Amensalism is a biological interaction where one species is inhibited or destroyed while the other remains unaffected, often observed in microbial ecosystems and plant communities. This relationship can influence biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics by limiting the growth or survival of certain species. Explore the rest of the article to understand how amensalism impacts ecological balance and species interactions.
Table of Comparison
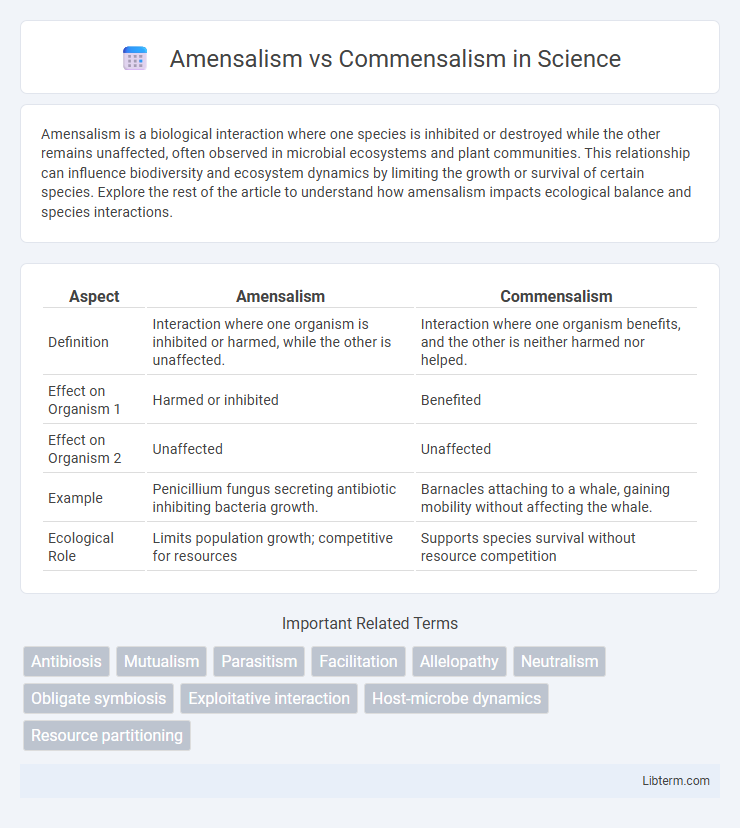
| Aspect | Amensalism | Commensalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interaction where one organism is inhibited or harmed, while the other is unaffected. | Interaction where one organism benefits, and the other is neither harmed nor helped. |
| Effect on Organism 1 | Harmed or inhibited | Benefited |
| Effect on Organism 2 | Unaffected | Unaffected |
| Example | Penicillium fungus secreting antibiotic inhibiting bacteria growth. | Barnacles attaching to a whale, gaining mobility without affecting the whale. |
| Ecological Role | Limits population growth; competitive for resources | Supports species survival without resource competition |
Introduction to Species Interactions
Amensalism and commensalism represent two distinct types of species interactions characterized by their differing effects on the organisms involved. In amensalism, one species experiences a negative impact while the other remains unaffected, as seen in the release of antibiotics by certain fungi inhibiting bacterial growth. Commensalism involves one species benefiting without harming or benefiting the other, such as barnacles attaching to whales for transportation and access to food resources without affecting the whale.
Defining Amensalism
Amensalism is an ecological interaction where one organism is inhibited or destroyed while the other remains unaffected, often seen in cases like the secretion of antibiotics by fungi that inhibit bacterial growth. This relationship contrasts with commensalism, where one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped. Understanding amensalism is crucial for studying species competition and ecosystem dynamics, particularly in microbial and plant communities.
Understanding Commensalism
Commensalism is a biological relationship where one organism benefits while the other remains unaffected, exemplified by barnacles attaching to whales for mobility and access to nutrients without harming the host. This interaction is crucial in ecosystems for promoting biodiversity and resource utilization without negative impacts on the host species. Understanding commensalism helps clarify species interactions and ecosystem dynamics, distinct from amensalism where one species is harmed while the other is unaffected.
Key Differences Between Amensalism and Commensalism
Amensalism involves one organism being harmed while the other remains unaffected, often seen in interactions where one species releases toxins that inhibit another. Commensalism describes a relationship where one organism benefits and the other experiences no harm or benefit, such as epiphytic plants growing on trees for support. The key difference lies in the impact on the unaffected organism--amensalism causes harm, whereas commensalism does not.
Ecological Significance of Amensalism
Amensalism plays a crucial ecological role by regulating species populations without direct competition, often through the release of biochemicals that inhibit the growth or survival of competitors, such as allelopathic plants suppressing neighboring vegetation. This interaction maintains biodiversity and stabilizes ecosystems by preventing dominance of aggressive species, promoting habitat heterogeneity. Unlike commensalism, where one species benefits without harming the other, amensalism influences community dynamics through asymmetric negative effects essential for ecological balance.
Ecological Role of Commensalism
Commensalism plays a crucial ecological role by enabling one species to benefit without harming or helping the other, often facilitating resource utilization and habitat enhancement. This interaction supports biodiversity by allowing species to coexist and occupy ecological niches without direct competition or antagonism. Unlike amensalism, where one species is harmed and the other is unaffected, commensalism contributes positively to ecosystem stability and species interdependence.
Real-World Examples of Amensalism
Amensalism occurs when one organism is inhibited or destroyed while the other remains unaffected, exemplified by the black walnut tree releasing juglone, a chemical that suppresses the growth of nearby plants. In marine environments, penicillium mold secretes antibiotics that kill bacteria, demonstrating amensalism as the mold benefits without impact from the bacteria. This contrasts with commensalism, where one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped, such as barnacles attaching to whales.
Common Examples of Commensalism
Commensalism frequently occurs in nature, exemplified by barnacles attaching to whale skin, gaining transportation and access to food without harming the host. Another common example includes epiphytic plants, such as orchids, growing on tree branches to access sunlight while not affecting the tree's health. Additionally, cattle egrets feed on insects disturbed by grazing livestock, benefiting from the foraging activity without impacting the cattle.
Impact on Ecosystem Dynamics
Amensalism negatively affects one species while having no impact on the other, often leading to the suppression of population growth and altered resource availability, which can shift competitive balances in ecosystems. Commensalism benefits one species by providing resources or habitat without harming or benefiting the other, promoting species diversity and stability by enabling coexistence without direct competition. These interactions shape ecosystem dynamics by influencing species distribution, community structure, and resource allocation, ultimately affecting ecosystem resilience and function.
Conclusion: Importance of Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships like amensalism and commensalism play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by influencing species interactions and resource distribution. Understanding these interactions helps in biodiversity conservation and ecosystem stability by revealing how organisms affect each other's survival and reproduction. The study of amensalism and commensalism highlights the complexity of ecological networks and the importance of preserving diverse habitats for sustaining life on Earth.
Amensalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com