Exogamy is the social practice of marrying outside one's specific social group, clan, or community to promote genetic diversity and social alliances. This custom plays a significant role in shaping cultural identities and maintaining social cohesion across generations. Explore the article to understand how exogamy influences relationships and societal structures in various cultures.
Table of Comparison
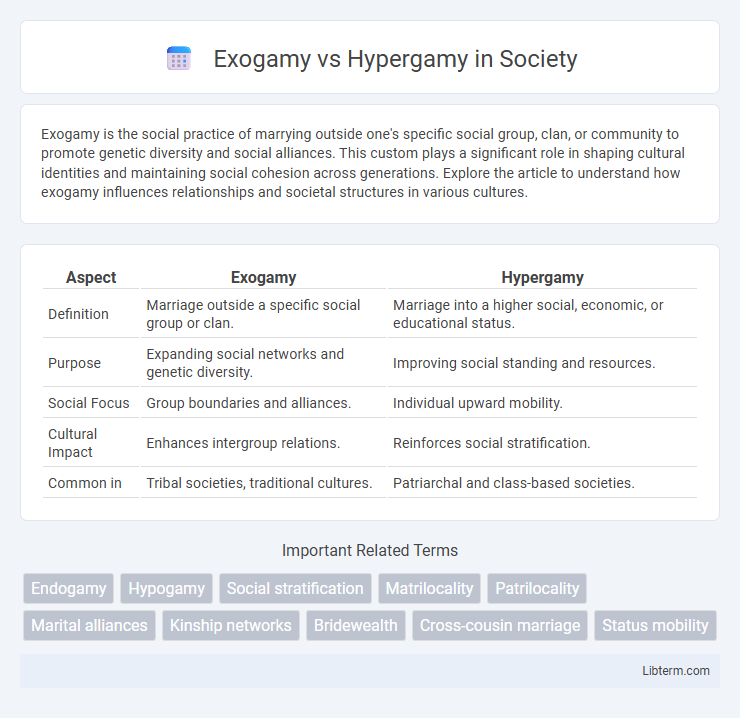
| Aspect | Exogamy | Hypergamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marriage outside a specific social group or clan. | Marriage into a higher social, economic, or educational status. |
| Purpose | Expanding social networks and genetic diversity. | Improving social standing and resources. |
| Social Focus | Group boundaries and alliances. | Individual upward mobility. |
| Cultural Impact | Enhances intergroup relations. | Reinforces social stratification. |
| Common in | Tribal societies, traditional cultures. | Patriarchal and class-based societies. |
Defining Exogamy: Meaning and Origins
Exogamy refers to the social practice of marrying outside one's specific social group, clan, or community, aiming to promote genetic diversity and strengthen intergroup relations. Originating from the Greek words "exo" meaning "outside" and "gamos" meaning "marriage," exogamy has been a fundamental norm in many cultures worldwide to prevent inbreeding and enhance social alliances. This custom contrasts with hypergamy, which centers on marrying into a higher social status rather than focusing on group boundaries.
Understanding Hypergamy: Concepts and Contexts
Hypergamy refers to the social practice where individuals marry partners of higher socioeconomic status, emphasizing upward social mobility through marital alliances. This concept is deeply rooted in cultural, economic, and historical contexts, influencing mate selection based on perceived benefits such as wealth, education, and social prestige. Understanding hypergamy requires analyzing its role in maintaining social hierarchies and its interaction with gender norms and societal expectations.
Historical Perspectives on Exogamy
Historical perspectives on exogamy reveal its role in promoting social cohesion and expanding kinship networks by discouraging marriage within one's immediate community or clan. Anthropological studies show that exogamous practices helped prevent inbreeding and fostered alliances among diverse groups, which was crucial for survival and resource exchange in early societies. These patterns contrast with hypergamy, which prioritizes marrying "up" in social status, demonstrating how exogamy primarily addresses genetic diversity and social integration rather than status mobility.
Evolutionary Roots of Hypergamy
Hypergamy, rooted in evolutionary biology, describes the social practice where individuals, often women, seek partners of higher socioeconomic status or superior genetic quality to ensure better resources and offspring survival. This behavior contrasts with exogamy, which emphasizes mating outside a specific social or kin group to promote genetic diversity. Evolutionary theories suggest hypergamy evolved to maximize reproductive success by aligning mate choice with indicators of resource acquisition and social dominance.
Exogamy Across Cultures: Global Practices
Exogamy, the practice of marrying outside one's social group, tribe, or community, varies widely across cultures as a tool for fostering alliances and genetic diversity. In many indigenous societies, exogamous marriage rules ensure social cohesion by preventing inbreeding and encouraging broader kinship ties, evident in practices like clan exogamy among Native American tribes and caste exogamy in certain South Asian communities. These global exogamy patterns contrast with hypergamy, where marriage often involves upward social mobility, emphasizing the differing social functions of each marital strategy.
Hypergamy in Modern Society
Hypergamy in modern society refers to the practice where individuals, often women, seek partners with higher socioeconomic status, education, or social standing than themselves. This social behavior influences dating dynamics, marriage trends, and economic mobility, reflecting shifting gender roles and aspirations. Research shows hypergamy impacts partner selection algorithms on dating platforms and correlates with increased educational attainment among women aiming for upward mobility through marriage.
Social Implications: Exogamy vs Hypergamy
Exogamy promotes social cohesion by encouraging marriage outside one's social group, which fosters alliances and reduces intra-group conflicts. Hypergamy often reinforces social stratification by motivating individuals, particularly women, to marry into higher social classes, thereby sustaining or amplifying existing inequalities. The distinct social implications of exogamy and hypergamy influence patterns of social mobility and group integration in complex ways.
Gender Roles and Mate Selection
Exogamy requires individuals to marry outside their social group, influencing gender roles by encouraging diverse alliances and balancing power dynamics between groups. Hypergamy involves marrying up in social status, often reinforcing traditional gender roles where women seek higher-status male partners to enhance social mobility. Both practices shape mate selection strategies by intertwining societal expectations and individual preferences tied to gender norms.
Economic Factors Influencing Mating Strategies
Economic factors significantly influence exogamy and hypergamy by shaping mating strategies in various cultures. Exogamy often arises from the need to form alliances and share resources across social groups, promoting economic stability and diversification. Hypergamy reflects economic aspirations, with individuals seeking partners of higher socioeconomic status to enhance financial security, social capital, and upward mobility.
Future Trends: Exogamy and Hypergamy in a Changing World
Exogamy and hypergamy are evolving as global connectivity and social mobility reshape partner selection criteria, with younger generations increasingly valuing shared values and compatibility over traditional norms. Technological advancements in online dating platforms are facilitating diverse and cross-cultural relationships, accelerating exogamous unions beyond conventional boundaries. Economic shifts and gender role transformations are challenging hypergamous patterns, promoting more egalitarian partnerships based on mutual aspirations and personal growth.
Exogamy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com