Civic nationalism emphasizes shared values, citizenship, and political participation over ethnic or cultural identity, fostering an inclusive sense of belonging within a nation. This form of nationalism supports democratic principles and equality, encouraging unity based on common laws and civic duties. Explore the rest of the article to understand how civic nationalism shapes modern societies and your role within it.
Table of Comparison
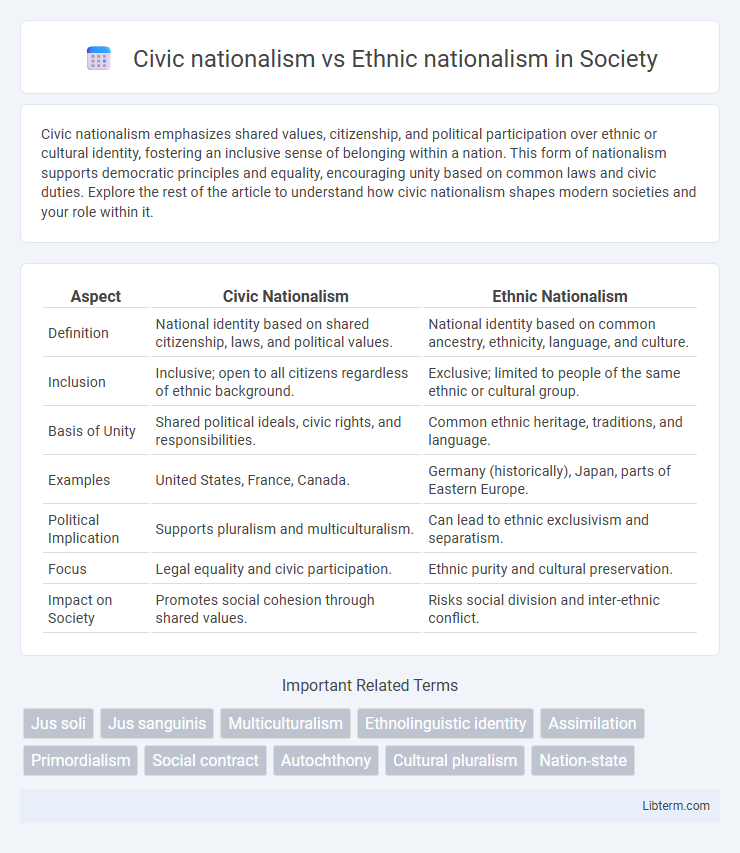
| Aspect | Civic Nationalism | Ethnic Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | National identity based on shared citizenship, laws, and political values. | National identity based on common ancestry, ethnicity, language, and culture. |
| Inclusion | Inclusive; open to all citizens regardless of ethnic background. | Exclusive; limited to people of the same ethnic or cultural group. |
| Basis of Unity | Shared political ideals, civic rights, and responsibilities. | Common ethnic heritage, traditions, and language. |
| Examples | United States, France, Canada. | Germany (historically), Japan, parts of Eastern Europe. |
| Political Implication | Supports pluralism and multiculturalism. | Can lead to ethnic exclusivism and separatism. |
| Focus | Legal equality and civic participation. | Ethnic purity and cultural preservation. |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social cohesion through shared values. | Risks social division and inter-ethnic conflict. |
Defining Civic Nationalism
Civic nationalism emphasizes shared citizenship, political rights, and allegiance to common institutions regardless of ethnicity, promoting inclusion based on legal and social membership within a state. It fosters unity through collective values, democratic participation, and respect for individual freedoms, distinguishing it from ethnic nationalism, which bases national identity on ancestry, culture, or language. Civic nationalism supports pluralism and multiculturalism, making it adaptable to diverse, modern societies.
Understanding Ethnic Nationalism
Ethnic nationalism defines the nation based on shared heritage, culture, language, and often ancestry, emphasizing common ethnic identity as the foundation of national belonging. It contrasts with civic nationalism, which centers on political values, citizenship, and allegiance to institutions regardless of ethnic background. Understanding ethnic nationalism involves recognizing its role in shaping group solidarity, influencing political movements, and sometimes fueling exclusion or conflict based on ethnic distinctions.
