A superstructure serves as the upper part of a building or ship, supporting load-bearing walls, roofs, and other structural elements. It plays a crucial role in distributing weight and ensuring stability, directly impacting the safety and durability of the construction. Explore the rest of this article to understand how a well-designed superstructure enhances your project's overall performance.
Table of Comparison
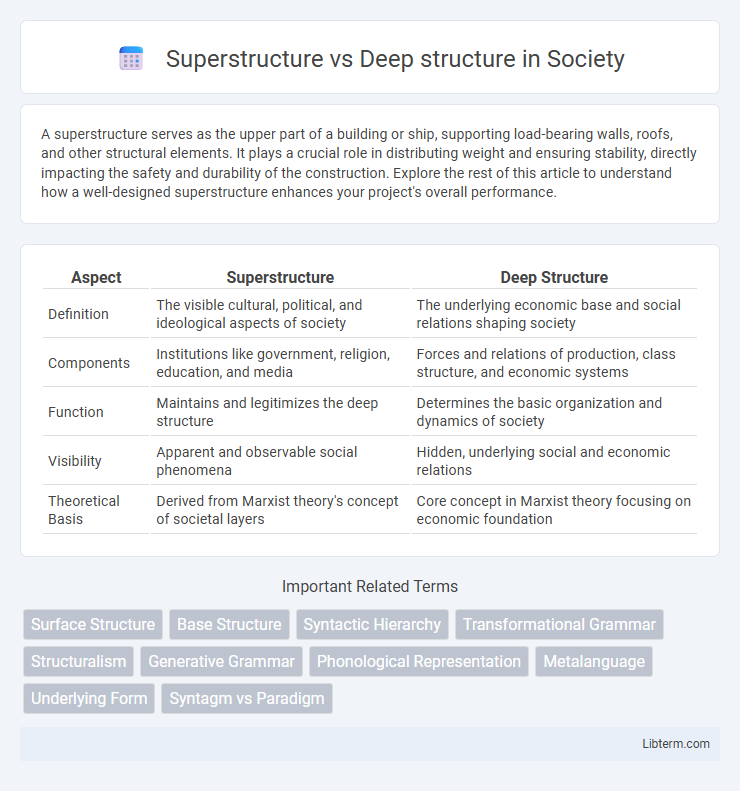
| Aspect | Superstructure | Deep Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The visible cultural, political, and ideological aspects of society | The underlying economic base and social relations shaping society |
| Components | Institutions like government, religion, education, and media | Forces and relations of production, class structure, and economic systems |
| Function | Maintains and legitimizes the deep structure | Determines the basic organization and dynamics of society |
| Visibility | Apparent and observable social phenomena | Hidden, underlying social and economic relations |
| Theoretical Basis | Derived from Marxist theory's concept of societal layers | Core concept in Marxist theory focusing on economic foundation |
Introduction to Superstructure and Deep Structure
Superstructure refers to the overarching organizational framework governing language syntax and sentence construction, while deep structure represents the underlying, abstract semantic relationships within a sentence. Understanding the distinction between superstructure and deep structure is essential for linguistic analysis in transformational grammar, as it explains how meaning is preserved through syntactic variations. The transformation from deep structure to superstructure involves applying grammatical rules that generate coherent, surface-level sentences from the core semantic representation.
Defining Superstructure in Linguistics and Architecture
Superstructure in linguistics refers to the surface level of language comprising phonetic, syntactic, and morphological forms that convey meaning, contrasting with the deep structure which represents the underlying abstract grammatical relationships. In architecture, superstructure denotes the part of a building above the foundation, including walls, columns, and roofs, designed to support loads and resist environmental forces. Both disciplines emphasize superstructure as the observable and functional layer built upon a foundational base, crucial for interpretation in language and stability in construction.
Understanding Deep Structure: Origins and Concepts
Deep structure, a fundamental concept in transformational-generative grammar introduced by Noam Chomsky, represents the underlying syntactic relationships and semantic meaning of a sentence before any surface-level transformations occur. It originates from the idea that sentences have an abstract form capturing their core meaning, independent of the varied ways they can be expressed in spoken or written language. Understanding deep structure is essential for analyzing how different sentence forms share the same meaning and for exploring the cognitive processes underlying language comprehension.
Key Differences Between Superstructure and Deep Structure
Superstructure refers to the overall framework or external form of a sentence, encompassing its syntactic organization and surface elements, while deep structure represents the underlying semantic relationships and grammatical components that convey meaning at a more abstract level. Key differences include superstructure's focus on sentence order, clause boundaries, and observable patterns, whereas deep structure emphasizes the core syntactic relations, thematic roles, and argument structure underlying these patterns. Linguists analyze superstructure to understand language expression and deep structure to uncover the cognitive processes behind sentence formation and meaning interpretation.
The Role of Superstructure in Social Theory
The superstructure in social theory comprises cultural institutions, ideologies, and political systems that arise from and support the economic base, shaping society's collective consciousness and norms. It functions to maintain and legitimize the existing mode of production by influencing law, education, religion, and media, thereby reinforcing social hierarchies and power relations. This dynamic relationship underscores the superstructure's critical role in reproducing societal order and controlling ideological discourse.
Deep Structure in Linguistics and Cognitive Science
Deep structure in linguistics and cognitive science refers to the underlying, abstract syntactic representation of a sentence that captures its core semantic relationships before any transformational rules are applied. It encodes the fundamental meaning and grammatical relations that remain constant despite variations in surface form or superstructure. Understanding deep structure is essential for analyzing sentence meaning, language acquisition, and the mental processes involved in language comprehension and generation.
Applications of Superstructure Across Disciplines
Superstructure, as a concept in linguistics and social sciences, finds varied applications across disciplines such as architecture, sociology, and computational linguistics. In architecture, it refers to the portion of a building above the foundation, influencing design and structural integrity. In sociology, superstructure encompasses cultural, ideological, and institutional systems shaped by economic base, facilitating analysis of social dynamics and power relations.
Deep Structure’s Influence on Meaning and Interpretation
Deep structure represents the underlying syntactic relationships and semantic roles within a sentence, providing the foundation for meaning beyond surface form. Its influence on meaning and interpretation is evident as it captures the core propositional content that guides how information is understood and processed mentally. Variations in deep structure often lead to different interpretations despite similar surface structures, highlighting its critical role in linguistic analysis and natural language understanding.
Comparative Analysis: Superstructure vs Deep Structure
Superstructure emphasizes the organization and sequencing of ideas in discourse, shaping how information is presented to guide reader or listener expectations, while deep structure focuses on the underlying syntactic relationships that form the core meaning of a sentence. Superstructure involves the overall framework of communicative acts, such as narrative or explanation patterns, contrasting with deep structure's role in capturing transformational grammar's base representations. Comparative analysis reveals that superstructure guides pragmatic coherence and thematic progression, whereas deep structure ensures syntactic integrity and semantic interpretation across varied contexts.
Conclusion: Implications and Future Perspectives
The distinction between superstructure and deep structure reveals critical implications for linguistic theory and natural language processing, emphasizing the need for models that integrate both surface syntax and underlying meaning. Future research should focus on developing hybrid frameworks that bridge generative grammar with semantic interpretation to enhance machine understanding and language generation. Advances in neural network architectures and symbolic approaches hold promise for capturing complex interactions between deep structures and observable linguistic patterns.
Superstructure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com