Independence empowers you to make decisions confidently and take control of your life's direction. Embracing self-reliance fosters personal growth, resilience, and a deeper understanding of your values. Discover how cultivating independence can transform your mindset and daily experiences in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
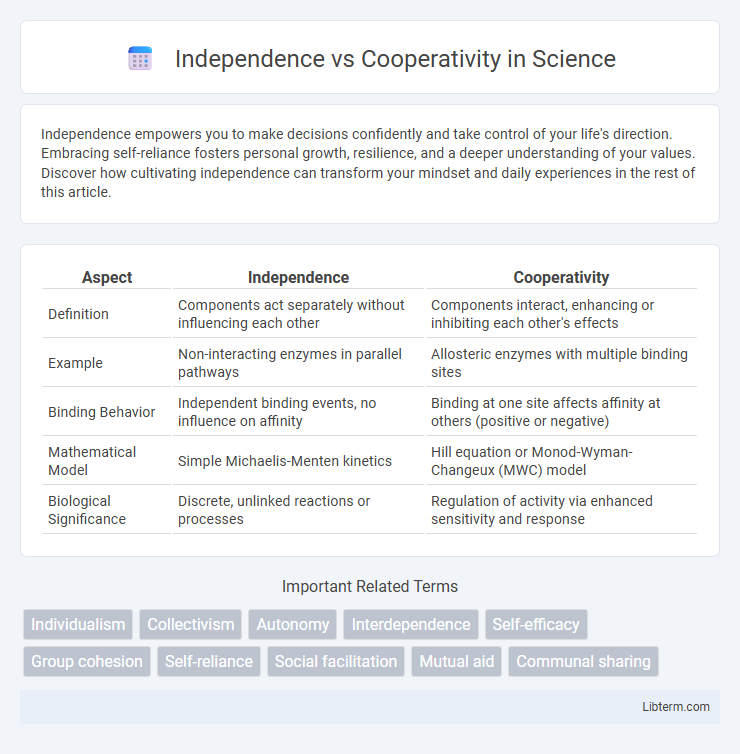
| Aspect | Independence | Cooperativity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Components act separately without influencing each other | Components interact, enhancing or inhibiting each other's effects |
| Example | Non-interacting enzymes in parallel pathways | Allosteric enzymes with multiple binding sites |
| Binding Behavior | Independent binding events, no influence on affinity | Binding at one site affects affinity at others (positive or negative) |
| Mathematical Model | Simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics | Hill equation or Monod-Wyman-Changeux (MWC) model |
| Biological Significance | Discrete, unlinked reactions or processes | Regulation of activity via enhanced sensitivity and response |
Understanding Independence and Cooperativity
Independence refers to events or variables occurring without influencing each other, often measured using statistical metrics like correlation coefficients close to zero or probabilities that multiply exactly. Cooperativity describes scenarios where elements or processes interact synergistically, enhancing or inhibiting each other's effects, commonly seen in biochemical systems such as enzyme kinetics or receptor-ligand binding with Hill coefficients above one. Understanding independence and cooperativity is crucial for analyzing complex systems in fields ranging from molecular biology to economics, as it determines whether components act autonomously or interdependently.
Key Differences Between Independence and Cooperativity
Independence in molecular interactions refers to components acting without influencing each other's binding affinities or activities, whereas cooperativity involves a scenario where the binding of one molecule affects the binding affinity of additional molecules, often enhancing their interaction. The key difference lies in the presence of allosteric effects in cooperativity, which causes non-linear binding curves, contrasted with linear and additive effects observed under independence. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in biochemistry for interpreting enzyme kinetics, protein-ligand interactions, and signal transduction mechanisms.
Psychological Foundations of Independent Behavior
Independent behavior is rooted in psychological foundations such as intrinsic motivation, self-determination theory, and personal agency, which emphasize autonomy and internal control. Cognitive processes like self-regulation and individual goal-setting support independence by allowing individuals to prioritize personal values over social conformity. Neural correlates involving the prefrontal cortex highlight decision-making mechanisms that facilitate independent choices distinct from cooperative group dynamics.
The Social Dynamics of Cooperative Actions
The social dynamics of cooperative actions hinge on the interplay between individual independence and collective cooperativity, where individuals balance personal goals with group objectives to achieve shared benefits. Cooperation enhances social cohesion and trust, promoting efficient problem-solving and resource sharing across communities. Understanding these dynamics reveals how cooperative behavior emerges from social norms, mutual dependencies, and reciprocal interactions within diverse group settings.
Benefits of Independence in Personal Growth
Independence in personal growth fosters self-reliance, enabling individuals to develop critical decision-making skills and build confidence in their abilities. It promotes resilience by encouraging problem-solving without reliance on external support, leading to stronger emotional intelligence and adaptability. Cultivating independence also enhances personal accountability, driving continuous self-improvement and a clearer understanding of one's values and goals.
Advantages of Cooperativity in Team Settings
Cooperativity in team settings enhances problem-solving by leveraging diverse perspectives, leading to more innovative and comprehensive solutions. It fosters a strong sense of shared responsibility and trust, which increases motivation and commitment among team members. This collaborative approach improves communication efficiency, reduces errors, and accelerates project completion compared to independent work.
Balancing Independence and Cooperativity in Daily Life
Balancing independence and cooperativity in daily life involves managing personal autonomy while fostering meaningful collaboration with others. Effective decision-making requires recognizing when to rely on self-direction versus seeking input and support from teams or social groups. Striking this balance enhances productivity, strengthens relationships, and promotes overall well-being by integrating individual goals with collective efforts.
Case Studies: When to Choose Independence or Cooperativity
Case studies reveal that choosing independence is optimal in scenarios demanding rapid innovation and flexibility, such as startups exploring diverse product ideas. Conversely, cooperativity excels in large organizations requiring coordination, shared resources, and unified goal pursuit, evident in complex projects like aerospace engineering. Understanding project scale, complexity, and team expertise guides the strategic decision between independent and cooperative approaches for maximizing productivity and innovation.
Cultural Perspectives on Independence vs Cooperativity
Cultural perspectives on independence versus cooperativity reveal significant variations in how societies value individual autonomy or group harmony. Western cultures often emphasize independence, encouraging self-reliance and personal achievement, while many Eastern and indigenous cultures prioritize cooperativity, stressing community interdependence and collective decision-making. These differing cultural values impact social behavior, communication styles, and conflict resolution strategies, shaping diverse approaches to collaboration and individual responsibility.
Strategies for Fostering Both Independence and Cooperativity
Effective strategies for fostering both independence and cooperativity include implementing project-based learning that encourages individual accountability while promoting teamwork. Creating structured group roles and clear communication channels supports collaboration as each member contributes unique skills independently. Integrating reflective practices helps students develop self-regulation alongside social responsibility, balancing autonomous problem-solving with cooperative engagement.
Independence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com