Practicing responsible consumption involves making mindful choices that minimize environmental impact and promote social equity. By selecting sustainable products and reducing waste, you contribute to preserving resources for future generations. Explore our article to learn effective strategies for adopting responsible consumption in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
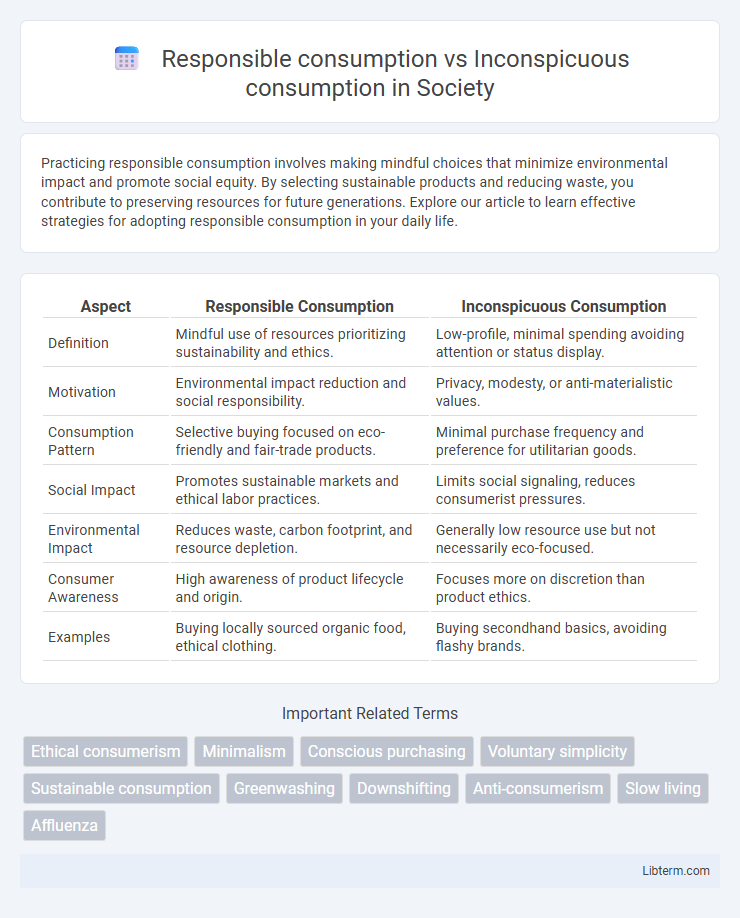
| Aspect | Responsible Consumption | Inconspicuous Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mindful use of resources prioritizing sustainability and ethics. | Low-profile, minimal spending avoiding attention or status display. |
| Motivation | Environmental impact reduction and social responsibility. | Privacy, modesty, or anti-materialistic values. |
| Consumption Pattern | Selective buying focused on eco-friendly and fair-trade products. | Minimal purchase frequency and preference for utilitarian goods. |
| Social Impact | Promotes sustainable markets and ethical labor practices. | Limits social signaling, reduces consumerist pressures. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, carbon footprint, and resource depletion. | Generally low resource use but not necessarily eco-focused. |
| Consumer Awareness | High awareness of product lifecycle and origin. | Focuses more on discretion than product ethics. |
| Examples | Buying locally sourced organic food, ethical clothing. | Buying secondhand basics, avoiding flashy brands. |
Understanding Responsible Consumption
Responsible consumption involves making purchasing decisions that prioritize sustainability, ethical sourcing, and minimal environmental impact, promoting long-term well-being for society and the planet. It emphasizes careful consideration of product life cycles, waste reduction, and supporting brands committed to fair labor practices and eco-friendly materials. Understanding responsible consumption requires awareness of how individual choices affect global resources and the collective shift toward more conscious consumer behavior.
Defining Inconspicuous Consumption
Inconspicuous consumption refers to purchasing and using goods or services with minimal visibility to others, prioritizing personal satisfaction over external display or social status. This behavior contrasts with responsible consumption, which emphasizes mindful purchasing decisions that support sustainability, ethical production, and environmental impact reduction. Inconspicuous consumption often involves discreet, subtle use of products that do not attract attention, highlighting privacy and intrinsic value rather than ostentatious consumption patterns.
