Pluralism embraces diverse beliefs, cultures, and values within a society, promoting coexistence and mutual respect. It fosters open dialogue and collaboration among different groups, leading to more inclusive and dynamic communities. Discover how pluralism shapes social harmony and why it matters for your understanding of modern society in the full article.
Table of Comparison
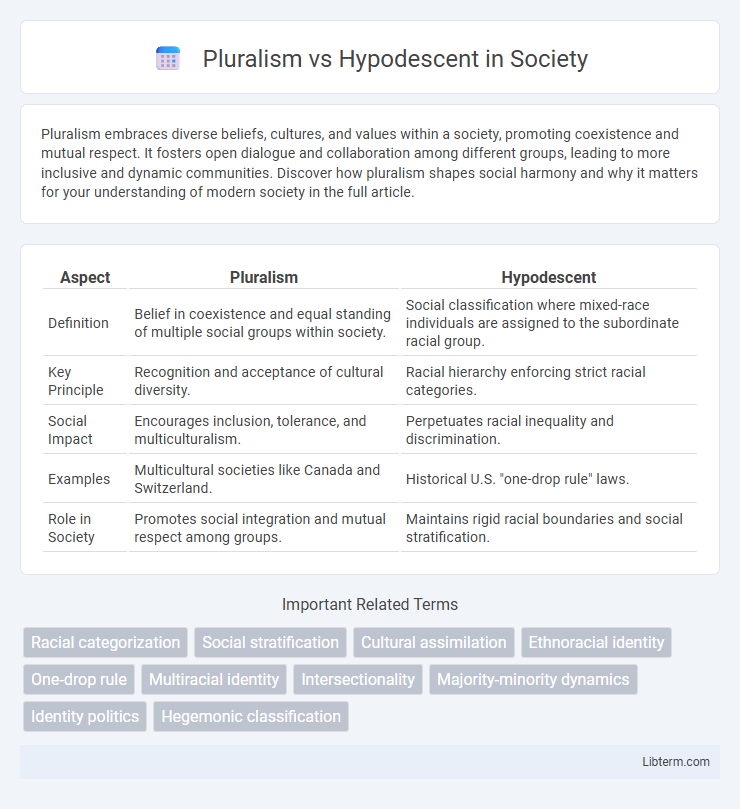
| Aspect | Pluralism | Hypodescent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in coexistence and equal standing of multiple social groups within society. | Social classification where mixed-race individuals are assigned to the subordinate racial group. |
| Key Principle | Recognition and acceptance of cultural diversity. | Racial hierarchy enforcing strict racial categories. |
| Social Impact | Encourages inclusion, tolerance, and multiculturalism. | Perpetuates racial inequality and discrimination. |
| Examples | Multicultural societies like Canada and Switzerland. | Historical U.S. "one-drop rule" laws. |
| Role in Society | Promotes social integration and mutual respect among groups. | Maintains rigid racial boundaries and social stratification. |
Understanding Pluralism: Definition and Key Concepts
Pluralism refers to the coexistence and mutual recognition of diverse cultural, ethnic, and social groups within a society, emphasizing equality and respect for differences. It involves key concepts such as cultural diversity, societal integration, and the retention of distinct group identities without forcing assimilation. Pluralism contrasts with hypodescent, which assigns mixed-race individuals to the socially subordinate group, whereas pluralism promotes acceptance of multiple identities and shared societal participation.
Exploring Hypodescent: Historical Origins and Meaning
Hypodescent, also known as the "one-drop rule," originated in the United States during the 19th century as a legal and social principle classifying individuals with any African ancestry as Black, regardless of their mixed heritage. This practice reinforced racial hierarchies and segregation by denying multiracial identities and emphasizing a binary racial classification system. Understanding hypodescent reveals how racial boundaries have been rigidly constructed and maintained through laws and social norms, contrasting with pluralism's emphasis on recognizing and valuing multiple racial and ethnic identities.
