Qualitative research offers deep insights into human behavior by exploring emotions, motivations, and experiences through methods like interviews and focus groups. This approach helps uncover underlying reasons behind patterns that quantitative data might miss. Discover how qualitative techniques can transform your understanding by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
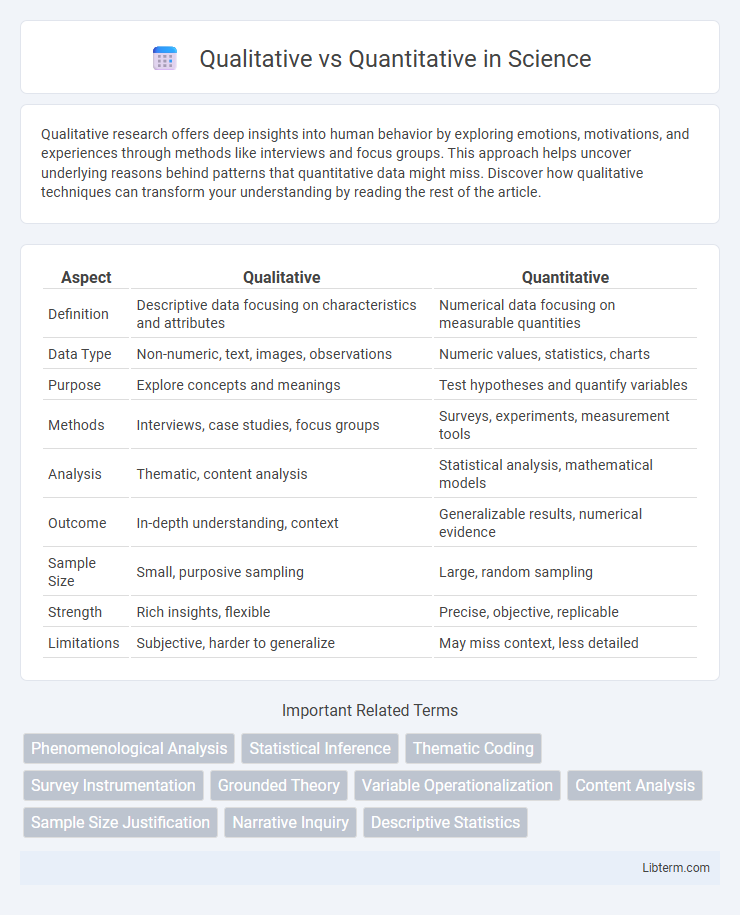
| Aspect | Qualitative | Quantitative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descriptive data focusing on characteristics and attributes | Numerical data focusing on measurable quantities |
| Data Type | Non-numeric, text, images, observations | Numeric values, statistics, charts |
| Purpose | Explore concepts and meanings | Test hypotheses and quantify variables |
| Methods | Interviews, case studies, focus groups | Surveys, experiments, measurement tools |
| Analysis | Thematic, content analysis | Statistical analysis, mathematical models |
| Outcome | In-depth understanding, context | Generalizable results, numerical evidence |
| Sample Size | Small, purposive sampling | Large, random sampling |
| Strength | Rich insights, flexible | Precise, objective, replicable |
| Limitations | Subjective, harder to generalize | May miss context, less detailed |
Definition of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a methodological approach focused on exploring phenomena through detailed, non-numerical data collection such as interviews, observations, and textual analysis to understand meanings, experiences, and social contexts. It emphasizes depth over breadth, providing rich insights into human behavior, motivations, and cultural patterns. This research type is foundational in social sciences, psychology, and market research for generating theories and hypotheses.
Definition of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation that primarily focuses on quantifying data through statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It emphasizes measurable variables and numeric data to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and establish causal relationships. This research method often utilizes surveys, experiments, and secondary data analysis to produce objective and generalizable findings.
Core Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
Qualitative methods emphasize exploring complex phenomena through detailed, non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys, aiming to understand meanings, experiences, and social contexts. Quantitative methods focus on numerical data collection and statistical analysis to identify patterns, measure variables, and test hypotheses across larger populations. Core differences lie in qualitative research's subjective, exploratory nature versus quantitative research's objective, confirmatory approach, affecting data types, analysis techniques, and outcomes.
Data Collection Techniques: Qualitative vs Quantitative
Qualitative data collection techniques include interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys that capture detailed, contextual insights and subjective experiences. Quantitative data collection relies on structured methods such as questionnaires with closed-ended questions, experiments, and statistical sampling to produce measurable and generalizable results. Each approach distinctively serves different research objectives, with qualitative methods emphasizing depth and meaning, while quantitative techniques prioritize numerical analysis and statistical validation.
Strengths and Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research excels in exploring complex phenomena through rich, detailed data, offering deep insights into human behaviors, emotions, and social contexts that quantitative methods may overlook. Its strengths lie in flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to capture meaning and context, making it invaluable for hypothesis generation and theory development. Limitations include smaller sample sizes, potential researcher bias, and challenges in generalizing findings to broader populations due to its subjective and non-numeric nature.
Strengths and Limitations of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research excels in collecting large-scale numerical data, enabling statistical analysis and generalizable results across populations. Its strengths lie in objectivity, replicability, and the ability to identify patterns or correlations through structured surveys, experiments, and measurable variables. Limitations include lack of contextual depth, inflexibility in exploring complex human behaviors, and potential oversimplification of nuanced phenomena.
When to Use Qualitative vs Quantitative Approaches
Qualitative approaches are best used when exploring complex behaviors, motivations, and experiences to gain deep, contextual understanding, especially in early-stage research or when seeking rich, detailed insights. Quantitative methods are ideal for testing hypotheses, measuring variables, and generalizing findings across larger populations using statistical analysis. Choose qualitative when the goal is exploratory and descriptive, and quantitative when the focus is on quantification and objective measurement.
Key Examples in Practice
Qualitative research methods include interviews, focus groups, and thematic analysis, which capture detailed insights and explore participant experiences deeply. Quantitative approaches involve surveys, experiments, and statistical modeling to quantify patterns and test hypotheses numerically. Key examples in practice show companies use qualitative data to understand customer motivations, while quantitative data drives decision-making through measurable trends and performance metrics.
Combining Qualitative and Quantitative Methods (Mixed Methods)
Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed methods research leverages the strengths of both approaches, providing comprehensive insights by integrating numerical data with rich contextual understanding. This approach enhances validity through data triangulation, allowing researchers to explore complex phenomena from multiple perspectives. Mixed methods are particularly effective in social sciences, healthcare, and education, where both statistical trends and personal experiences are critical for informed decision-making.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Research
Choosing the right research approach depends on the nature of your research questions and objectives. Qualitative methods excel in exploring complex phenomena and understanding participant perspectives through interviews, focus groups, and thematic analysis. Quantitative approaches provide measurable data and statistical validation using surveys, experiments, and numerical datasets to test hypotheses and assess patterns across large samples.
Qualitative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com