Master status is a social position that dominates other statuses and shapes a person's identity and social interactions significantly. This status often influences how others perceive you and dictates the roles you assume in various contexts. Explore the rest of this article to understand how master status impacts your social life and relationships.
Table of Comparison
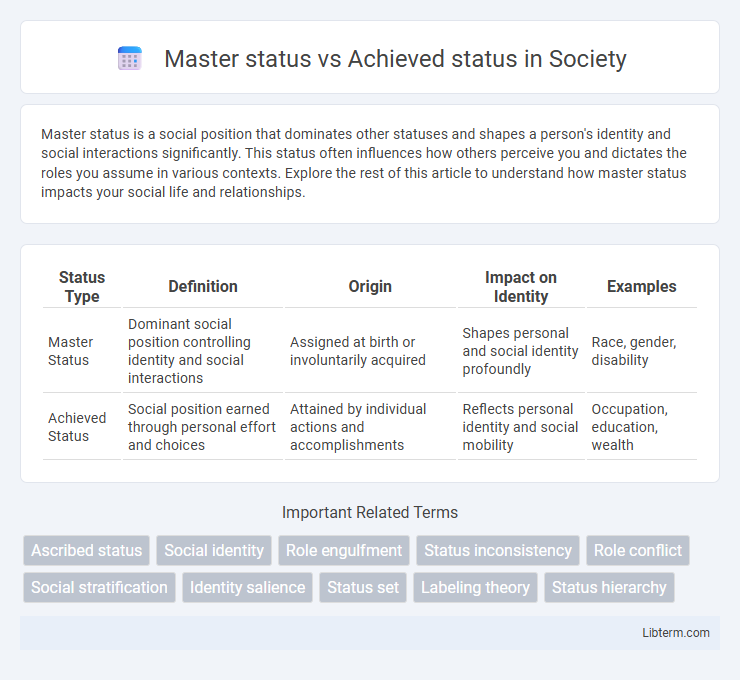
| Status Type | Definition | Origin | Impact on Identity | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master Status | Dominant social position controlling identity and social interactions | Assigned at birth or involuntarily acquired | Shapes personal and social identity profoundly | Race, gender, disability |
| Achieved Status | Social position earned through personal effort and choices | Attained by individual actions and accomplishments | Reflects personal identity and social mobility | Occupation, education, wealth |
Understanding Social Status: An Overview
Master status represents a social identity that dominates an individual's social interactions and self-concept, often overriding other statuses they hold. Achieved status refers to a social position earned or chosen based on personal efforts, skills, or accomplishments, reflecting individual agency within social structures. Understanding social status involves analyzing how master status shapes perceptions and social roles more prominently than achieved status, influencing social dynamics and identity formation.
Defining Master Status
Master status represents the dominant social identity that shapes an individual's overall self-concept and social interactions, often overshadowing other statuses. This status profoundly influences perceptions, behaviors, and life choices, serving as the primary lens through which others perceive the individual. Examples include occupation, race, or disability, which consistently affect one's social standing and opportunities across various contexts.
Defining Achieved Status
Achieved status refers to a social position a person attains through their actions, efforts, skills, or accomplishments, distinguishing it from ascribed statuses given at birth. This concept highlights individual agency and personal success, reflecting roles such as professional careers, educational attainment, or social roles chosen by the individual. Achieved status influences social mobility and can significantly impact one's identity and societal interactions.
Key Differences Between Master and Achieved Status
Master status is a social position that dominates other statuses and shapes a person's identity, often assigned at birth or through immutable characteristics like race or gender. Achieved status results from personal efforts, skills, or accomplishments, such as education, occupation, or income level. Key differences include the origin--master status is ascribed and involuntary, while achieved status is earned and reflects individual agency.
Examples of Master Status in Society
Master status refers to the primary social identity that shapes an individual's life and interactions, often overriding other statuses. Examples of master status in society include race, gender, and occupation, such as being a doctor, which significantly influences how others perceive and relate to the individual. These statuses often define social roles, expectations, and access to resources within communities.
Examples of Achieved Status in Society
Achieved status refers to social positions individuals earn through their actions, skills, and efforts, such as becoming a doctor, artist, or entrepreneur. Examples include a teacher gaining recognition for excellence in education, an athlete winning championships, or a business professional ascending corporate ranks. These statuses highlight personal accomplishment and societal contributions, contrasting with ascribed statuses assigned at birth.
The Role of Social Identity in Master and Achieved Status
Master status defines an individual's primary social identity, often shaping their societal interactions and how others perceive them, such as race, gender, or disability. Achieved status reflects the social position attained through personal effort, education, or accomplishments, influencing self-identity and social mobility. The dynamic interplay between master and achieved status highlights how social identity frameworks affect one's roles and opportunities within a community.
Impact of Master and Achieved Status on Life Opportunities
Master status, often ascribed at birth such as race or gender, profoundly influences life opportunities by shaping social identity and expectations, often determining access to resources and social mobility. Achieved status, earned through personal effort like education or career success, can modify or reinforce one's social position, allowing individuals to improve or sometimes challenge the limitations imposed by their master status. The interaction between master and achieved statuses creates a dynamic framework that affects economic prospects, social networks, and overall quality of life.
Social Mobility: Moving Between Achieved and Master Status
Master status defines an individual's dominant social position shaping identity and social interactions, while achieved status results from personal efforts and actions, reflecting social mobility. Movement between achieved and master statuses illustrates dynamic social mobility, where individuals can alter their primary social identity through educational attainment, career advancement, or changes in social roles. Social mobility studies emphasize how shifts in achieved status can elevate or transform a person's master status across different social strata.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Social Status
Master status often overshadows achieved status, leading to challenges in recognizing individual accomplishments independent of dominant social identities such as race or gender. Controversies arise when master status perpetuates stereotypes and systemic inequalities, complicating efforts to achieve social mobility based on merit. The tension between ascribed and achieved status highlights ongoing debates about fairness, identity, and societal structure in sociological research.
Master status Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com