Prescriptive norms dictate the behaviors individuals are expected to follow within a society, shaping everyday interactions and decisions. Understanding these norms can help you navigate social situations more effectively and improve your relationships. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how prescriptive norms influence your behavior and social dynamics.
Table of Comparison
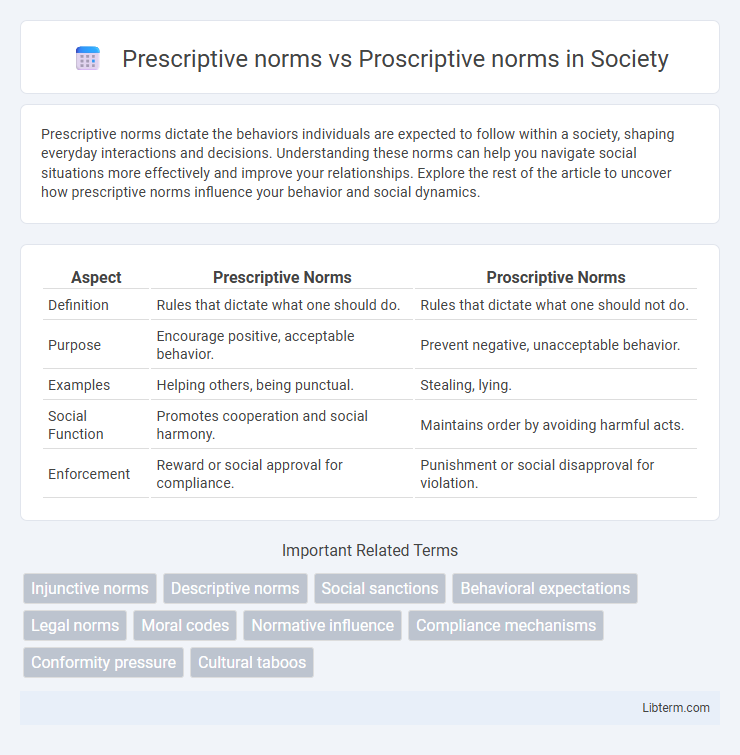
| Aspect | Prescriptive Norms | Proscriptive Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules that dictate what one should do. | Rules that dictate what one should not do. |
| Purpose | Encourage positive, acceptable behavior. | Prevent negative, unacceptable behavior. |
| Examples | Helping others, being punctual. | Stealing, lying. |
| Social Function | Promotes cooperation and social harmony. | Maintains order by avoiding harmful acts. |
| Enforcement | Reward or social approval for compliance. | Punishment or social disapproval for violation. |
Understanding Prescriptive and Proscriptive Norms
Prescriptive norms dictate behaviors that individuals are encouraged to follow, promoting positive actions within social contexts, while proscriptive norms specify actions that are forbidden, preventing negative behaviors. Understanding prescriptive and proscriptive norms is essential for analyzing cultural expectations and social control mechanisms that guide individual conduct. This distinction aids in recognizing how social groups enforce standards through rewards for compliance and sanctions for violations.
Key Differences Between Prescriptive and Proscriptive Norms
Prescriptive norms dictate behaviors that individuals are encouraged or expected to follow, such as saying "thank you" or recycling. Proscriptive norms, on the other hand, involve behaviors that are prohibited or discouraged, like littering or lying. The key differences lie in their function: prescriptive norms promote positive actions, while proscriptive norms restrict negative or harmful behaviors within a social context.
Historical Evolution of Social Norms
Prescriptive norms, which dictate behaviors that individuals are encouraged to perform, and proscriptive norms, which specify behaviors to avoid, have evolved alongside human societies to regulate social conduct and maintain order. Historically, prescriptive norms emerged from cultural rituals and collective goals, reinforcing positive behaviors like cooperation and reciprocity, while proscriptive norms often developed through taboos and prohibitions rooted in religious, legal, and moral frameworks. The dynamic interplay between these norms shaped complex social institutions, influencing the codification of laws and ethical standards that guide modern social interactions.
Linguistic Examples of Prescriptive vs Proscriptive Norms
Prescriptive norms in linguistics dictate the preferred or correct way to use language, such as the rule "use whom instead of who in object positions." Proscriptive norms prohibit certain language usages, like avoiding double negatives or split infinitives, considered incorrect or improper. Examples include the prescriptive rule advising "use whom for the object of a verb" versus the proscriptive norm forbidding "ain't" in formal speech.
Psychological Impact of Norm Adherence
Prescriptive norms, which dictate behaviors that individuals should perform, foster positive psychological outcomes such as increased social acceptance and heightened self-esteem when followed. Proscriptive norms, which prohibit certain behaviors, can induce anxiety, guilt, or fear of social exclusion if violated, impacting mental well-being negatively. Adherence to both types of norms influences conformity, shaping individual identity and social cohesion through internalized expectations.
Cultural Variability in Norms
Prescriptive norms dictate behaviors that are encouraged or required within a culture, while proscriptive norms define actions that are forbidden or discouraged, reflecting distinct cultural values and priorities. The variability in these norms across societies highlights how cultural context shapes expectations, with some cultures emphasizing harmonious social roles through prescriptive rules, and others enforcing strict prohibitions to maintain order. Understanding this cultural variability aids in interpreting social interactions and resolving cross-cultural misunderstandings.
Norms in Professional and Educational Settings
Prescriptive norms in professional and educational settings guide appropriate behaviors by recommending actions, such as punctuality and collaboration, to enhance productivity and learning outcomes. Proscriptive norms explicitly prohibit behaviors like plagiarism or harassment, ensuring ethical standards and a respectful environment. Understanding these norms is crucial for maintaining organizational culture and fostering academic integrity.
Challenges Associated with Proscriptive Norms
Proscriptive norms, which dictate behaviors to avoid, often pose challenges due to their restrictive nature, leading to resistance and non-compliance in social groups. The ambiguity surrounding what is prohibited can cause confusion and hinder consistent enforcement, affecting social cohesion and individual autonomy. These challenges complicate norm internalization and complicate efforts to regulate behavior effectively in organizational or cultural contexts.
The Role of Norms in Shaping Social Behavior
Prescriptive norms guide social behavior by signaling what actions are encouraged or approved within a community, fostering cooperation and positive social interactions. Proscriptive norms establish boundaries by defining what behaviors are unacceptable or forbidden, thereby preventing social discord and maintaining order. Together, these norms create a balanced framework that influences individuals' decisions, promotes conformity, and upholds societal values.
Future Trends in the Study of Social Norms
Future trends in the study of social norms emphasize the increasing integration of prescriptive norms, which dictate behaviors that individuals should follow, with proscriptive norms that outline forbidden actions, to better predict and influence social behavior. Advances in computational social science and machine learning enable more precise modeling of how these norms evolve and interact across digital platforms and global communities. Research also focuses on the dynamic interplay between cultural shifts and normative enforcement mechanisms, highlighting the role of real-time data in understanding norm adherence and change.
Prescriptive norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com