Formal groups are structured organizations characterized by defined roles, rules, and procedures that guide member interactions and decision-making processes. They are typically established to achieve specific goals, maintain order, and ensure efficient coordination within businesses, institutions, or communities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how formal groups function and impact your professional environment.
Table of Comparison
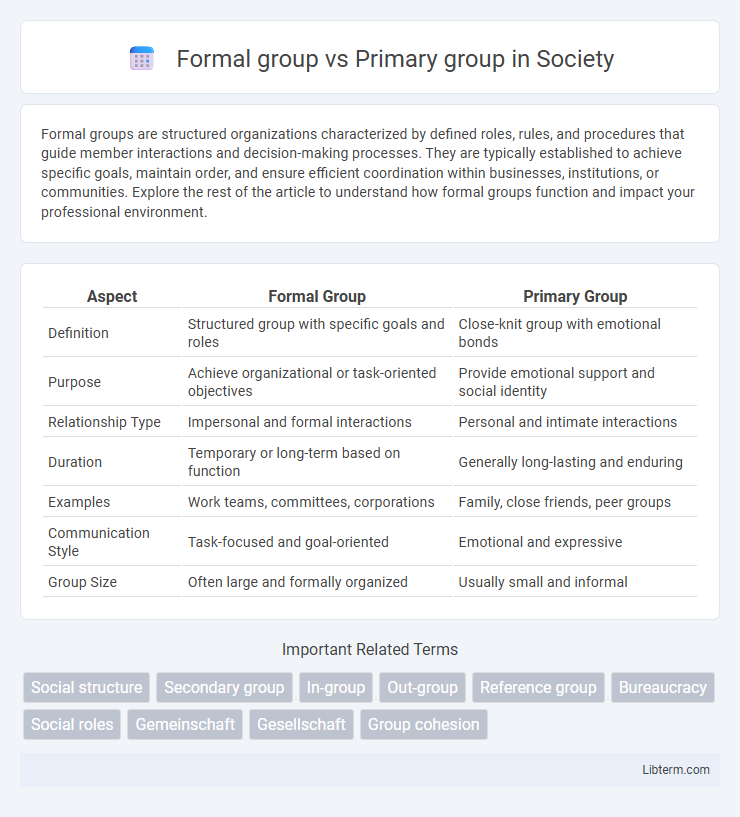
| Aspect | Formal Group | Primary Group |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured group with specific goals and roles | Close-knit group with emotional bonds |
| Purpose | Achieve organizational or task-oriented objectives | Provide emotional support and social identity |
| Relationship Type | Impersonal and formal interactions | Personal and intimate interactions |
| Duration | Temporary or long-term based on function | Generally long-lasting and enduring |
| Examples | Work teams, committees, corporations | Family, close friends, peer groups |
| Communication Style | Task-focused and goal-oriented | Emotional and expressive |
| Group Size | Often large and formally organized | Usually small and informal |
Definition of Formal Groups
Formal groups are structured collectives created to achieve specific goals through clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and rules within an organization. These groups operate based on official authority and are characterized by established hierarchies and assigned tasks that align with organizational objectives. Unlike primary groups, which are informal and based on personal relationships, formal groups emphasize systematic coordination and goal-oriented collaboration.
Definition of Primary Groups
Primary groups are small social groups characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships, often involving family and close friends. These groups provide emotional support, social identity, and a sense of belonging, forming the foundation for individual social development. Unlike formal groups, which are larger and organized around specific goals with defined roles, primary groups emphasize intimate, face-to-face interactions and strong emotional ties.
Key Characteristics of Formal Groups
Formal groups are defined by structured roles, specific goals, and clear organizational guidelines that dictate member behavior and interaction. These groups emphasize task completion, hierarchy, and official communication channels, ensuring efficiency and accountability within the organization. Unlike primary groups, formal groups prioritize objectives and performance over emotional connections and personal relationships.
Key Characteristics of Primary Groups
Primary groups are characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships that foster a strong sense of identity and emotional support. These groups typically feature face-to-face interactions, intimate knowledge of each member, and a strong sense of loyalty and commitment. Unlike formal groups, which are task-oriented and governed by explicit roles and rules, primary groups emphasize emotional bonds and social cohesion.
Formation and Structure Differences
Formal groups form through organizational goals and structured rules, exhibiting an official hierarchy and clearly defined roles. Primary groups develop organically based on personal relationships, emotional bonds, and face-to-face interactions, lacking formal structures. The rigid framework of formal groups contrasts with the flexible, intimate nature of primary groups in terms of formation and structure.
Roles and Relationships in Formal Groups
Formal groups consist of structured roles defined by organizational rules, emphasizing task-oriented relationships that facilitate goal achievement and efficiency. Roles in formal groups are explicitly assigned, promoting predictable interactions and accountability among members. Relationships within formal groups are often impersonal and based on positions rather than personal connections, contrasting with the emotional bonds found in primary groups.
Roles and Relationships in Primary Groups
Primary groups feature close-knit, enduring relationships that foster emotional support and personal growth, emphasizing expressive roles over task-oriented roles typical of formal groups. Members of primary groups engage in face-to-face interactions, developing strong bonds that influence identity and socialization processes. In contrast, formal groups prioritize specific roles defined by organizational goals, with relationships primarily based on task completion rather than emotional connections.
Functions and Purposes of Each Group
Formal groups are structured entities established to achieve specific organizational goals through defined roles and procedures, emphasizing task accomplishment, coordination, and efficiency. Primary groups prioritize emotional support, socialization, and the development of personal identity, facilitating close, face-to-face interactions and long-term relationships. While formal groups drive productivity and goal attainment, primary groups foster belongingness and emotional well-being essential for individual development.
Examples of Formal and Primary Groups
Formal groups include work teams such as project groups in corporations, committees in organizations, and task forces in government agencies, where roles and goals are clearly defined. Primary groups encompass family units, close friends, and intimate peer groups, characterized by strong emotional bonds and long-term relationships. These examples highlight the structural and relational distinctions between formal and primary groups in social contexts.
Major Differences: Formal Group vs Primary Group
Formal groups consist of members organized to achieve specific goals and follow established rules, often found in workplaces or institutions, emphasizing structured roles and tasks. Primary groups, such as family and close friends, are characterized by intimate, emotional bonds and long-lasting relationships that provide social support and personal identity. The major difference lies in the purpose and nature of interaction: formal groups prioritize goal-oriented collaboration, whereas primary groups focus on emotional connections and social fulfillment.
Formal group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com