Aerobic exercise boosts cardiovascular health by increasing heart rate and improving oxygen circulation throughout the body. Regular aerobic activity enhances endurance, supports weight management, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. Discover how incorporating aerobic workouts can transform your fitness routine in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
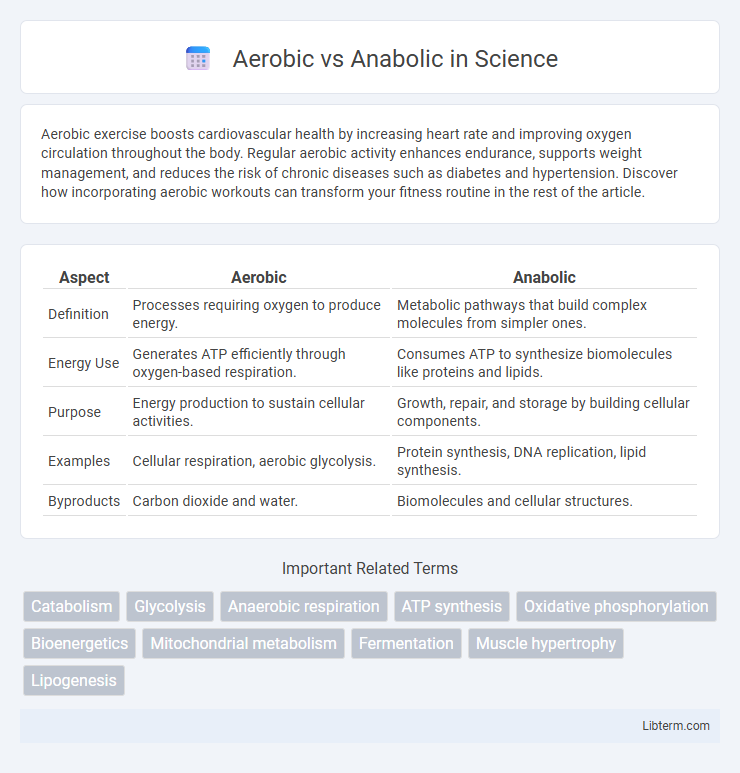
| Aspect | Aerobic | Anabolic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes requiring oxygen to produce energy. | Metabolic pathways that build complex molecules from simpler ones. |
| Energy Use | Generates ATP efficiently through oxygen-based respiration. | Consumes ATP to synthesize biomolecules like proteins and lipids. |
| Purpose | Energy production to sustain cellular activities. | Growth, repair, and storage by building cellular components. |
| Examples | Cellular respiration, aerobic glycolysis. | Protein synthesis, DNA replication, lipid synthesis. |
| Byproducts | Carbon dioxide and water. | Biomolecules and cellular structures. |
Understanding Aerobic and Anabolic Processes
Aerobic processes involve the use of oxygen to convert glucose into energy, supporting endurance and sustained physical activities through efficient ATP production. Anabolic processes focus on building complex molecules like proteins and muscle tissue from simpler substances, essential for growth, repair, and recovery. Understanding the balance between these processes helps optimize physical performance and metabolic health.
Key Differences Between Aerobic and Anabolic Metabolism
Aerobic metabolism generates energy through the oxidation of glucose or fatty acids in the presence of oxygen, producing ATP, carbon dioxide, and water as byproducts. Anabolic metabolism, in contrast, involves biosynthetic processes that build complex molecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids from simpler precursors, requiring energy input typically derived from ATP. The key difference lies in their roles: aerobic metabolism primarily supports energy production for cellular activities, while anabolic metabolism focuses on growth, repair, and synthesis of cellular components.
The Role of Oxygen in Aerobic Reactions
Aerobic reactions require oxygen as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling efficient ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation. The presence of oxygen drives the complete oxidation of glucose into carbon dioxide and water, maximizing energy yield in cellular respiration. In contrast, anabolic processes do not rely on oxygen directly but use energy generated from these aerobic reactions to synthesize complex biomolecules.
Energy Production: Aerobic vs Anabolic Pathways
Aerobic energy production relies on oxygen to efficiently generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, supporting sustained muscular activity. Anabolic pathways, in contrast, consume ATP to synthesize complex molecules like proteins and nucleic acids, essential for growth and repair. Aerobic pathways maximize energy yield per glucose molecule, whereas anabolic processes prioritize biosynthesis over immediate energy release.
Common Examples of Aerobic Activities
Common examples of aerobic activities include running, swimming, cycling, and brisk walking, which increase heart rate and improve oxygen consumption. These exercises primarily use aerobic metabolism, relying on oxygen to produce energy for prolonged physical activity. Aerobic workouts enhance cardiovascular endurance, support fat burning, and improve overall lung capacity.
Mechanisms of Anabolic Reactions in the Body
Anabolic reactions in the body involve the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, primarily driven by enzyme-catalyzed processes that require energy input, typically from ATP. These mechanisms include protein synthesis from amino acids, glycogen formation from glucose, and lipid synthesis from fatty acids, all vital for tissue growth and repair. Hormones such as insulin, growth hormone, and testosterone regulate these pathways by activating signaling cascades that promote the expression of genes involved in anabolic metabolism.
Benefits of Aerobic Metabolism for Health
Aerobic metabolism enhances cardiovascular health by efficiently producing energy through oxygen utilization, which supports sustained physical activity and endurance. It helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and hypertension by improving insulin sensitivity and promoting fat oxidation. Aerobic processes also facilitate efficient muscle recovery and support brain function by increasing oxygen supply and nutrient delivery to tissues.
Importance of Anabolic Processes in Muscle Growth
Anabolic processes play a crucial role in muscle growth by synthesizing new proteins that repair and build muscle tissue after exercise. These biochemical pathways facilitate the uptake of amino acids and promote muscle hypertrophy, essential for strength and endurance development. Unlike aerobic metabolism, which primarily generates energy through oxygen consumption, anabolic reactions focus on cellular growth and recovery, making them fundamental for effective muscle adaptation.
Exercise Approaches: Aerobic vs Anabolic Focus
Aerobic exercise prioritizes sustained, oxygen-dependent activities such as running, cycling, or swimming to improve cardiovascular endurance and fat metabolism. Anabolic-focused exercises emphasize resistance training and weightlifting to stimulate muscle protein synthesis and promote hypertrophy. Combining both methods optimizes overall fitness by enhancing endurance while simultaneously increasing muscle mass and strength.
Choosing the Best Approach: Aerobic or Anabolic?
Choosing between aerobic and anabolic approaches depends on fitness goals: aerobic exercise enhances cardiovascular endurance and burns fat by utilizing oxygen for energy, while anabolic activities promote muscle growth and strength through protein synthesis. For fat loss and improved stamina, aerobic workouts like running or cycling are optimal, whereas anabolic training, such as weightlifting, is ideal for muscle hypertrophy and strength gains. Combining both methods strategically supports overall health, balancing fat reduction and muscle development for comprehensive fitness results.
Aerobic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com