Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, comments or actions that convey prejudice or discrimination towards marginalized groups. These behaviors can accumulate over time, negatively impacting mental health and sense of belonging. Learn more about recognizing and addressing microaggressions in your environment in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
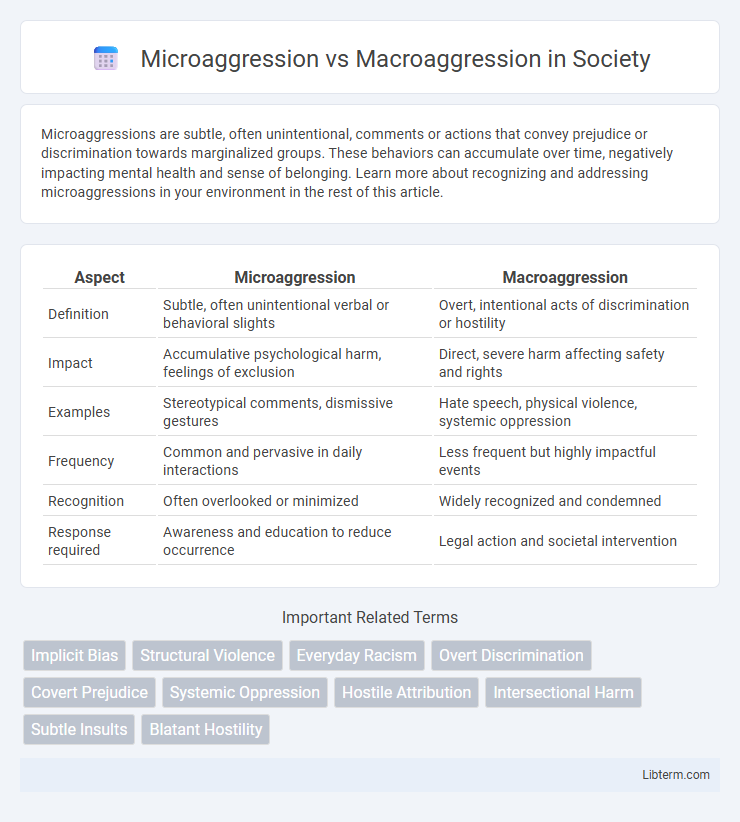
| Aspect | Microaggression | Macroaggression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subtle, often unintentional verbal or behavioral slights | Overt, intentional acts of discrimination or hostility |
| Impact | Accumulative psychological harm, feelings of exclusion | Direct, severe harm affecting safety and rights |
| Examples | Stereotypical comments, dismissive gestures | Hate speech, physical violence, systemic oppression |
| Frequency | Common and pervasive in daily interactions | Less frequent but highly impactful events |
| Recognition | Often overlooked or minimized | Widely recognized and condemned |
| Response required | Awareness and education to reduce occurrence | Legal action and societal intervention |
Understanding Microaggressions: Definition and Examples
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, verbal or behavioral slights that communicate negative or derogatory messages to marginalized groups, reflecting underlying biases or stereotypes. Examples include backhanded compliments like "You're so articulate" directed at a person of color or assumptions that a woman is less competent in a technical field. Recognizing microaggressions is crucial for addressing the cumulative psychological impact they have on individuals and fostering inclusive environments.
What Are Macroaggressions? Breaking Down the Basics
Macroaggressions refer to overt, intentional acts of discrimination or hostility that are large in scale and impact, often manifested through explicit behaviors or systemic policies targeting marginalized groups. Unlike microaggressions, which are subtle, often unconscious slights, macroaggressions involve clear, deliberate actions that reinforce power imbalances and perpetuate inequality. Understanding macroaggressions requires recognizing their role in maintaining structural oppression and addressing broader social injustices through systemic change.
Key Differences Between Microaggressions and Macroaggressions
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional actions or comments that communicate biased or derogatory messages toward marginalized groups, typically manifesting in everyday interactions. Macroaggressions consist of overt, deliberate acts of discrimination or hostility, such as hate crimes or systemic policies that enforce inequality. The key differences lie in the scale, intent, and visibility, with microaggressions being indirect and nuanced, while macroaggressions are direct and explicit forms of aggression.
The Psychological Impact of Microaggressions
Microaggressions, subtle verbal or nonverbal slights, accumulate psychological stress by reinforcing feelings of marginalization and invalidation in targeted individuals. This chronic exposure can lead to anxiety, depression, and diminished self-esteem, undermining mental health and well-being. Unlike macroaggressions, which are overt and intentional, microaggressions operate subtly but persistently, eroding psychological resilience over time.
Macroaggressions: Historical and Societal Consequences
Macroaggressions are overt, large-scale acts of discrimination or hostility rooted in systemic racism, sexism, or other forms of social inequality, often perpetuated by institutions and cultural norms. These aggressive actions have historically contributed to widespread societal harm, including economic disenfranchisement, segregation, and intergenerational trauma among marginalized communities. Understanding the historical and societal consequences of macroaggressions reveals the deep structural barriers that continue to hinder equity and social justice efforts worldwide.
Recognizing Microaggressive Behaviors in Daily Life
Microaggressive behaviors manifest as subtle, often unintentional, comments or actions that convey bias or discrimination toward marginalized groups, frequently embedded in everyday interactions. Common examples include using stereotypes, backhanded compliments, or dismissive language that undermines an individual's identity or experiences. Recognizing microaggressions requires awareness of these nuanced behaviors and understanding their cumulative psychological impact on affected individuals.
Identifying Macroaggressive Actions in Social Structures
Macroaggressive actions manifest as systemic policies or institutional practices that perpetuate inequality, such as discriminatory hiring practices or biased law enforcement targeting marginalized communities. These large-scale behaviors reinforce power imbalances through legislation, organizational culture, or socioeconomic structures, often invisibly embedded within social institutions. Recognizing macroaggressions requires analyzing patterns of exclusion or disadvantage codified into laws, workplace rules, or educational systems that sustain collective harm beyond individual encounters.
How to Address Microaggressions: Practical Strategies
Addressing microaggressions requires creating an open environment that encourages honest conversations and active listening to validate experiences. Implementing targeted training programs on implicit bias helps individuals recognize and correct subtle discriminatory behaviors before they escalate. Empowering bystanders to intervene respectfully can disrupt microaggressions and promote a culture of inclusion and empathy.
Confronting Macroaggressions: Advocacy and Systemic Change
Confronting macroaggressions requires strategic advocacy aimed at dismantling systemic inequalities embedded in institutions and policies. Effective approaches involve coalition-building, policy reform, and amplifying marginalized voices to challenge power structures perpetuating widespread discrimination. Empowering communities through education and legal action fosters systemic change that addresses root causes rather than isolated incidents.
Promoting Inclusive Environments: Solutions for Both Aggression Types
Promoting inclusive environments requires addressing both microaggressions and macroaggressions through targeted strategies such as comprehensive diversity training, clear policies against discriminatory behavior, and fostering open dialogue among all community members. Organizations implementing regular workshops that educate about subtle biases alongside systemic discrimination facilitate awareness and empathy, creating safer spaces for marginalized groups. Empowering bystanders to intervene and support affected individuals reinforces a culture of accountability and respect, essential for mitigating the impacts of both microaggressions and macroaggressions.
Microaggression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com