Integration streamlines your business processes by connecting disparate systems into a unified workflow, enhancing efficiency and data consistency. Seamless integration reduces manual tasks and minimizes errors, enabling better decision-making based on real-time information. Explore the rest of this article to discover how integration can transform your operations and drive growth.
Table of Comparison
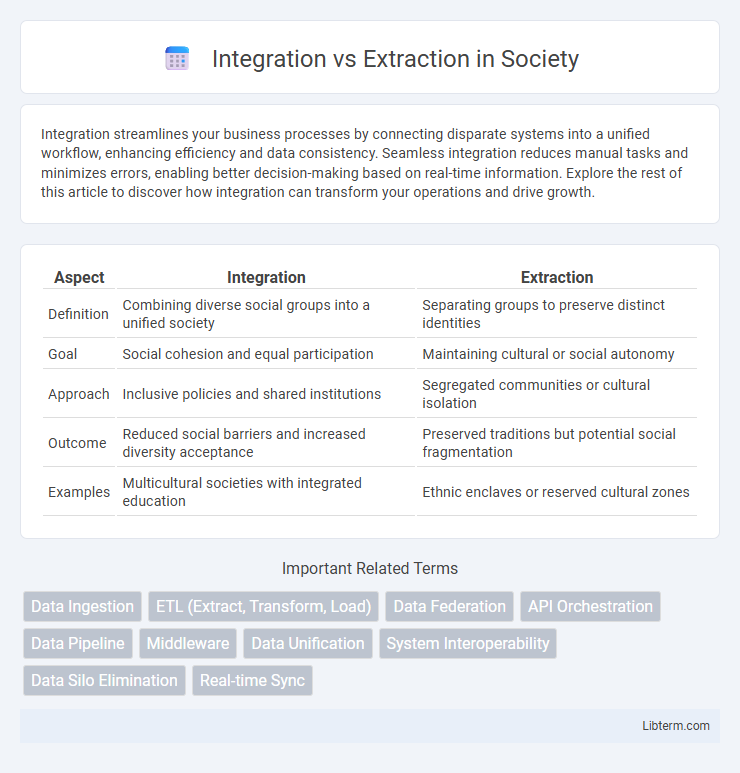
| Aspect | Integration | Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining diverse social groups into a unified society | Separating groups to preserve distinct identities |
| Goal | Social cohesion and equal participation | Maintaining cultural or social autonomy |
| Approach | Inclusive policies and shared institutions | Segregated communities or cultural isolation |
| Outcome | Reduced social barriers and increased diversity acceptance | Preserved traditions but potential social fragmentation |
| Examples | Multicultural societies with integrated education | Ethnic enclaves or reserved cultural zones |
Understanding Integration and Extraction
Understanding integration involves combining data from multiple sources into a unified system, enhancing data consistency, accuracy, and accessibility for comprehensive analysis. Extraction focuses on retrieving specific data sets from various databases or storage systems, enabling targeted data processing and reporting. Both processes are essential in data management strategies, where integration supports holistic views and extraction facilitates precise data utilization.
Key Differences Between Integration and Extraction
Integration combines data from multiple sources into a unified system to provide a comprehensive view, while extraction involves retrieving specific data from a source for analysis or processing. Integration ensures data consistency and supports real-time or batch processing across databases, applications, or platforms, whereas extraction focuses on isolating relevant data, often for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) workflows. Key differences include scope, with integration addressing holistic data unification, and extraction targeting selective data retrieval tasks.
When to Use Integration in Data Systems
Use integration in data systems when combining data from multiple sources to create a unified view, improving decision-making and operational efficiency. Integration is essential for real-time data access, enabling consistent and accurate information across departments. It is ideal for complex environments requiring synchronization, data consistency, and streamlined workflows.
Scenarios Favoring Data Extraction
Data extraction is favored in scenarios requiring rapid access to specific data subsets without altering existing systems, such as generating targeted reports or performing ad-hoc analysis. This approach is optimal when integrating with legacy systems that lack compatibility for seamless data integration or when the volume of data extracted is relatively small and manageable. Extraction supports data migration projects where source systems remain operational, enabling incremental data capture for validation and synchronization purposes.
Advantages of Integrating Data Sources
Integrating data sources enhances data consistency by consolidating disparate databases into a unified system, improving accuracy across analytics and reporting. It enables real-time access to comprehensive datasets, which supports better decision-making and operational efficiency. Integration reduces data redundancy and maintenance costs by streamlining workflows and eliminating the need for multiple data extraction processes.
Challenges Associated with Data Extraction
Data extraction faces challenges such as poor data quality, inconsistent formats, and unstructured sources, making accurate retrieval difficult. High volumes of diverse data require advanced tools for efficient parsing and transformation. Ensuring data security and compliance during extraction further complicates the process, impacting overall integration workflows.
Impact of Integration on Business Intelligence
Integration enhances Business Intelligence by consolidating data from multiple sources into a unified system, improving data accuracy and accessibility. This consolidation enables real-time analytics and comprehensive reporting, facilitating faster, data-driven decision-making. Streamlined data integration reduces operational silos, driving efficiency and fostering a holistic understanding of business performance.
Extraction Methods and Best Practices
Extraction methods in data management involve systematically retrieving specific data sets from diverse sources such as databases, web pages, or files using techniques like web scraping, API calls, and SQL queries. Best practices emphasize ensuring data accuracy through validation, maintaining data integrity with consistent formatting, and automating processes to minimize manual errors and boost efficiency. Employing robust tools like Apache Nifi, Talend, and Python libraries (BeautifulSoup, Scrapy) enhances extraction scalability while adhering to compliance standards ensures secure and ethical data handling.
Integration Tools and Technologies
Integration tools and technologies enable seamless connectivity between disparate systems, facilitating data synchronization and unified workflows across enterprises. Platforms like Apache Camel, MuleSoft Anypoint, and Microsoft Azure Logic Apps provide robust APIs, pre-built connectors, and orchestration capabilities to streamline complex integration scenarios. These tools support real-time data exchange, event-driven architectures, and cloud-native integrations, enhancing scalability and reducing latency in multi-system environments.
Making the Right Choice: Integration or Extraction
Choosing between integration and extraction depends on data accessibility and analytical goals; integration combines data from multiple sources into a unified system, enhancing comprehensive analysis and operational efficiency, while extraction focuses on retrieving specific data sets for targeted examination or migration. Integration suits organizations seeking real-time insights and centralized data management across platforms like CRM, ERP, and cloud services. Extraction is optimal when handling legacy systems, data archiving, or preparing datasets for data warehousing and advanced analytics.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com