Social change transforms communities by altering cultural norms, behaviors, and relationships within societies. It stems from various factors such as technological advancements, economic shifts, and social movements, reshaping how individuals interact and live. Explore the article further to understand the driving forces behind social change and how it influences your world.
Table of Comparison
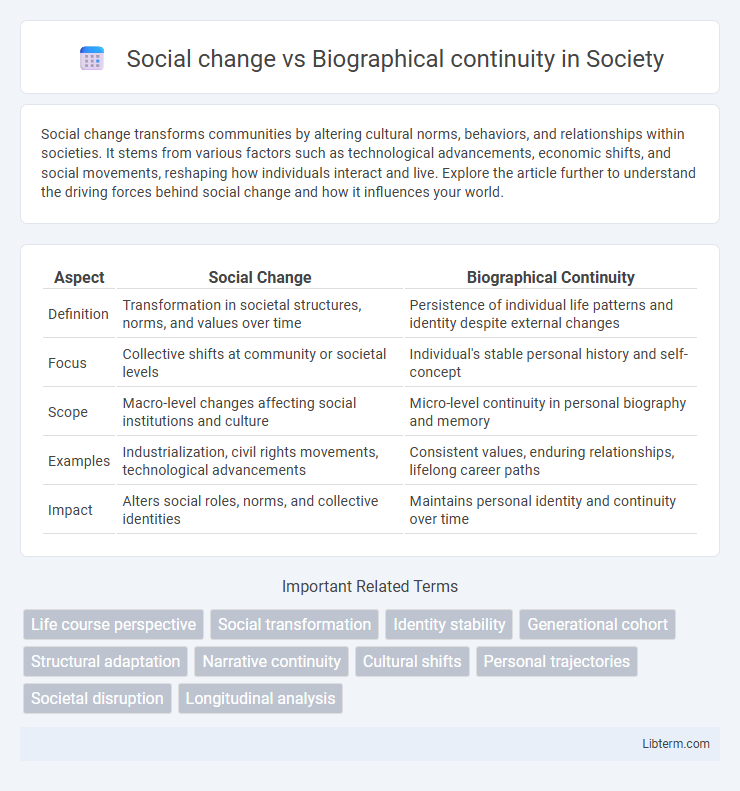
| Aspect | Social Change | Biographical Continuity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transformation in societal structures, norms, and values over time | Persistence of individual life patterns and identity despite external changes |
| Focus | Collective shifts at community or societal levels | Individual's stable personal history and self-concept |
| Scope | Macro-level changes affecting social institutions and culture | Micro-level continuity in personal biography and memory |
| Examples | Industrialization, civil rights movements, technological advancements | Consistent values, enduring relationships, lifelong career paths |
| Impact | Alters social roles, norms, and collective identities | Maintains personal identity and continuity over time |
Understanding Social Change: Definition and Impact
Social change refers to significant alterations over time in behavior patterns, cultural values, and social structures within a society. It impacts individuals and communities by reshaping institutions, norms, and power dynamics, which can challenge biographical continuity--the steady development of an individual's life story and identity. Understanding social change involves analyzing historical trends, social movements, and technological advancements that drive transformation and redefine collective and personal experiences.
Biographical Continuity: Meaning and Importance
Biographical continuity refers to the sustained patterns and consistent behaviors in an individual's life despite external social changes. It highlights the importance of personal identity, memory, and lived experience in maintaining a sense of stability over time. Understanding biographical continuity is crucial for fields such as psychology and sociology to analyze how individuals adapt to or resist transformations in their social environment.
Historical Perspectives on Social Change
Historical perspectives on social change emphasize large-scale transformations in societal structures, norms, and institutions, contrasting with biographical continuity, which highlights the persistence of individual life courses despite shifting social contexts. Scholars such as Karl Marx and Max Weber analyze social change through economic and cultural lenses, revealing how class struggles and ideological shifts drive systemic evolution over time. Understanding this dynamic interplay is crucial for comprehending how societies adapt while individuals maintain continuity in their personal identities.
Theories Explaining Biographical Continuity
Theories explaining biographical continuity emphasize the persistence of individual identity and life patterns despite social changes, highlighting mechanisms like narrative identity and life course perspective. Narrative identity theory posits that individuals maintain a coherent sense of self by constructing life stories that integrate past experiences with current realities. The life course perspective underlines the importance of timing, social roles, and historical context in sustaining continuity amidst changing social environments.
Interplay Between Social Change and Personal Narratives
The interplay between social change and biographical continuity reveals how individual life stories adapt amid shifting cultural norms and historical contexts. Personal narratives often reflect broader societal transformations, illustrating resilience or resistance in maintaining identity across generations. Understanding this dynamic highlights the reciprocal influence between evolving social structures and the stability of personal experiences.
Factors Disrupting Biographical Continuity
Factors disrupting biographical continuity include major life events such as migration, trauma, or sudden health crises that alter an individual's life narrative and personal identity. Social upheavals like economic recessions, political instability, and cultural shifts also contribute to breaks in the continuity of personal biographies by reshaping social roles and expectations. These disruptions challenge the stability of self-concept and may necessitate adaptive coping mechanisms to reconstruct a coherent life story.
Case Studies: Individuals Amid Societal Transformation
Case studies examining individuals amid societal transformation highlight the tension between social change and biographical continuity, revealing how personal identities adapt or resist evolving cultural norms. Research on urban migration, civil rights movements, and technological shifts demonstrates varied strategies individuals employ to maintain a coherent life narrative while navigating rapid external changes. These cases underscore the importance of contextual factors and personal agency in mediating the impact of broad social transformations on individual biographies.
Social Institutions and the Shaping of Biographical Paths
Social institutions play a pivotal role in shaping biographical paths by providing structured frameworks that influence individual life courses and social roles over time. While social change can alter institutional norms and opportunities, biographical continuity reflects how individuals navigate, adapt to, or resist these evolving structures based on accumulated experiences and social positioning. The dynamic interplay between institutional transformations and personal histories determines the extent to which life trajectories maintain stability or embrace change.
Negotiating Identity During Social Upheaval
Negotiating identity during social upheaval involves balancing social change and biographical continuity as individuals reconcile evolving societal norms with personal history. Identity construction becomes a dynamic process where past experiences inform responses to new social realities, enabling adaptive strategies that maintain a coherent sense of self. This interplay highlights the tension between collective transformations and individual life narratives, shaping resilience and self-concept amid instability.
Balancing Tradition and Change: Navigating Continuity
Balancing tradition and change requires understanding social change as the collective evolution of cultural norms, institutions, and behaviors, while biographical continuity emphasizes the individual's consistent identity and values over time. Navigating continuity involves integrating new social dynamics with personal histories, allowing individuals to adapt without losing their core sense of self. This interplay ensures that societal transformations respect individual narratives, fostering harmony between collective progress and personal legacy.
Social change Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com