Analytical thinking enhances your ability to break down complex problems into manageable parts, leading to more effective decision-making and problem-solving skills. This approach relies on data interpretation, logical reasoning, and critical evaluation, essential for achieving precision and clarity. Dive deeper into the article to discover practical strategies for developing a sharp analytical mindset.
Table of Comparison
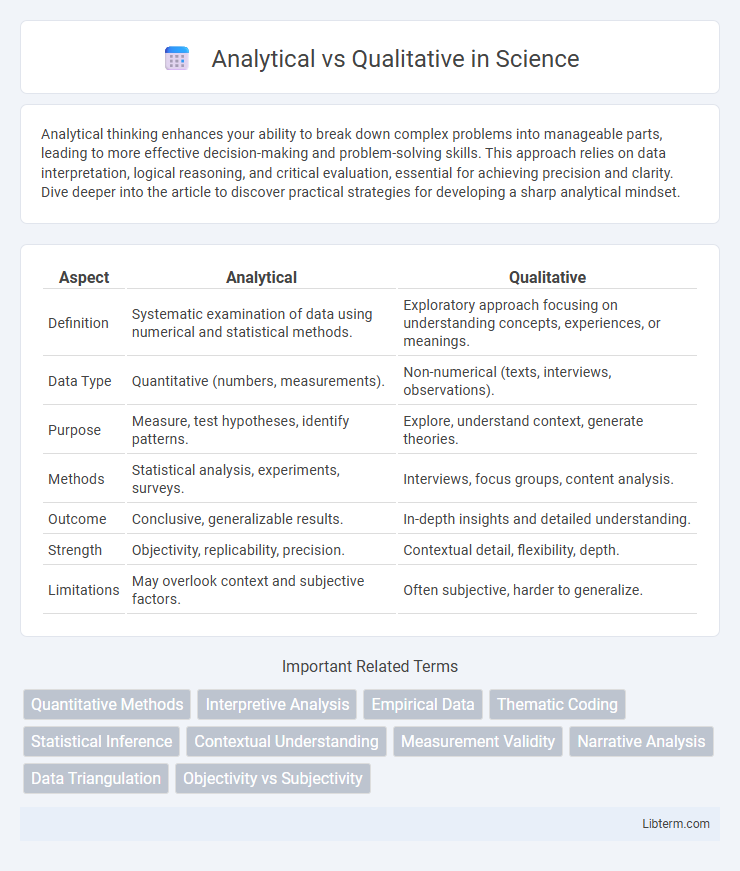
| Aspect | Analytical | Qualitative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic examination of data using numerical and statistical methods. | Exploratory approach focusing on understanding concepts, experiences, or meanings. |
| Data Type | Quantitative (numbers, measurements). | Non-numerical (texts, interviews, observations). |
| Purpose | Measure, test hypotheses, identify patterns. | Explore, understand context, generate theories. |
| Methods | Statistical analysis, experiments, surveys. | Interviews, focus groups, content analysis. |
| Outcome | Conclusive, generalizable results. | In-depth insights and detailed understanding. |
| Strength | Objectivity, replicability, precision. | Contextual detail, flexibility, depth. |
| Limitations | May overlook context and subjective factors. | Often subjective, harder to generalize. |
Introduction to Analytical and Qualitative Approaches
Analytical approaches focus on breaking down complex data into measurable components using statistical, logical, or mathematical techniques to derive objective insights. Qualitative approaches emphasize understanding human behavior, experiences, and social contexts through interviews, observations, and thematic analysis to capture subjective meanings. Both methods serve distinct purposes: analytical for quantification and hypothesis testing, qualitative for exploring depth and context in research.
Defining Analytical Methods
Analytical methods encompass precise, data-driven techniques used to quantify and identify substances within a sample, relying on instruments like chromatography, spectroscopy, and titration for accurate measurement. These methods prioritize reproducibility, sensitivity, and specificity to provide objective numerical data, essential for validating hypotheses and making data-backed decisions. Analytical procedures contrast with qualitative approaches by delivering measurable results that facilitate statistical analysis and quality control in scientific research and industrial applications.
Understanding Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods emphasize exploring human behavior and social phenomena through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and thematic analysis to capture rich, contextual insights. These approaches prioritize understanding participants' perspectives, emotions, and motivations beyond numerical data. Key qualitative techniques include ethnography, narrative analysis, and case studies, which provide comprehensive interpretations of complex social dynamics.
Key Differences Between Analytical and Qualitative Approaches
Analytical approaches emphasize numerical data, statistical analysis, and objective measurement to identify patterns and test hypotheses. Qualitative approaches focus on understanding underlying meanings, experiences, and social contexts through methods like interviews, focus groups, and thematic analysis. Key differences lie in data types, with analytical methods relying on quantifiable variables and qualitative methods exploring narrative-rich, descriptive information.
Advantages of Analytical Methods
Analytical methods offer precise quantification and reproducibility, enabling accurate measurement of chemical compositions and concentrations in complex samples. These techniques provide objective data with high sensitivity and specificity, facilitating detailed structural and compositional analysis. Their capability for automation and rapid processing enhances efficiency in quality control and research environments.
Benefits of Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods offer deep insights into human behavior, motivations, and experiences that analytical approaches often miss, enabling richer understanding of complex social phenomena. These methods facilitate flexibility in data collection, allowing for exploration of emerging themes through interviews, focus groups, and observations. This adaptability supports the development of nuanced, context-specific solutions that enhance decision-making and policy formulation.
Applications in Research and Industry
Analytical methods in research and industry emphasize quantitative data, measuring variables with statistical rigor for precise results in fields like pharmaceuticals and finance. Qualitative approaches explore contextual insights through interviews, observations, and thematic analysis, particularly valuable in social sciences, market research, and user experience studies. Combining both methodologies enhances comprehensive understanding and decision-making in product development, policy formulation, and customer behavior analysis.
Challenges and Limitations
Analytical methods face challenges such as data complexity, measurement errors, and limited contextual understanding, which can lead to incomplete or biased outcomes. Qualitative approaches struggle with subjectivity, limited scalability, and difficulty in generalizing findings beyond specific cases. Both methods require careful design and validation to mitigate these limitations and enhance the reliability of results.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Choosing the right approach between analytical and qualitative methods depends on your objectives and data type. Analytical methods excel in quantifying data, identifying patterns, and providing statistical insights, making them ideal for large datasets and hypothesis testing. Qualitative approaches focus on understanding experiences, motivations, and contexts through interviews, observations, and thematic analysis, offering depth and nuance where human behavior and subjective interpretations are critical.
Future Trends in Analytical and Qualitative Analysis
Future trends in analytical and qualitative analysis emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance data accuracy and interpretation speed. Advanced predictive analytics and natural language processing enable deeper insights from complex datasets, transforming decision-making processes across industries. Embracing automation and real-time analytics will drive innovations in both quantitative measurements and qualitative assessments, fostering more comprehensive and actionable outcomes.
Analytical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com