Temporary solutions provide short-term relief but often fail to address underlying issues, leading to recurring problems. Prioritizing sustainable strategies ensures long-lasting benefits and minimizes disruptions in your daily life. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective approaches beyond temporary fixes.
Table of Comparison
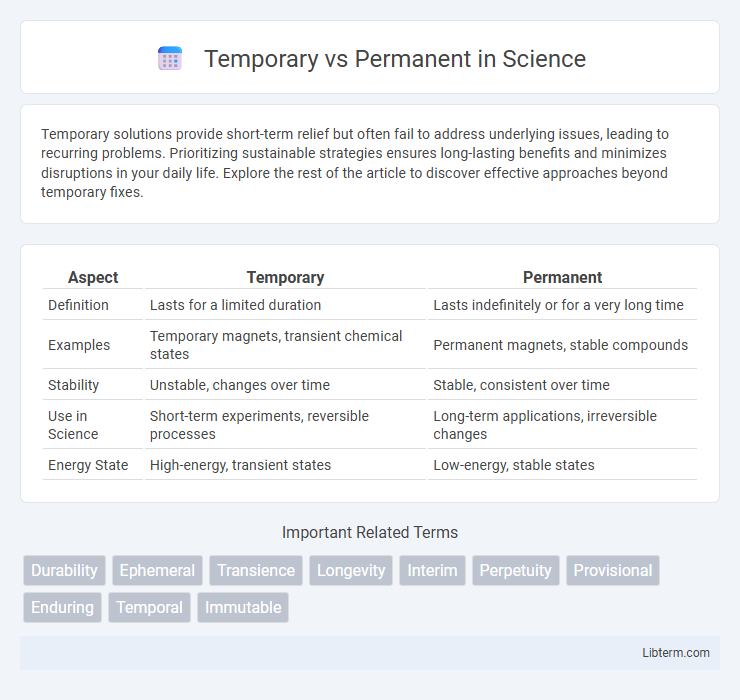
| Aspect | Temporary | Permanent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lasts for a limited duration | Lasts indefinitely or for a very long time |
| Examples | Temporary magnets, transient chemical states | Permanent magnets, stable compounds |
| Stability | Unstable, changes over time | Stable, consistent over time |
| Use in Science | Short-term experiments, reversible processes | Long-term applications, irreversible changes |
| Energy State | High-energy, transient states | Low-energy, stable states |
Introduction to Temporary vs Permanent
Temporary measures address immediate, short-term needs or conditions and are designed to be reversible or limited in duration. Permanent solutions aim to provide long-lasting or indefinite outcomes, often involving significant changes or commitments. Understanding the distinction between temporary and permanent is crucial for strategic planning and decision-making in various fields such as law, technology, and employment.
Defining Temporary and Permanent Solutions
Temporary solutions address immediate issues with short-term fixes designed for quick implementation and limited duration, often prioritizing speed over durability. Permanent solutions offer long-lasting results by resolving root causes through thorough analysis and strategic planning, emphasizing sustainability and long-term effectiveness. Understanding the distinction between temporary and permanent approaches is crucial for optimizing resource allocation and ensuring resilience in problem-solving.
Key Differences Between Temporary and Permanent
Temporary status refers to a limited duration with conditions for renewal or expiration, while permanent status denotes an indefinite period without expiration. Temporary arrangements often involve provisional rights or access, whereas permanent ones grant full rights and long-term stability. The key differences include duration, legal implications, and the ability to maintain or extend the status over time.
Advantages of Temporary Approaches
Temporary approaches offer flexibility, allowing quick adaptation to changing conditions or urgent needs without long-term commitments. They enable cost-effective solutions by reducing initial investment and maintenance expenses, making them ideal for short-term projects or trial phases. These methods also facilitate experimentation and iterative improvements, helping organizations refine strategies before implementing permanent changes.
Benefits of Permanent Solutions
Permanent solutions provide long-term stability and durability, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacements that temporary fixes often require. They enhance cost-efficiency by eliminating recurring expenses associated with short-term measures, offering a more sustainable investment over time. By addressing root causes comprehensively, permanent solutions improve overall reliability and performance in various applications, from infrastructure to technology systems.
Common Scenarios for Temporary Measures
Temporary measures often address urgent needs such as disaster relief, event security, or construction site safety. These solutions include temporary fencing, portable lighting, and provisional shelters designed for short-term use. In contrast, permanent measures involve long-lasting infrastructure like fixed barriers, permanent lighting systems, and established buildings.
When to Choose Permanent Over Temporary
Choosing permanent solutions over temporary ones is essential when long-term stability, durability, and cost-effectiveness matter most. Permanent options reduce recurring maintenance expenses and minimize disruptions compared to temporary fixes. Industries such as construction, infrastructure, and manufacturing prefer permanent installations to ensure sustained performance and safety standards.
Cost Considerations: Temporary vs Permanent
Temporary solutions often entail lower upfront costs but may incur higher long-term expenses due to recurring maintenance or replacements. Permanent installations typically require a larger initial investment but offer cost efficiency over time through durability and reduced need for frequent repairs. Businesses must evaluate budget constraints and lifecycle costs to determine the most economical option for their specific needs.
Long-Term Impact and Sustainability
Temporary solutions often address immediate needs but lack scalability and long-term viability, leading to repeated resource expenditure and environmental strain. Permanent solutions prioritize sustainable practices and infrastructure, ensuring lasting benefits and reducing future costs and ecological footprints. Investing in permanent frameworks fosters resilience and sustained development, aligning with long-term environmental and economic goals.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between temporary and permanent options requires evaluating factors such as duration, cost, and long-term benefits. Temporary solutions offer flexibility and lower upfront expenses, ideal for short-term needs, while permanent options provide durability and sustained value suitable for long-term goals. Assessing project timelines, budget constraints, and desired outcomes ensures the right decision aligned with specific objectives.
Temporary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com