Historical Origins of Both Ideologies
Civic nationalism traces its origins to the Enlightenment era, particularly in revolutionary France and the United States, emphasizing shared citizenship, legal equality, and common political institutions as the basis of national identity. Ethnic nationalism emerged in 19th-century Europe, notably within the German and Slavic nationalist movements, prioritizing shared ancestry, language, culture, and religion as core elements defining the nation. The historical development of civic nationalism aligns with liberal democratic values, while ethnic nationalism often corresponds with romantic nationalism and the formation of exclusive ethnically homogeneous states.
Key Principles and Values
Civic nationalism emphasizes shared citizenship, political rights, and allegiance to common institutions regardless of ethnicity, promoting inclusivity and equality under the law. Ethnic nationalism centers on shared heritage, culture, language, and ancestry, prioritizing ethnic homogeneity and cultural continuity as core national identity markers. Key values distinguishing civic nationalism include pluralism and legal equality, while ethnic nationalism values cultural preservation and ethnic solidarity.
Citizenship Criteria: Civic vs. Ethnic
Civic nationalism bases citizenship on shared political values, legal rights, and active participation within a state, emphasizing inclusivity regardless of ethnicity or cultural background. Ethnic nationalism links citizenship to common ancestry, language, and cultural heritage, prioritizing ethnic homogeneity and often excluding those outside the dominant group. These divergent criteria affect immigration policies, integration approaches, and national identity formation in various countries.
Inclusivity and Exclusivity Dynamics
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusivity by promoting membership based on shared values, political rights, and allegiance to institutions, regardless of ethnic or cultural backgrounds. Ethnic nationalism enforces exclusivity through a focus on common ancestry, language, or cultural heritage, often marginalizing or excluding those outside the dominant ethnic group. The dynamics between these forms of nationalism impact social cohesion, with civic nationalism fostering broader integration and ethnic nationalism potentially leading to division and conflict.
Case Studies: Civic Nationalism in Action
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusive citizenship based on shared political values and legal frameworks, as seen in the United States, where diverse ethnic groups unite under constitutional democracy and equal rights. Canada's multicultural policies further exemplify civic nationalism by promoting cultural diversity while fostering national unity through common civic participation and bilingualism. These case studies highlight how civic nationalism strengthens social cohesion by prioritizing political allegiance over ethnic identity.
Case Studies: Ethnic Nationalism in Practice
Ethnic nationalism manifests in case studies such as the Yugoslav Wars, where ethnic identity fueled conflict and state fragmentation among Serbs, Croats, and Bosniaks. In Rwanda, ethnic nationalism between Hutus and Tutsis culminated in the 1994 genocide, illustrating the dangers of exclusive national identity based on ethnicity. These examples reveal how ethnic nationalism often leads to social exclusion, violence, and challenges to political stability.
Impacts on Social Cohesion and Diversity
Civic nationalism fosters social cohesion by promoting inclusion based on shared citizenship and common values, enhancing multicultural diversity and equal rights within a society. Ethnic nationalism often prioritizes a single ethnic identity, which can lead to exclusion, social fragmentation, and reduced acceptance of cultural diversity. Consequently, civic nationalism generally supports greater social integration, whereas ethnic nationalism may heighten social tensions and undermine multicultural harmony.
Contemporary Relevance and Global Trends
Civic nationalism emphasizes inclusive citizenship based on shared values and legal frameworks, promoting social cohesion in multicultural societies. Ethnic nationalism centers on shared heritage, language, and ancestry, often influencing identity politics and migration debates worldwide. Contemporary global trends reveal rising civic nationalism in democratic states promoting integration, while ethnic nationalism gains traction amid populist movements challenging globalization and multiculturalism.
Civic nationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com