Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen, fueling their growth and energy needs. This vital biochemical reaction supports life on Earth by producing oxygen and forming the base of the food chain. Explore the full article to understand how photosynthesis sustains ecosystems and impacts your environment.
Table of Comparison
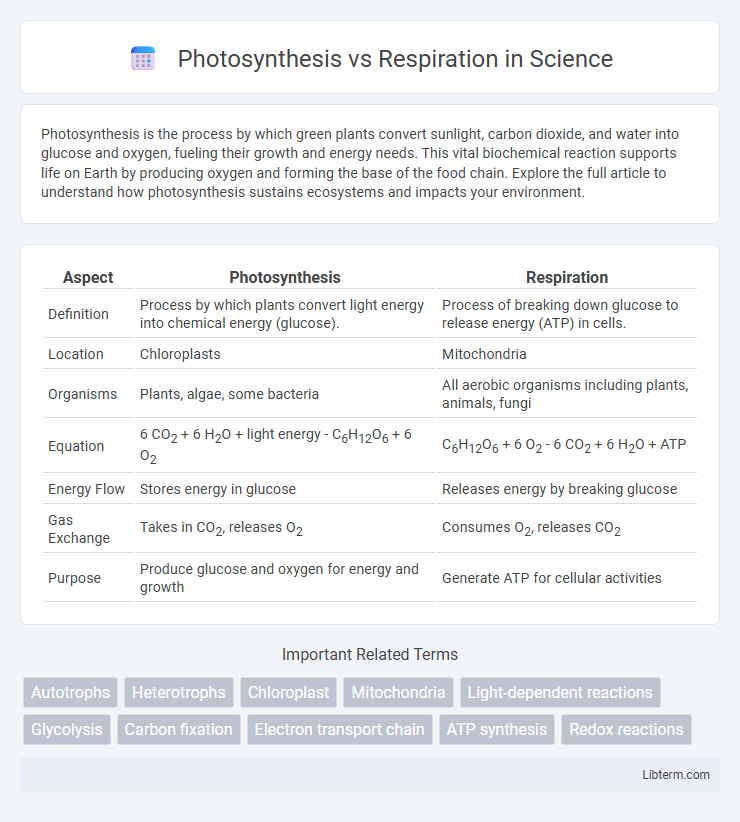
| Aspect | Photosynthesis | Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose). | Process of breaking down glucose to release energy (ATP) in cells. |
| Location | Chloroplasts | Mitochondria |
| Organisms | Plants, algae, some bacteria | All aerobic organisms including plants, animals, fungi |
| Equation | 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy - C6H12O6 + 6 O2 | C6H12O6 + 6 O2 - 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP |
| Energy Flow | Stores energy in glucose | Releases energy by breaking glucose |
| Gas Exchange | Takes in CO2, releases O2 | Consumes O2, releases CO2 |
| Purpose | Produce glucose and oxygen for energy and growth | Generate ATP for cellular activities |
Introduction to Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. Respiration is a metabolic process that breaks down glucose in the presence of oxygen to release energy in the form of ATP, along with carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. Both processes are fundamental to the energy balance and carbon cycling in ecosystems, linking autotrophic production with heterotrophic consumption.
Overview of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process in plants, algae, and certain bacteria that converts light energy into chemical energy stored as glucose, using carbon dioxide and water. Chlorophyll pigments absorb sunlight, driving the light-dependent reactions that generate ATP and NADPH, which fuel the Calvin cycle for carbon fixation. This process produces oxygen as a byproduct, playing a crucial role in maintaining atmospheric oxygen levels and supporting aerobic respiration.
Overview of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that converts glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water, primarily occurring in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. This process involves three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, collectively producing up to 36 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. Cellular respiration is essential for providing the energy required for various cellular activities and contrasts with photosynthesis, which stores energy by synthesizing glucose.
Key Chemical Equations
Photosynthesis is represented by the equation 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy - C6H12O6 + 6O2, highlighting the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight. Cellular respiration, with the equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP, demonstrates the breakdown of glucose and oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP, along with carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. These equations emphasize the complementary nature of these biochemical processes in the energy cycle of living organisms.
Main Sites of Occurrence in Cells
Photosynthesis primarily occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically within the thylakoid membranes where light-dependent reactions take place, and the stroma for the Calvin cycle. Cellular respiration mainly takes place in the mitochondria of both plant and animal cells, involving processes such as glycolysis in the cytoplasm and the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain inside the mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane. These specialized organelles enable efficient energy conversion by compartmentalizing the biochemical pathways essential for energy capture and release.
Energy Flow and Transformation
Photosynthesis captures solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, storing energy in chemical bonds. Cellular respiration breaks down glucose molecules in the presence of oxygen to release energy as ATP, which powers cellular activities. This cyclical flow transforms energy from sunlight into chemical energy and subsequently into usable cellular energy, sustaining life processes.
Role in Carbon and Oxygen Cycles
Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in the carbon and oxygen cycles by converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight, thereby reducing atmospheric CO2 and replenishing oxygen levels. Cellular respiration, in contrast, breaks down glucose in the presence of oxygen to release energy, producing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts that re-enter the environment. Together, these processes maintain the balance of carbon and oxygen in ecosystems, supporting life and regulating global climate.
Similarities Between Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis and respiration both involve electron transport chains essential for energy conversion in cells. Both processes utilize membranes, such as the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts and the inner mitochondrial membrane in mitochondria, to create proton gradients that drive ATP synthesis. Additionally, they depend on redox reactions and share common molecules like ATP, NADH, and oxygen as key components in energy metabolism.
Differences Between Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using light energy, primarily occurring in chloroplasts of plant cells. Respiration breaks down glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP, taking place in the mitochondria of both plant and animal cells. Photosynthesis is an anabolic process storing energy, while respiration is a catabolic process releasing energy.
Importance in Ecosystems and Human Life
Photosynthesis drives the production of oxygen and organic compounds essential for the survival of nearly all life forms, forming the base of most food chains and supporting ecosystem biodiversity. Cellular respiration converts these organic compounds back into energy, sustaining the metabolic processes of plants, animals, and microorganisms, thereby maintaining ecological balance. The interdependence of photosynthesis and respiration regulates atmospheric gases, influences climate stability, and directly impacts food security and human health worldwide.
Photosynthesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com