A welfare state ensures citizens receive essential services like healthcare, education, and social security to promote overall well-being and reduce inequality. Governments fund these programs through taxation to provide a safety net for vulnerable populations and support economic stability. Discover how welfare policies impact society and what they mean for your future by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
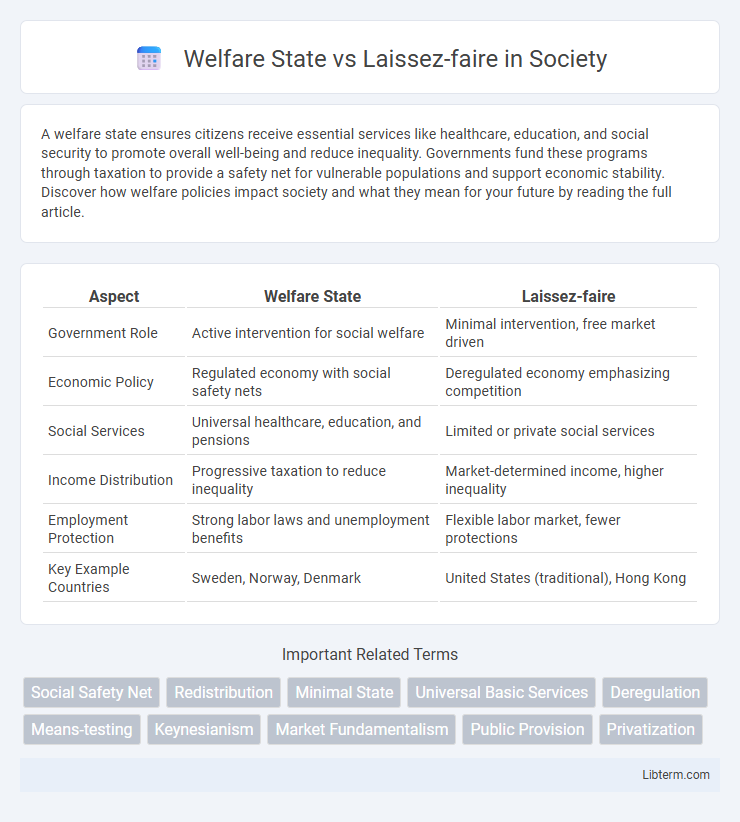
| Aspect | Welfare State | Laissez-faire |
|---|---|---|
| Government Role | Active intervention for social welfare | Minimal intervention, free market driven |
| Economic Policy | Regulated economy with social safety nets | Deregulated economy emphasizing competition |
| Social Services | Universal healthcare, education, and pensions | Limited or private social services |
| Income Distribution | Progressive taxation to reduce inequality | Market-determined income, higher inequality |
| Employment Protection | Strong labor laws and unemployment benefits | Flexible labor market, fewer protections |
| Key Example Countries | Sweden, Norway, Denmark | United States (traditional), Hong Kong |
Understanding the Welfare State Model
The welfare state model emphasizes government intervention to provide social safety nets like healthcare, education, and unemployment benefits, aiming to reduce inequality and promote social justice. It contrasts with laissez-faire economics, which advocates minimal state interference in markets, trusting free-market mechanisms to allocate resources efficiently. Understanding the welfare state requires analyzing its role in redistributing wealth, ensuring economic stability, and supporting vulnerable populations.
Core Principles of Laissez-faire Economics
Laissez-faire economics centers on minimal government intervention, emphasizing free markets where supply and demand determine prices and production. The core principle is that individuals pursuing their self-interest lead to efficient resource allocation and economic growth through competition. This approach advocates for private property rights, limited regulation, and the belief that market forces naturally correct imbalances without state interference.
Historical Development of Both Systems
The welfare state emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as industrialization and urbanization exposed social inequalities, leading governments in Europe, especially Germany under Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, to implement social insurance programs and labor protections. In contrast, laissez-faire economics gained prominence during the 18th and 19th centuries with classical economists like Adam Smith advocating minimal state intervention, emphasizing free markets and individual entrepreneurship as drivers of economic growth. The historical development of these systems reflects divergent responses to industrial capitalism: welfare states prioritizing social safety nets and economic regulation, while laissez-faire upholds market autonomy and limited government role.
Key Differences in Government Intervention
Welfare state policies emphasize active government intervention to provide social safety nets, public healthcare, education, and economic redistribution, ensuring minimum living standards and reducing inequality. In contrast, laissez-faire advocates minimal government involvement, promoting free-market mechanisms and individual self-reliance to regulate economic activities and resource allocation. The key difference lies in the welfare state's commitment to social protection funded by taxation versus laissez-faire's reliance on market forces with limited regulatory oversight.
Social Safety Nets: Pros and Cons
Social safety nets in welfare states provide crucial support such as unemployment benefits, healthcare, and pensions, reducing poverty and income inequality. Laissez-faire approaches emphasize minimal government intervention, promoting economic freedom but often resulting in inadequate social protections for vulnerable populations. While welfare state policies enhance social stability and public health, they can create dependency and higher public expenditures, whereas laissez-faire systems encourage individual responsibility but may increase social disparities.
Economic Growth and Stability Comparisons
The welfare state promotes economic growth and stability by investing in social safety nets, healthcare, and education, which enhance human capital and consumer demand. Laissez-faire economies rely on minimal government intervention, prioritizing market-driven innovation and efficiency but often face greater volatility and income inequality. Empirical studies show welfare states tend to experience steadier growth and lower unemployment rates, while laissez-faire models may achieve higher short-term growth at the risk of economic instability.
Poverty Reduction: Which System Performs Better?
Welfare states demonstrate greater effectiveness in poverty reduction by providing extensive social safety nets, including unemployment benefits, healthcare, and housing support, which directly improve the living standards of low-income populations. Laissez-faire economies, characterized by minimal government intervention, often rely on market forces to address poverty but may result in higher inequality and insufficient access to essential services. Empirical studies show countries with robust welfare policies, such as the Nordic nations, consistently achieve lower poverty rates and enhanced social mobility compared to laissez-faire-oriented economies.
Case Studies: Countries Exemplifying Each System
Sweden exemplifies the welfare state model with its comprehensive social safety nets, including universal healthcare, funded by high taxes to reduce inequality and promote social cohesion. In contrast, Hong Kong represents laissez-faire capitalism, characterized by minimal government intervention, low taxes, and a free market economy that drives robust economic growth and entrepreneurial innovation. These case studies highlight how welfare state policies prioritize social welfare, while laissez-faire systems emphasize market freedom and individual enterprise.
Public Opinion and Political Influence
Public opinion on welfare state versus laissez-faire economic policies varies significantly across demographics and regions, with surveys showing stronger support for welfare programs in countries experiencing economic inequality and social insecurity. Political influence plays a crucial role as parties advocating for welfare expansion often mobilize voter bases concerned with healthcare, education, and social safety nets, while proponents of laissez-faire emphasize free markets and minimal government intervention to encourage entrepreneurship and economic growth. Policy decisions and electoral outcomes frequently reflect the tension between public demand for social protections and the political power of business-oriented interest groups championing deregulation.
Future Outlook: Evolving Economic Paradigms
The future outlook of economic paradigms suggests a potential shift toward hybrid models combining welfare state principles with laissez-faire dynamics to balance social safety nets and market efficiency. Emerging trends emphasize digital transformation, inclusive growth, and sustainable development, influencing policy adjustments that prioritize both economic freedom and social equity. Data from global economic forums indicate increasing experimentation with flexible regulatory frameworks to adapt to technological innovation and demographic changes.
Welfare State Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com