Social isolation significantly impacts mental and physical health by increasing risks of depression, anxiety, and cardiovascular problems. Prolonged loneliness can weaken your immune system and accelerate cognitive decline, making it essential to maintain social connections. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for overcoming social isolation and improving your well-being.
Table of Comparison
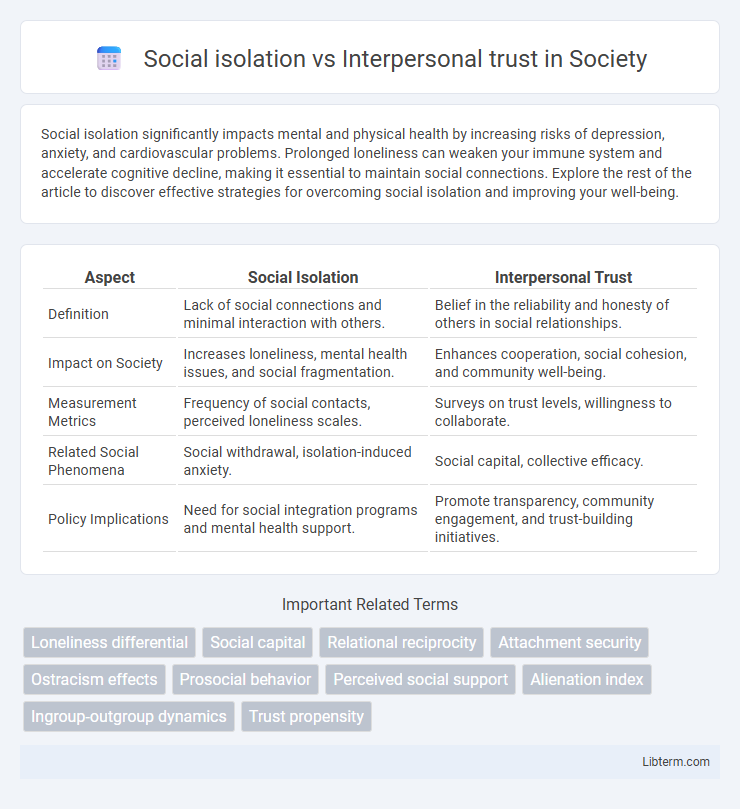
| Aspect | Social Isolation | Interpersonal Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of social connections and minimal interaction with others. | Belief in the reliability and honesty of others in social relationships. |
| Impact on Society | Increases loneliness, mental health issues, and social fragmentation. | Enhances cooperation, social cohesion, and community well-being. |
| Measurement Metrics | Frequency of social contacts, perceived loneliness scales. | Surveys on trust levels, willingness to collaborate. |
| Related Social Phenomena | Social withdrawal, isolation-induced anxiety. | Social capital, collective efficacy. |
| Policy Implications | Need for social integration programs and mental health support. | Promote transparency, community engagement, and trust-building initiatives. |
Understanding Social Isolation: Key Concepts
Social isolation refers to the objective state of having few social contacts or interactions, which can negatively impact emotional well-being and cognitive health. Interpersonal trust involves the belief in others' reliability and benevolence, often diminishing as social isolation increases due to reduced positive social experiences. Understanding social isolation requires examining its psychological, social, and environmental factors that contribute to an individual's sense of disconnection and vulnerability to decreased interpersonal trust.
Defining Interpersonal Trust in Relationships
Interpersonal trust in relationships refers to the expectation that others will act with honesty, reliability, and benevolence, forming the foundation for meaningful social connections. High levels of trust reduce social isolation by fostering emotional safety and open communication, which strengthen relational bonds. Trust is critical in mitigating feelings of loneliness and promoting psychological well-being through consistent and supportive interactions.
The Psychological Impact of Social Isolation
Social isolation significantly diminishes interpersonal trust by fostering feelings of loneliness and insecurity, which negatively impact an individual's ability to form and maintain social bonds. Research in psychology reveals that prolonged social isolation alters brain function, increasing anxiety and reducing empathy, thereby eroding trust in others. Consequently, the psychological effects of social isolation create barriers to social connection, undermining the foundational elements of interpersonal trust.
How Interpersonal Trust Shapes Social Connections
Interpersonal trust significantly influences the quality and depth of social connections by fostering open communication and mutual support, which reduces feelings of social isolation. High levels of trust encourage individuals to engage more deeply in relationships, creating stronger social bonds and networks that mitigate loneliness. Conversely, low interpersonal trust can lead to withdrawal and weakened social ties, exacerbating social isolation and its associated negative health outcomes.
Factors Contributing to Social Isolation
Limited social interactions due to factors such as geographic mobility, digital communication preferences, and mental health challenges significantly contribute to social isolation. Economic disparities and lack of community engagement diminish opportunities for building interpersonal trust among individuals. These conditions create a feedback loop where decreased interpersonal trust further exacerbates feelings of isolation and social withdrawal.
The Role of Trust in Reducing Social Isolation
Interpersonal trust plays a crucial role in reducing social isolation by fostering a sense of safety and connection within communities. High levels of trust encourage individuals to engage more openly in social networks, facilitating supportive relationships and collective well-being. Research indicates that communities with strong interpersonal trust experience lower rates of loneliness and enhanced social cohesion.
Social Isolation and Mental Health: A Trust Perspective
Social isolation significantly undermines mental health by eroding interpersonal trust, which is essential for emotional support and social cohesion. Reduced trust in others leads to heightened feelings of vulnerability and anxiety, exacerbating symptoms of depression and loneliness. Strengthening social connections and fostering trust are critical strategies for mitigating the negative psychological impacts associated with prolonged social isolation.
Building Interpersonal Trust in Isolated Communities
Building interpersonal trust in socially isolated communities requires intentional engagement through consistent and transparent communication channels. Establishing local support networks, such as community groups or online forums, fosters shared experiences that reduce feelings of alienation and promote mutual understanding. Trust development relies on reciprocal interactions and collective activities that reinforce social bonds, ultimately enhancing community resilience.
Social Isolation vs Interpersonal Trust: Comparative Analysis
Social isolation negatively impacts interpersonal trust by reducing opportunities for social interactions and weakening community bonds. Research indicates that individuals experiencing higher levels of social isolation demonstrate lower levels of trust towards others, which can hinder cooperative behaviors and social cohesion. Comparative analyses reveal that societies with strong interpersonal trust tend to exhibit lower rates of social isolation, highlighting the reciprocal relationship between these factors.
Strategies to Foster Trust and Decrease Isolation
Building strong community networks and encouraging regular social interactions are effective strategies to foster interpersonal trust and reduce social isolation. Implementing programs that promote group activities, peer support, and open communication enhances feelings of belonging and mutual reliability. Leveraging digital platforms to connect isolated individuals also plays a crucial role in strengthening trust and social cohesion.
Social isolation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com