Legal justice ensures fairness by upholding laws and protecting individual rights within a structured judicial system. It addresses disputes impartially, aiming to deliver equitable outcomes for all parties involved. Discover how legal justice impacts your rights and society by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
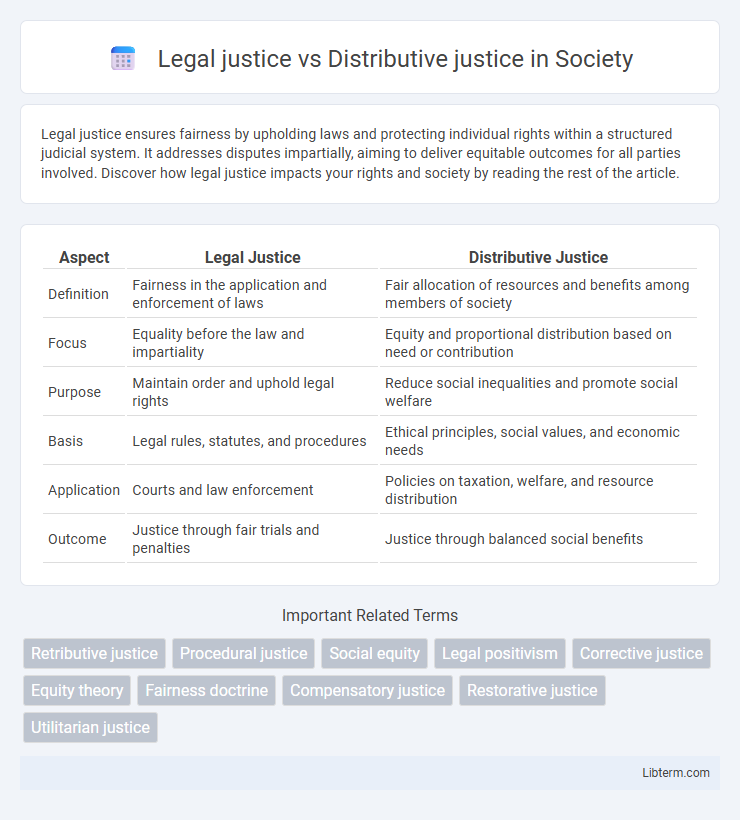
| Aspect | Legal Justice | Distributive Justice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fairness in the application and enforcement of laws | Fair allocation of resources and benefits among members of society |
| Focus | Equality before the law and impartiality | Equity and proportional distribution based on need or contribution |
| Purpose | Maintain order and uphold legal rights | Reduce social inequalities and promote social welfare |
| Basis | Legal rules, statutes, and procedures | Ethical principles, social values, and economic needs |
| Application | Courts and law enforcement | Policies on taxation, welfare, and resource distribution |
| Outcome | Justice through fair trials and penalties | Justice through balanced social benefits |
Introduction to Legal Justice and Distributive Justice
Legal justice ensures fairness through the application and enforcement of laws, emphasizing equal treatment and adherence to established rules within judicial systems. Distributive justice addresses the equitable allocation of resources and benefits among individuals in a society, focusing on fairness in economic and social outcomes. Both concepts serve foundational roles in shaping moral and institutional frameworks that govern societal interactions and public policy.
Defining Legal Justice: Concepts and Principles
Legal justice refers to the fair application and enforcement of laws within a society, emphasizing equality before the law and impartiality in judicial processes. It is grounded in principles such as due process, legal rights, and adherence to established rules to ensure accountability and protect individual freedoms. Unlike distributive justice, which concerns the equitable allocation of resources, legal justice focuses on upholding order, resolving disputes, and maintaining social stability through consistent legal frameworks.
Understanding Distributive Justice: Key Theories
Distributive justice centers on the equitable allocation of resources and benefits within a society, contrasting with legal justice, which emphasizes adherence to laws and fairness in legal processes. Key theories of distributive justice include John Rawls's theory of justice as fairness, which advocates for inequalities only if they benefit the least advantaged, and Robert Nozick's entitlement theory that prioritizes individual property rights. Utilitarian perspectives also influence distributive justice, seeking the greatest overall happiness through resource distribution, highlighting the philosophical diversity in approaches to social equity.
Historical Evolution of Justice Systems
Legal justice historically emerged from codified laws aimed at maintaining order and resolving disputes impartially within societies, with roots tracing back to ancient Mesopotamian codes like Hammurabi's. Distributive justice developed as societies recognized the need for fair allocation of resources and opportunities, gaining prominence during Enlightenment debates on equality and social rights. Modern justice systems integrate both concepts, balancing rule-based legal frameworks with principles of equitable distribution to address complex social dynamics.
Fundamental Differences Between Legal and Distributive Justice
Legal justice centers on the fair application of laws and upholding rights through impartial procedures within a judicial system. Distributive justice focuses on equitable allocation of resources and benefits among members of society based on needs, contributions, or merit. The fundamental difference lies in legal justice enforcing uniform laws, while distributive justice addresses fairness in outcomes and resource distribution.
The Role of Law in Upholding Justice
Legal justice ensures fairness by enforcing laws that protect individual rights and maintain social order, emphasizing impartial application and due process. Distributive justice focuses on the equitable allocation of resources and opportunities, seeking to correct social and economic inequalities. The role of law in upholding justice bridges these concepts by creating frameworks that both regulate behavior and promote fairness in the distribution of benefits and burdens within society.
Distributive Justice in Social and Economic Contexts
Distributive justice in social and economic contexts emphasizes the equitable allocation of resources, opportunities, and privileges among diverse groups, aiming to reduce inequalities and promote fairness in wealth distribution. It addresses how economic benefits and social goods are shared, advocating policies like progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and equal access to education and healthcare. This approach contrasts legal justice, which focuses on the enforcement of laws and rights rather than the equitable distribution of societal assets.
Case Studies: Legal Justice vs Distributive Justice in Practice
Case studies reveal that legal justice emphasizes the strict application of laws and statutes to ensure fairness and equality before the law, exemplified by landmark rulings that uphold constitutional rights regardless of social status. Distributive justice focuses on the equitable allocation of resources and opportunities, illustrated by social welfare programs and affirmative action policies aimed at reducing systemic inequalities. Comparative analyses in practice highlight tensions where legal justice's formal equality clashes with distributive justice's goal of substantive fairness, such as in decisions involving access to healthcare and education.
Contemporary Debates and Challenges
Contemporary debates on legal justice versus distributive justice center on balancing strict adherence to laws with equitable resource distribution to address systemic inequalities. Challenges include reconciling formal legal equality with substantive social justice, especially amidst rising socioeconomic disparities and demands for inclusive policies. Critical discussions explore how legal systems can adapt to promote distributive fairness without compromising rule of law principles.
Towards a Balanced Approach: Integrating Legal and Distributive Justice
Legal justice ensures fairness through impartial application of laws, maintaining order and protecting individual rights, while distributive justice focuses on equitable allocation of resources based on need and social welfare. Integrating these concepts requires crafting policies that uphold legal principles while addressing systemic inequalities, thus promoting both rule of law and social equity. This balanced approach fosters a justice system that respects individual rights and simultaneously advances collective fairness across society.
Legal justice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com