Pluralism vs Hypodescent: Core Differences
Pluralism emphasizes the coexistence and equal recognition of diverse racial and cultural identities within a society, promoting mutual respect and interaction among groups. Hypodescent, or the "one-drop rule," assigns individuals with mixed racial heritage to the subordinate or minority group, reinforcing rigid racial boundaries and social hierarchies. The core difference lies in pluralism fostering inclusivity and multiple identities, whereas hypodescent enforces exclusion through categorical racial descent.
The Role of Identity in Pluralistic Societies
In pluralistic societies, identity plays a pivotal role in shaping social dynamics by recognizing and valuing multiple cultural, ethnic, and racial backgrounds as distinct and equal contributors to the community. Hypodescent, or the "one-drop rule," contrasts sharply by enforcing rigid racial boundaries that categorize individuals based on simplified ancestry, often marginalizing mixed or minority identities. Emphasizing pluralism fosters inclusivity and mutual respect, allowing diverse identities to coexist without hierarchical classification based on racial purity.
Hypodescent and Racial Classification Systems
Hypodescent, often known as the "one-drop rule," categorizes individuals with any trace of minority ancestry into a subordinate racial group, reinforcing rigid racial hierarchies. This racial classification system contrasts with pluralism by limiting identity fluidity and maintaining social stratification through legally and socially enforced boundaries. Hypodescent's role in racial classification perpetuates systemic inequalities by defining race in binary, exclusionary terms rather than embracing diverse, multiethnic identities.
Social Impacts of Pluralism in Multicultural Societies
Pluralism in multicultural societies fosters social cohesion by encouraging the coexistence and mutual respect of diverse cultural identities, leading to increased social capital and cross-cultural understanding. This framework reduces systemic discrimination by valuing each group's contributions, promoting equitable access to resources and political representation. The social impacts of pluralism include enhanced social integration, reduction of ethnic tensions, and the creation of inclusive policies that support diversity as a societal asset.
Hypodescent in Legal and Social Contexts
Hypodescent, often referred to as the "one-drop rule," is a legal and social principle that classifies individuals with any trace of minority ancestry as belonging to the subordinate group, historically used to maintain racial hierarchies in the United States. Legally, hypodescent has influenced statutes and court rulings that determine racial identity for purposes such as segregation laws, voting rights, and marriage restrictions. Socially, this doctrine has perpetuated systemic discrimination and reinforced rigid racial boundaries, contrasting sharply with pluralism's emphasis on recognizing and valuing multiple identities.
Challenges and Critiques of Pluralism
Pluralism faces critiques related to its optimistic view of cultural coexistence, often overlooking power imbalances and systemic inequalities that persist among racial and ethnic groups. Critics argue that pluralism can mask ongoing discrimination by emphasizing surface-level diversity without addressing deeper societal structures that enforce hypodescent classifications. This tension highlights challenges in achieving true multicultural integration when social hierarchies and historical legacies of hypodescent remain unaddressed.
Addressing the Consequences of Hypodescent
Hypodescent, the practice of assigning mixed-race individuals to the socially subordinate group, perpetuates systemic inequalities and reinforces racial hierarchies, contrasting with pluralism's emphasis on embracing and valuing multiple racial identities. Addressing hypodescent requires dismantling legal and social frameworks that enforce one-drop rules and challenging societal biases that marginalize multiracial identities. Promoting pluralism involves creating inclusive policies that recognize and celebrate complex racial ancestries, fostering equity and reducing the negative consequences of hypodescent on identity and social status.
Towards Inclusive Identity: Moving Beyond Hypodescent
Moving beyond hypodescent involves embracing pluralism to foster inclusive identities that reflect the complex, multi-ethnic realities of contemporary societies. Pluralism promotes recognition and respect for diverse cultural backgrounds, challenging the traditional hypodescent rule that assigns mixed-race individuals to a single racial category, often marginalizing their multifaceted heritage. Inclusive identity frameworks prioritize self-identification and intersectionality, enabling individuals to assert multiple, intersecting identities that resist reductive racial classifications.
Pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com