Dehydrated skin lacks essential moisture, leading to a dull, tight, and flaky appearance that affects your natural glow. Proper hydration with water and moisturizing products containing humectants can restore skin balance and improve texture. Discover effective strategies to rehydrate your skin and maintain a radiant complexion in the full article.
Table of Comparison
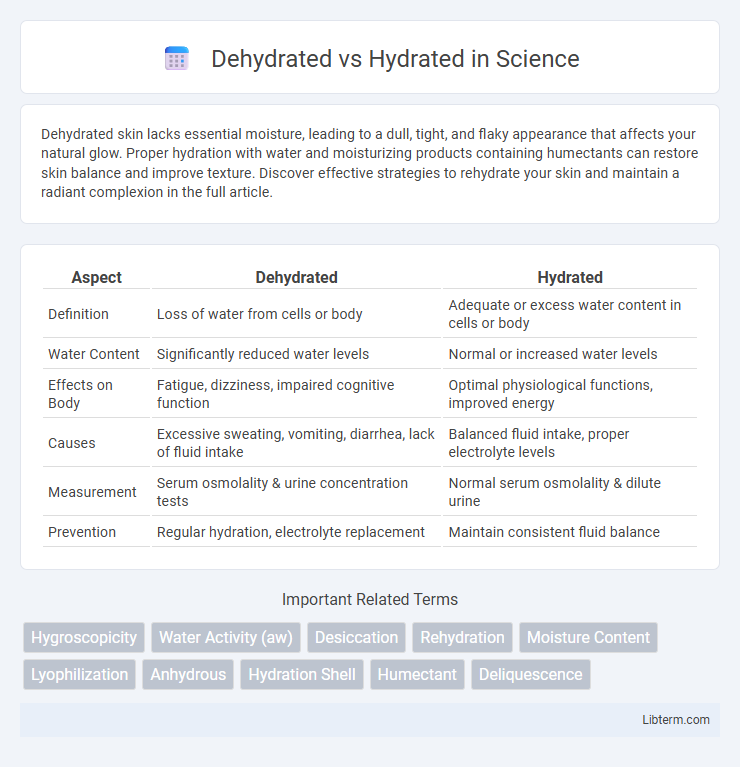
| Aspect | Dehydrated | Hydrated |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of water from cells or body | Adequate or excess water content in cells or body |
| Water Content | Significantly reduced water levels | Normal or increased water levels |
| Effects on Body | Fatigue, dizziness, impaired cognitive function | Optimal physiological functions, improved energy |
| Causes | Excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, lack of fluid intake | Balanced fluid intake, proper electrolyte levels |
| Measurement | Serum osmolality & urine concentration tests | Normal serum osmolality & dilute urine |
| Prevention | Regular hydration, electrolyte replacement | Maintain consistent fluid balance |
Understanding Hydration: The Basics
Hydration involves maintaining the body's optimal fluid balance, crucial for cellular function, temperature regulation, and overall health. Dehydration occurs when fluid loss exceeds intake, leading to impaired cognitive and physical performance, electrolyte imbalance, and potential organ stress. Monitoring hydration status through indicators like urine color, thirst level, and body weight changes helps prevent complications and supports vital physiological processes.
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
Dehydration manifests through key signs and symptoms such as intense thirst, dry mouth, and reduced urine output, often dark yellow in color. Other indicators include fatigue, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and decreased skin elasticity, signaling the body's need for rehydration. Severe dehydration can lead to confusion, sunken eyes, and low blood pressure, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Health Benefits of Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated maintains optimal bodily functions by regulating temperature, supporting digestion, and enhancing cognitive performance. Proper hydration boosts energy levels, improves skin health, and aids in detoxification by flushing out toxins through urine. Dehydration can lead to headaches, fatigue, and impaired physical performance, highlighting the critical health benefits of consistent fluid intake.
Consequences of Chronic Dehydration
Chronic dehydration leads to impaired cognitive function, persistent fatigue, and increased risk of kidney stones due to prolonged insufficient water intake. It disrupts electrolyte balance, causing muscle cramps and negatively affecting cardiovascular health by increasing blood viscosity and strain on the heart. Long-term dehydration can also accelerate the progression of chronic kidney disease and reduce overall cellular function, impacting metabolic processes.
Hydrated vs. Dehydrated: Performance and Energy Levels
Hydrated individuals maintain optimal cognitive function and physical performance due to efficient cellular hydration and electrolyte balance, which supports energy metabolism and muscle function. Dehydration impairs cognitive abilities, reduces endurance, and increases fatigue by disrupting blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscles. Consistent hydration sustains energy levels and delays the onset of exhaustion during exercise or daily activities.
Impact on Skin and Physical Appearance
Dehydrated skin lacks water, resulting in a dull, tight, and flaky appearance, while hydrated skin appears plump, smooth, and radiant due to optimal moisture levels. Dehydration triggers increased sensitivity and fine lines as the skin's barrier function weakens, whereas well-hydrated skin maintains elasticity and resilience against environmental stressors. Maintaining hydration through topical moisturizers and proper water intake significantly improves skin texture and overall physical appearance.
Cognitive Function: Dehydrated vs. Hydrated Brain
Hydrated brains maintain optimal cognitive function by supporting efficient neural communication, memory retention, and concentration levels. Dehydration impairs brain volume and activity, leading to decreased attention, slower reaction times, and compromised executive functions. Proper hydration enhances synaptic plasticity and cerebral blood flow, crucial for maintaining mental performance and preventing cognitive decline.
Best Practices for Optimal Hydration
Maintaining optimal hydration involves balancing fluid intake with electrolyte levels, as dehydration impairs cellular function and cognitive performance. Consuming water alongside electrolyte-rich beverages, such as those containing sodium, potassium, and magnesium, supports efficient rehydration and prevents imbalances. Monitoring urine color for a pale yellow shade and drinking consistently throughout the day ensures sustained hydration, especially during intense physical activity or hot climates.
Common Myths About Dehydration
Common myths about dehydration often include beliefs such as only intense exercise or heat causes dehydration, while mild activities and cool environments can also contribute to fluid loss. Another misconception is that thirst is the most reliable indicator of dehydration; however, early signs like dry mouth and dark urine often appear before thirst is triggered. Contrary to popular belief, drinking excessive water does not always prevent dehydration, as electrolyte imbalance plays a crucial role in proper hydration.
Choosing the Right Fluids for Proper Hydration
Choosing the right fluids for proper hydration involves considering electrolyte content, absorption rates, and individual needs. Hydrated fluids like water and oral rehydration solutions provide immediate hydration and maintain electrolyte balance, while dehydrated options such as powdered electrolyte mixes offer convenience and long-term storage without volume concerns. Optimal hydration supports cellular function, athletic performance, and cognitive health, making fluid selection crucial for hydration efficiency.
Dehydrated Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com