Theoretical knowledge forms the foundation for understanding complex concepts and frameworks across various disciplines, enabling a deeper grasp of abstract principles. Mastering theoretical approaches enhances your ability to analyze and solve problems effectively in practical scenarios. Explore the rest of this article to discover how theoretical insights can be applied to real-world challenges.
Table of Comparison
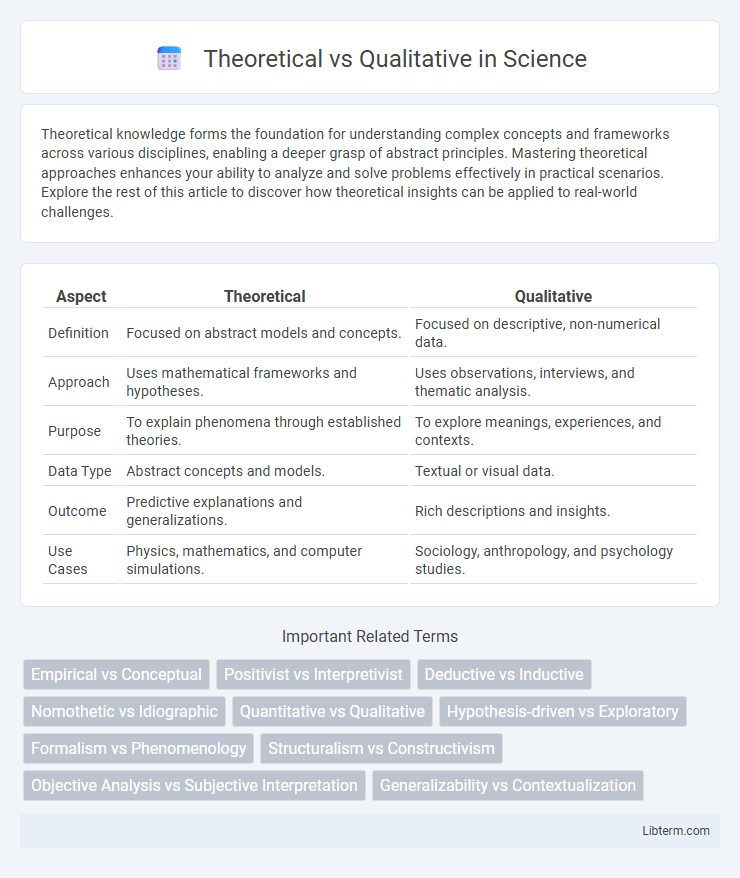
| Aspect | Theoretical | Qualitative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused on abstract models and concepts. | Focused on descriptive, non-numerical data. |
| Approach | Uses mathematical frameworks and hypotheses. | Uses observations, interviews, and thematic analysis. |
| Purpose | To explain phenomena through established theories. | To explore meanings, experiences, and contexts. |
| Data Type | Abstract concepts and models. | Textual or visual data. |
| Outcome | Predictive explanations and generalizations. | Rich descriptions and insights. |
| Use Cases | Physics, mathematics, and computer simulations. | Sociology, anthropology, and psychology studies. |
Introduction to Theoretical and Qualitative Research
Theoretical research involves developing abstract concepts and models to explain phenomena, relying heavily on existing literature and logical reasoning. Qualitative research emphasizes understanding human experiences and social contexts through data collection methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations. Both approaches contribute essential insights, with theoretical research offering foundational frameworks and qualitative research providing depth and context to empirical findings.
Defining Theoretical Research
Theoretical research focuses on developing abstract principles and models to explain phenomena, relying heavily on existing literature, logical reasoning, and hypothesis formulation. It aims to build frameworks that predict relationships between variables without immediate practical experimentation. This contrasts with qualitative research, which emphasizes understanding human experiences and social contexts through data such as interviews and observations.
Understanding Qualitative Research
Qualitative research emphasizes understanding human experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena through methods like interviews, focus groups, and content analysis. It seeks to explore meanings, patterns, and perspectives rather than quantifying data or testing hypotheses typical in theoretical research. This approach provides rich, detailed insights crucial for fields like sociology, anthropology, and psychology.
Core Objectives: Theory Development vs. Contextual Insight
Theoretical research aims to develop and refine abstract models or frameworks that explain phenomena through hypothesis formulation and testing, emphasizing generalizability and predictive power. Qualitative research focuses on gathering contextual insights by exploring human experiences, behaviors, and social processes in depth, prioritizing richness and complexity over generalization. Core objectives differ as theory development seeks universal principles, whereas contextual insight values understanding specific settings and meanings.
Methodologies: Approaches and Techniques
Theoretical methodologies prioritize frameworks and models to formulate hypotheses, utilizing deductive reasoning for data analysis. Qualitative approaches emphasize exploratory techniques such as interviews, focus groups, and content analysis to gather rich, contextual insights. Combining both methods enhances the depth and validity of research outcomes by integrating abstract theory with empirical observation.
Data Collection: Abstract vs. Empirical Methods
Theoretical data collection relies on abstract methods such as conceptual analysis and modeling to develop frameworks without direct interaction with empirical evidence. Qualitative data collection emphasizes empirical methods including interviews, observations, and case studies to capture participants' experiences and contextual insights. This contrast highlights the abstract versus grounded nature of data gathering in theoretical and qualitative research paradigms.
Analytical Processes: Conceptual vs. Interpretive
Analytical processes in theoretical approaches prioritize conceptual frameworks, utilizing abstract models to explain phenomena through structured hypotheses and systematic logic. In contrast, qualitative methods emphasize interpretive analysis, focusing on understanding meanings, experiences, and social contexts through detailed textual or visual data. Theoretical analysis seeks to generalize patterns, while qualitative interpretation uncovers nuanced insights grounded in specific cultural or situational realities.
Strengths and Limitations of Theoretical Research
Theoretical research provides a strong foundation for hypothesis development and conceptual clarity by systematically analyzing existing knowledge and frameworks, enabling researchers to identify gaps and generate new theories. Its strengths lie in offering comprehensive insights without the constraints of empirical data collection, fostering innovative thinking and abstraction. However, theoretical research faces limitations in practical applicability and empirical validation, as it relies heavily on logical reasoning rather than observed evidence, which may result in theories that lack real-world testing or measurable outcomes.
Advantages and Challenges of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers in-depth insights into human behavior, beliefs, and experiences through methods like interviews and focus groups, providing rich, contextual data that theoretical approaches may overlook. Its main advantages include flexibility in exploring complex phenomena and capturing nuances in social interactions, but challenges include subjectivity in data interpretation, difficulties in ensuring reliability, and limited generalizability due to smaller sample sizes. Researchers must carefully address potential biases and maintain rigorous analytical frameworks to enhance the validity and trustworthiness of qualitative findings.
Integrating Theoretical and Qualitative Approaches
Integrating theoretical and qualitative approaches enhances research by combining conceptual frameworks with rich, contextual data, leading to deeper insights and more nuanced interpretations. Theoretical models guide qualitative data collection and analysis, ensuring that findings are grounded in established knowledge while allowing for emergent themes and patterns. This synergy supports the development of robust theories that are both empirically informed and contextually relevant.
Theoretical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com