Key Differences Between Responsible and Inconspicuous Consumption
Responsible consumption emphasizes ethical purchasing decisions that prioritize sustainability, environmental impact, and social responsibility, often involving transparent sourcing and minimal waste. Inconspicuous consumption, by contrast, revolves around understated or subtle spending patterns aimed at avoiding attention or social judgment, prioritizing privacy or modesty rather than ethical impact. The key differences lie in the motivation and visibility: responsible consumption aims for positive global outcomes, while inconspicuous consumption seeks personal discretion without necessarily addressing sustainability concerns.
The Rise of Ethical Consumerism
The rise of ethical consumerism reflects a growing shift towards responsible consumption, where consumers prioritize products that are sustainably sourced, cruelty-free, and socially equitable. In contrast, inconspicuous consumption often involves buying goods that emphasize subtlety and status without overt brand display, aligning less with environmental and social responsibility. Retailers and brands adopting transparent supply chains and eco-friendly practices increasingly attract conscientious buyers seeking to minimize their ecological footprint.
Environmental Impact: Responsible vs Inconspicuous Choices
Responsible consumption prioritizes environmentally sustainable choices, such as buying eco-friendly products, reducing waste, and supporting renewable resources, which significantly lowers carbon footprints and conserves natural ecosystems. Inconspicuous consumption often involves subtle, continuous purchasing that may appear modest but cumulatively leads to higher resource depletion, increased pollution, and greater environmental degradation. Understanding the environmental impact reveals that responsible consumption fosters long-term ecological balance, whereas inconspicuous consumption contributes to hidden but substantial ecological harm.
Social Implications of Consumption Habits
Responsible consumption encourages mindful purchasing that prioritizes ethical sourcing, environmental sustainability, and social equity, fostering communities that support fair labor practices and reduce ecological footprints. In contrast, inconspicuous consumption often shifts focus towards minimalism and subtlety to avoid conspicuous displays of wealth, which can diminish social pressure to engage in competitive consumption but may also obscure the origins and impacts of products. Both consumption habits significantly shape social values around status, identity, and environmental responsibility, influencing societal norms and collective behaviors towards sustainability and ethical awareness.
Motivations Behind Inconspicuous Consumption
Inconspicuous consumption is driven by motivations such as the desire for social distinction, identity expression, and avoidance of overt status signaling, contrasting sharply with responsible consumption that prioritizes sustainability and ethical considerations. Consumers engaging in inconspicuous consumption seek subtle indicators of wealth or values that resonate with niche social groups rather than broad public recognition. Psychological factors like status anxiety and peer influence further fuel the preference for understated luxury over conspicuous consumption's ostentatious displays.
Challenges in Practicing Responsible Consumption
Responsible consumption faces challenges such as limited consumer awareness, higher costs of sustainable products, and limited availability of eco-friendly options in many markets. Inconspicuous consumption, characterized by subtle or low-profile purchasing behaviors, often undermines transparency and accountability, making it harder to promote sustainable habits. Overcoming these obstacles requires enhanced education, affordable green alternatives, and systemic shifts in production and retail practices.
Brands and Marketing: Influencing Consumption Patterns
Brands leveraging responsible consumption emphasize sustainability, ethical sourcing, and transparency to attract eco-conscious consumers, thereby reshaping marketing strategies toward value-driven messaging. In contrast, inconspicuous consumption thrives on subtle branding and understated luxury, appealing to consumers seeking status without overt display, influencing brands to craft minimalist yet aspirational campaigns. Marketing patterns reveal a growing shift as brands balance authenticity and exclusivity, aligning product narratives with evolving consumer values to influence purchasing behaviors effectively.
Strategies for Fostering Responsible Consumption
Promoting responsible consumption involves strategies such as implementing eco-labeling to increase product transparency, encouraging minimalistic lifestyle choices through educational campaigns, and incentivizing sustainable purchasing behaviors via subsidies or discounts on eco-friendly products. Governments and businesses can foster responsible consumption by developing policies that reduce waste, support circular economies, and prioritize renewable resources. Empowering consumers with information about environmental impact and social responsibility enhances conscious decision-making, thus shifting consumption patterns away from inconspicuous consumption driven by status or excess.
Responsible consumption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com