State-centric approaches prioritize the role of governments and central authorities in shaping policies, security, and economic development. Understanding this perspective is essential to grasp how power dynamics influence global and domestic affairs. Explore the rest of the article to uncover the implications of state-centric strategies on your environment and beyond.
Table of Comparison
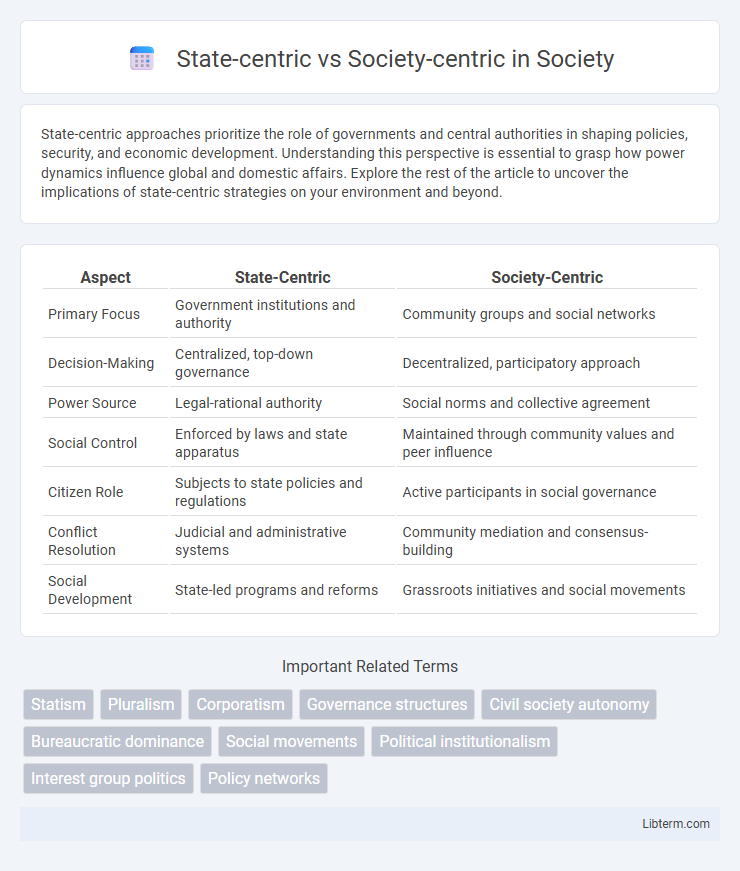
| Aspect | State-Centric | Society-Centric |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Government institutions and authority | Community groups and social networks |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, top-down governance | Decentralized, participatory approach |
| Power Source | Legal-rational authority | Social norms and collective agreement |
| Social Control | Enforced by laws and state apparatus | Maintained through community values and peer influence |
| Citizen Role | Subjects to state policies and regulations | Active participants in social governance |
| Conflict Resolution | Judicial and administrative systems | Community mediation and consensus-building |
| Social Development | State-led programs and reforms | Grassroots initiatives and social movements |
Understanding State-Centric and Society-Centric Approaches
Understanding state-centric approaches emphasizes the central role of the government as the primary actor in political, economic, and social processes, prioritizing state sovereignty and institutional authority. Society-centric approaches highlight the influence of civil society, grassroots movements, and non-state actors, focusing on social relations, community interests, and participatory governance. Analyzing the interplay between these perspectives reveals how power dynamics shape policy-making, development strategies, and social cohesion within different political frameworks.
Historical Evolution of State- and Society-Centered Theories
State-centric theories emerged prominently during the 20th century, emphasizing the central role of the state in shaping political order and national development. Society-centric perspectives evolved as critiques, highlighting the influence of social groups, civil society, and cultural dynamics in governance and policy-making. The historical evolution reflects a shift from viewing the state as the sole actor to recognizing the interplay between state institutions and societal forces in political theory.
Core Principles of State-Centric Perspectives
State-centric perspectives prioritize sovereignty, centralized authority, and national security as core principles guiding governance and policy-making. This approach emphasizes the state's role in maintaining order, enforcing laws, and protecting territorial integrity against internal and external threats. Centralized decision-making institutions and a strong bureaucratic apparatus are fundamental to asserting state control and achieving political stability.
Foundations of Society-Centric Approaches
Society-centric approaches emphasize the role of social structures, cultural norms, and collective identities in shaping political and economic systems, contrasting with the top-down perspective of state-centric models. Foundations of society-centric approaches include social contract theory, which highlights mutual agreements among individuals, and constructivist views that prioritize shared meanings and social interactions. These frameworks underscore the importance of civil society, grassroots movements, and interpersonal relationships as essential drivers of social order and change.
Key Differences Between State and Society-Centric Models
State-centric models prioritize government institutions, emphasizing centralized control, policy enforcement, and sovereignty, whereas society-centric models highlight the role of social groups, grassroots movements, and cultural dynamics. The state-centric approach assumes a top-down power hierarchy, contrasting with society-centric frameworks that advocate for bottom-up participation and pluralism. State-centric models often focus on legal frameworks and formal authority, while society-centric perspectives underscore informal networks and social capital in shaping political outcomes.
Impact on Governance and Policy-Making
State-centric models prioritize centralized authority and top-down decision-making, leading to governance structures where policies are often designed to reinforce state control and maintain order. Society-centric approaches emphasize participatory governance and stakeholder engagement, resulting in policies that reflect diverse social interests and promote inclusive development. The impact on policy-making is evident as state-centric systems may streamline implementation but risk authoritarianism, whereas society-centric governance fosters transparency and responsiveness but can face challenges in consensus-building.
Role of Civil Society in Society-Centric Frameworks
Society-centric frameworks emphasize the active role of civil society as a catalyst for social change, governance, and accountability, fostering grassroots participation and community empowerment. Civil society organizations mobilize citizens to influence policy, promote transparency, and ensure government responsiveness to public needs. This approach prioritizes collaborative governance, recognizing diverse social actors as essential contributors to democratic processes and sustainable development.
Critiques of State-Centric Analysis
State-centric analysis often faces criticism for its narrow focus on governmental institutions, overlooking the critical roles of civil society, non-state actors, and grassroots movements in shaping political dynamics. This approach tends to marginalize the influence of social networks, cultural identities, and economic actors that operate beyond formal state boundaries. Critics argue that a society-centric perspective provides a more comprehensive understanding of power distribution, social change, and conflict resolution by highlighting the complex interactions within society itself.
Contemporary Case Studies: State vs Society Approaches
Contemporary case studies reveal varying outcomes in governance when comparing state-centric models, which emphasize centralized authority and top-down policy implementation, with society-centric approaches that prioritize grassroots participation and civil society engagement. In countries like China, state-centric strategies have driven rapid economic development through strong government control, while in contrast, Scandinavian nations exemplify society-centric governance with robust social welfare systems supported by citizen involvement. Effective policy outcomes often depend on the dynamic balance between state power and societal input, influencing stability, development, and public trust.
Future Trends in State and Society-Centered Debates
State-centric approaches emphasize government control in managing resources and security, while society-centric models prioritize civil society and community engagement in policymaking. Future trends indicate increasing hybrid governance, blending state authority with grassroots participation to address complex challenges like climate change and digital governance. Advances in AI and data analytics will enhance this synergy by improving transparency and citizen involvement in decision-making processes.
State-centric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com