Social inclusion promotes equal opportunities and active participation for all individuals regardless of background or ability. It fosters community cohesion, reduces inequality, and enhances well-being by ensuring everyone feels valued and supported. Discover how your community can embrace social inclusion and the benefits it brings in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
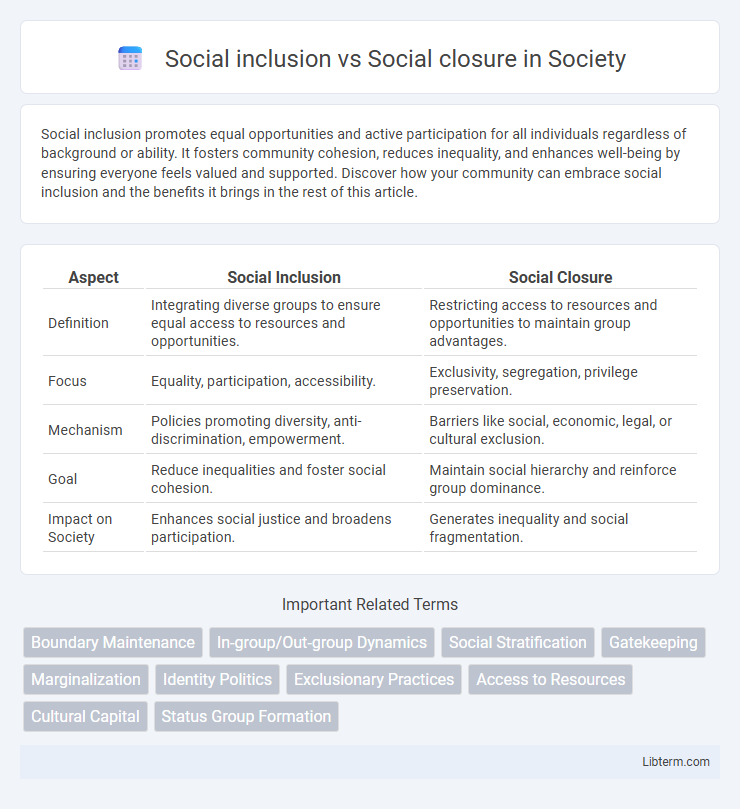
| Aspect | Social Inclusion | Social Closure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrating diverse groups to ensure equal access to resources and opportunities. | Restricting access to resources and opportunities to maintain group advantages. |
| Focus | Equality, participation, accessibility. | Exclusivity, segregation, privilege preservation. |
| Mechanism | Policies promoting diversity, anti-discrimination, empowerment. | Barriers like social, economic, legal, or cultural exclusion. |
| Goal | Reduce inequalities and foster social cohesion. | Maintain social hierarchy and reinforce group dominance. |
| Impact on Society | Enhances social justice and broadens participation. | Generates inequality and social fragmentation. |
Understanding Social Inclusion
Social inclusion involves creating equitable opportunities for marginalized groups to participate fully in social, economic, and political life, emphasizing access to resources, rights, and recognition. It contrasts with social closure, which refers to mechanisms that restrict access to privileges and exclude certain groups from social participation. Understanding social inclusion requires analyzing policies, social practices, and institutional frameworks that promote diversity, reduce inequalities, and foster a sense of belonging within communities.
Defining Social Closure
Social closure refers to the process by which social groups maintain exclusivity and restrict access to resources, opportunities, or privileges by enforcing boundaries and social norms. This mechanism ensures that certain groups consolidate power while excluding outsiders, often based on criteria like class, ethnicity, or education. Understanding social closure reveals how systemic barriers perpetuate inequality by limiting social mobility and reinforcing group dominance.
Historical Perspectives on Social Integration
Historical perspectives on social integration highlight social inclusion as the process of enabling marginalized groups to participate fully in societal institutions, promoting equality and diversity. In contrast, social closure refers to mechanisms by which dominant groups maintain privileges by restricting access to resources and opportunities, reinforcing social boundaries. These contrasting dynamics shaped class structures and power relations throughout history, influencing patterns of inequality and cohesion in societies.
Key Differences: Inclusion vs. Closure
Social inclusion fosters access and participation by marginalized groups in social, economic, and political spheres, promoting diversity and equal opportunity. Social closure enforces boundaries by dominant groups to restrict access to resources and opportunities, maintaining inequality and exclusivity. The key difference lies in social inclusion's emphasis on expanding access, whereas social closure centers on limiting and controlling access.
Factors Influencing Social Inclusion
Social inclusion is influenced by factors such as equitable access to education, employment opportunities, and social services, which help reduce inequalities and promote participation across diverse groups. Cultural acceptance, inclusive policies, and community engagement play critical roles in fostering environments where marginalized populations can thrive. In contrast, social closure mechanisms, including discrimination, exclusionary practices, and systemic barriers, limit access to resources and maintain social stratification.
Mechanisms of Social Closure
Mechanisms of social closure operate through exclusionary practices such as barriers to entry in education, employment, and social networks, which restrict access to resources and opportunities based on group membership. These processes reinforce social inequalities by preserving privilege within dominant groups and limiting upward mobility for marginalized communities. Examples include credentialism, licensing requirements, and selective recruitment that systematically exclude outsiders and maintain group boundaries.
Social and Economic Impacts
Social inclusion fosters equal access to resources, education, and employment opportunities, leading to enhanced economic growth and reduced poverty by integrating marginalized groups into the mainstream economy. Social closure, characterized by exclusionary practices and barriers based on class, race, or ethnicity, restricts access to social and economic capital, perpetuating inequality and limiting upward mobility. The economic impacts of social closure include increased unemployment rates and broader income disparities, whereas social inclusion promotes social cohesion and sustainable economic development.
Case Studies: Inclusion and Closure in Practice
Case studies on social inclusion and social closure reveal distinct dynamics shaping access to resources and opportunities across communities. In urban neighborhoods, inclusion programs foster diverse participation by targeting marginalized groups, enhancing social cohesion and reducing inequalities. Conversely, social closure practices emerge through exclusionary policies in elite institutions, where barriers like credentialism and cultural capital limit membership and preserve group privileges.
Strategies for Promoting Social Inclusion
Strategies for promoting social inclusion emphasize equal access to education, employment, and healthcare, ensuring marginalized groups participate fully in society. Policies such as affirmative action, community engagement programs, and inclusive urban planning help dismantle barriers created by social closure, which restricts opportunities based on identity or social status. Empowering disadvantaged communities through legal protections and economic resources drives equitable social integration and reduces systemic exclusion.
Building Inclusive Communities for the Future
Social inclusion fosters equitable access to resources, opportunities, and decision-making for marginalized groups, promoting diverse and resilient communities. Social closure, by contrast, reinforces exclusive boundaries through discrimination and restricted access, hindering community growth and cohesion. Building inclusive communities for the future necessitates dismantling structural barriers, implementing inclusive policies, and encouraging active participation from all social groups to enhance social capital and collective well-being.
Social inclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com