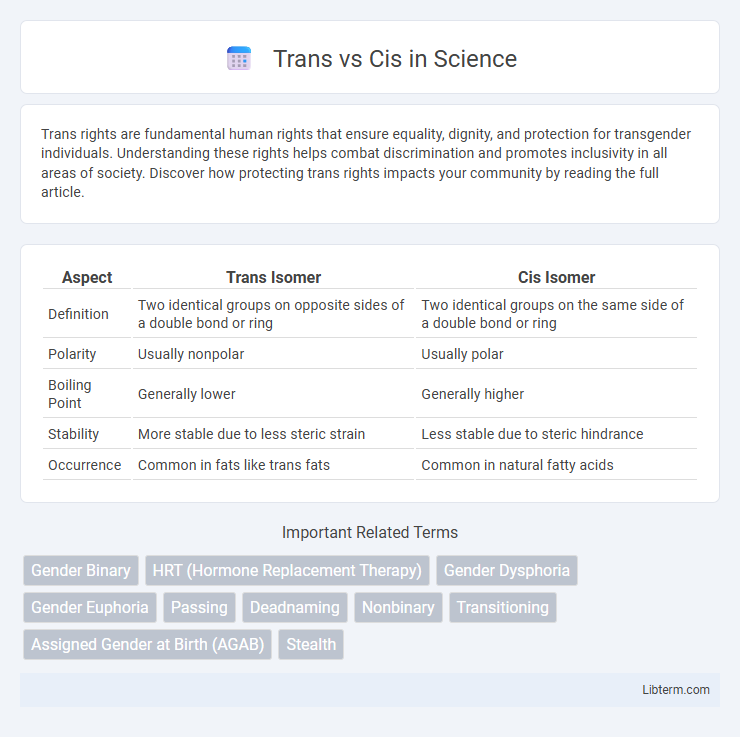
| Aspect | Trans Isomer | Cis Isomer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two identical groups on opposite sides of a double bond or ring | Two identical groups on the same side of a double bond or ring |
| Polarity | Usually nonpolar | Usually polar |
| Boiling Point | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Stability | More stable due to less steric strain | Less stable due to steric hindrance |
| Occurrence | Common in fats like trans fats | Common in natural fatty acids |
Understanding Trans and Cis: Definitions and Distinctions
Trans and cis are terms used primarily in chemistry and gender identity contexts, each representing distinct concepts. In chemistry, cis refers to molecules with functional groups on the same side of a double bond or ring structure, while trans describes those with groups on opposite sides, affecting physical properties and reactivity. In gender identity, cisgender denotes individuals whose gender identity aligns with their sex assigned at birth, whereas transgender describes those whose gender identity differs from their assigned sex.
The History of Trans and Cis Terminology
The terms "trans" and "cis" originated in chemistry in the 19th century to describe geometric isomers with differing configurations across a double bond. By the late 20th century, these prefixes were adopted in gender studies to denote individuals whose gender identity does (trans) or does not (cis) align with their sex assigned at birth. The introduction of "cisgender" aimed to create a non-stigmatizing counterpart to "transgender," facilitating clearer discussions about gender identity and social experience.
Navigating Gender Identity: Common Myths and Facts
Navigating gender identity involves understanding the differences between trans and cis individuals, where trans people identify with a gender different from their sex assigned at birth, while cis individuals align with their birth-assigned gender. Common myths include the misconception that gender identity is a choice or can be changed, whereas facts emphasize that gender identity is an intrinsic aspect of a person's sense of self. Recognizing the importance of respecting pronouns and supporting inclusive environments fosters acceptance and mental well-being for both trans and cis communities.
Biological Sex vs Gender Identity: What’s the Difference?
Biological sex is determined by chromosomes, hormones, and anatomy, typically classified as male or female at birth, while gender identity refers to an individual's internal sense of being male, female, both, neither, or somewhere along the gender spectrum. Transgender people have a gender identity that differs from their biological sex, whereas cisgender individuals' gender identity aligns with their assigned sex at birth. Understanding the distinction between biological sex and gender identity is essential for recognizing the diversity of human experiences and promoting acceptance of transgender and cisgender identities.
Societal Perceptions of Trans and Cis Experiences
Societal perceptions of trans and cis experiences often diverge, with cisgender identities generally normalized and trans identities frequently misunderstood or marginalized. Trans individuals face unique challenges including discrimination, misgendering, and limited legal protections, which influence public attitudes and social inclusion. Awareness and education about gender diversity are critical to fostering acceptance and reducing stigma surrounding trans experiences.
Representation of Trans vs Cis Individuals in Media
Media representation of trans individuals has increased significantly, highlighting diverse gender identities and experiences with more accuracy and empathy compared to historical portrayals. Cisgender characters remain predominant in mainstream media, often reinforcing traditional gender norms, which limits visibility and understanding of trans experiences. Increased inclusion of trans actors and narratives contributes to reducing stigma, fostering awareness, and promoting social acceptance across multiple platforms.
Health Care Disparities: Trans and Cis Perspectives
Transgender individuals face significant health care disparities compared to cisgender people, including higher rates of mental health issues, limited access to gender-affirming treatments, and increased experiences of discrimination in medical settings. Cisgender patients typically encounter more standardized and accessible health care services aligned with their gender identity, resulting in fewer barriers to receiving appropriate care. Addressing these disparities requires targeted training for health professionals and systemic reforms to ensure equitable, culturally competent care for transgender populations.
Legal Rights and Challenges: Trans vs Cis in Society
Trans individuals often face significant legal challenges compared to cisgender people, including difficulties in changing legal documents to reflect their gender identity, discrimination in employment, healthcare, and housing, and uneven protection under anti-discrimination laws. Cisgender individuals typically benefit from legal recognition and societal acceptance without the need for complex legal processes or fear of systemic bias. The disparity in legal rights and protections highlights the need for comprehensive legislation ensuring equality and safeguarding the rights of transgender people.
Creating Inclusive Environments for All Gender Identities
Creating inclusive environments for all gender identities involves recognizing and respecting both trans and cis individuals, fostering spaces where everyone feels valued and safe. Implementing inclusive policies, such as gender-neutral restrooms and pronoun awareness initiatives, promotes equity and reduces discrimination. Education and ongoing dialogue about gender diversity enhance understanding and support within communities and workplaces, ensuring acceptance for all identities.
Moving Forward: Advocacy and Allyship for Trans and Cis Communities
Advocacy for both trans and cis communities involves promoting understanding, respect, and equality through inclusive policies and education that dismantle systemic barriers and discrimination. Allyship requires active listening, amplifying trans voices, and collaborating to create safe spaces that honor diverse gender identities and experiences. Efforts focused on intersectionality and mutual support help build solidarity, fostering social environments where all individuals can thrive authentically.
Trans Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com