Acceptance is the key to freeing yourself from the burden of resistance and embracing life's challenges with a calm mindset. Recognizing and welcoming reality as it is allows you to move forward with clarity and resilience. Discover how cultivating acceptance can transform your outlook by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
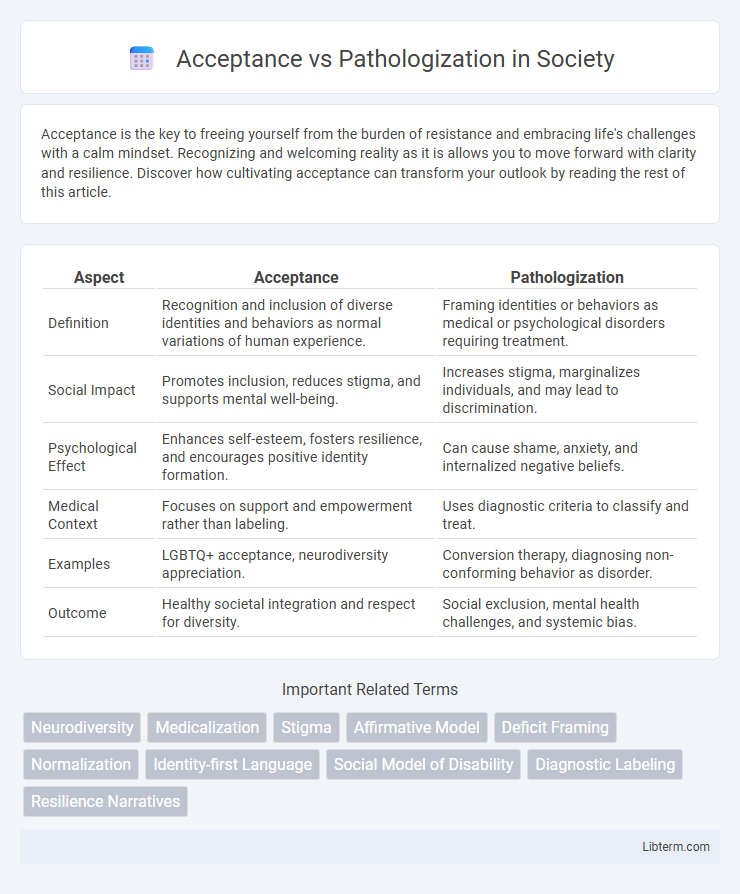
| Aspect | Acceptance | Pathologization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition and inclusion of diverse identities and behaviors as normal variations of human experience. | Framing identities or behaviors as medical or psychological disorders requiring treatment. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusion, reduces stigma, and supports mental well-being. | Increases stigma, marginalizes individuals, and may lead to discrimination. |
| Psychological Effect | Enhances self-esteem, fosters resilience, and encourages positive identity formation. | Can cause shame, anxiety, and internalized negative beliefs. |
| Medical Context | Focuses on support and empowerment rather than labeling. | Uses diagnostic criteria to classify and treat. |
| Examples | LGBTQ+ acceptance, neurodiversity appreciation. | Conversion therapy, diagnosing non-conforming behavior as disorder. |
| Outcome | Healthy societal integration and respect for diversity. | Social exclusion, mental health challenges, and systemic bias. |
Understanding Acceptance and Pathologization
Understanding acceptance involves recognizing behaviors, identities, or conditions as natural variations rather than anomalies requiring correction. Pathologization frames these differences as medical or psychological disorders, often leading to stigmatization and unnecessary treatment. Emphasizing acceptance promotes inclusivity and mental well-being by validating diverse experiences and reducing societal biases.
Defining Acceptance in Mental Health
Defining acceptance in mental health involves recognizing and embracing individual differences and experiences without judgment or attempts to forcibly change them. Acceptance promotes emotional resilience by encouraging individuals to acknowledge their thoughts and feelings as valid rather than symptoms needing correction. This approach contrasts with pathologization, which labels diverse mental states as disorders, often leading to stigma and marginalization.
What Does Pathologization Mean?
Pathologization refers to the process of categorizing normal variations in human behavior, emotions, or identities as medical or psychological disorders. This approach often leads to stigmatization and unnecessary treatment by framing differences as abnormalities requiring correction. Understanding pathologization is crucial for promoting acceptance and respecting diverse expressions of identity without imposing harmful labels.
Historical Perspectives on Pathologization
Historical perspectives on pathologization reveal how behaviors and identities once deemed pathological were often framed by cultural, medical, and social biases, particularly in psychiatry and psychology. For example, homosexuality was classified as a mental disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) until 1973, reflecting prevailing societal norms rather than objective pathology. The gradual removal of such classifications marks a critical shift toward acceptance and highlights the role of advocacy and evolving scientific understanding in challenging pathologization.
The Impact of Acceptance on Well-being
Acceptance of diverse identities and behaviors significantly enhances mental health by reducing stigma and fostering a supportive environment. Research indicates that individuals who experience acceptance show lower rates of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders compared to those subjected to pathologization. Positive social recognition promotes resilience and overall well-being, highlighting the critical role of acceptance in public health and psychology.
Negative Effects of Pathologization
Pathologization often leads to stigmatization, exacerbating mental health issues by framing natural variations in behavior or identity as disorders. This negative labeling can cause social exclusion, reduce self-esteem, and create barriers to seeking effective support. Treatment approaches driven by pathologization frequently overlook individual strengths and context, resulting in ineffective or harmful interventions.
Societal Attitudes: Acceptance vs Pathologization
Societal attitudes toward mental health have shifted from pathologization, where conditions are viewed as symptoms of disorder, to acceptance, which recognizes diverse experiences as part of human variation. Acceptance promotes inclusion and reduces stigma by validating individual differences rather than labeling them as deficits. This paradigm change fosters supportive environments, improves access to care, and enhances overall well-being across communities.
Clinical Implications for Therapists and Practitioners
Acceptance of diverse behaviors and identities promotes a strengths-based approach in therapeutic practice, encouraging resilience and self-efficacy in clients. Pathologization, by contrast, risks perpetuating stigma and may lead to misdiagnosis, unnecessary treatment, and client disempowerment. Therapists and practitioners benefit from distinguishing between normative variation and clinically significant distress or dysfunction to ensure ethical, effective interventions grounded in cultural competence and evidence-based assessment.
Embracing Neurodiversity: A Shift Toward Acceptance
Embracing neurodiversity highlights the importance of acceptance over pathologization by recognizing neurological differences as natural variations rather than disorders. This paradigm shift promotes inclusive environments that value diverse cognitive profiles, thereby reducing stigma and improving mental health outcomes. Emphasizing acceptance fosters empowerment and supports individualized strengths rather than focusing solely on deficits.
Toward a Balanced Approach: Integration and Future Directions
Achieving a balanced approach between acceptance and pathologization requires integrating diverse perspectives from psychology, psychiatry, and social sciences to foster nuanced understanding of human behaviors and experiences. Emphasizing individualized assessment over rigid diagnostic categories promotes respectful recognition of neurodiversity while ensuring appropriate support for those facing distress or impairment. Future directions involve advancing interdisciplinary research and developing flexible frameworks that accommodate evolving cultural norms and scientific insights.
Acceptance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com