Hypergamy refers to the practice of seeking a partner with higher social, economic, or educational status. Understanding hypergamy can provide insight into relationship dynamics and mating preferences across cultures. Discover how hypergamy shapes modern relationships and impacts your social connections in the full article.
Table of Comparison
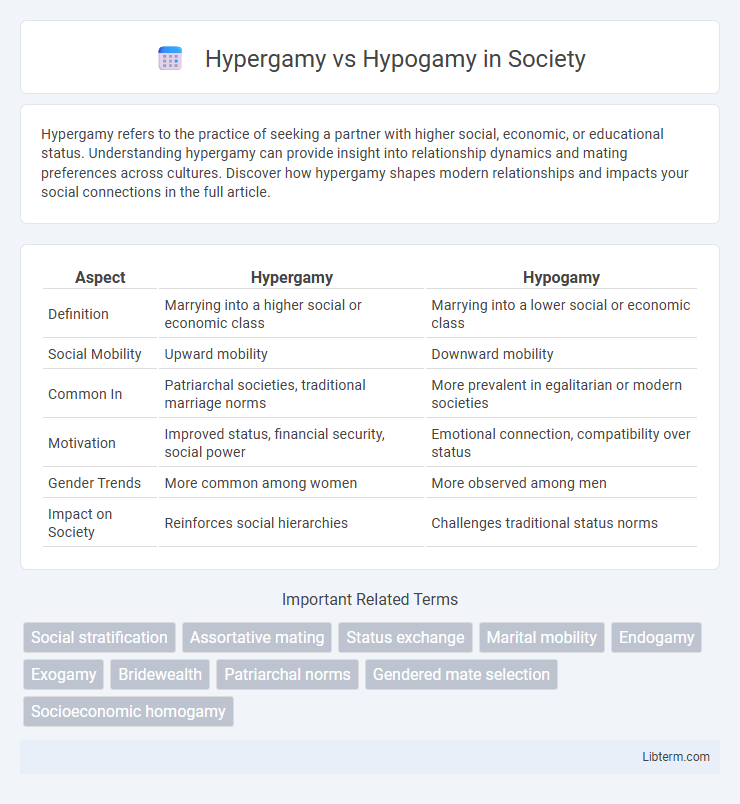
| Aspect | Hypergamy | Hypogamy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marrying into a higher social or economic class | Marrying into a lower social or economic class |
| Social Mobility | Upward mobility | Downward mobility |
| Common In | Patriarchal societies, traditional marriage norms | More prevalent in egalitarian or modern societies |
| Motivation | Improved status, financial security, social power | Emotional connection, compatibility over status |
| Gender Trends | More common among women | More observed among men |
| Impact on Society | Reinforces social hierarchies | Challenges traditional status norms |
Understanding Hypergamy and Hypogamy
Hypergamy refers to the practice of seeking a partner of higher socioeconomic status, often driven by social mobility and resource acquisition, while hypogamy involves choosing a partner with a lower status, sometimes linked to cultural or emotional factors. Understanding hypergamy and hypogamy requires analyzing their impact on relationship dynamics, mate selection, and societal structures. These concepts influence marriage patterns, gender roles, and economic disparities within various cultures.
Historical Perspectives on Mate Selection
Historical perspectives on mate selection reveal that hypergamy, the practice of marrying into a higher socioeconomic status, has been prevalent in many cultures to secure social mobility and resource access. Hypogamy, marrying into a lower status, although less common, has also occurred, often driven by personal choice or changing social norms. Anthropological studies show that these practices have been influenced by economic structures, inheritance laws, and gender roles throughout history.
Psychological Drivers Behind Hypergamy
Hypergamy, the practice of seeking a partner of higher socioeconomic status, is driven by psychological factors such as the desire for security, social prestige, and improved offspring prospects. Evolutionary psychology suggests that women may prioritize hypergamy to ensure resource access and stability, influenced by deeply ingrained survival mechanisms. This contrasts with hypogamy, where individuals partner with someone of lower status, often motivated by emotional affinity or different social factors rather than strategic resource acquisition.
The Social Roots of Hypogamy
Hypogamy, the practice of marrying someone of lower social or economic status, often stems from complex social roots including shifts in gender roles, economic independence, and changing societal norms. Economic restructuring and increased female labor force participation contribute to the rise of hypogamous unions by challenging traditional status hierarchies. Cultural acceptance and evolving values around marriage also play a critical role in the normalization of hypogamous relationships.
Cultural Variations in Partner Preferences
Hypergamy and hypogamy reveal distinct patterns in partner preferences shaped by cultural contexts, where hypergamy--marrying someone of higher social status--is prevalent in societies with rigid hierarchical structures, while hypogamy--marrying someone of lower status--appears in cultures valuing egalitarian or individualistic principles. In traditional collectivist cultures such as South Asia and parts of the Middle East, hypergamy aligns with social norms encouraging women to enhance family status through marriage, whereas Western societies exhibit more flexibility, often challenging these paradigms with increasing acceptance of hypogamous unions. Empirical studies link hypergamous trends to socioeconomic factors, dowry systems, and gender role expectations, contrasting with hypogamy's emergence in contexts prioritizing personal fulfillment and gender equality over social stratification.
Economic Influences on Relationship Choices
Economic influences significantly impact relationship choices, with hypergamy often driven by individuals seeking partners with higher socioeconomic status to improve financial stability and social standing. Conversely, hypogamy involves partnering with someone of lower economic status, which may be influenced by cultural factors or personal values rather than financial gain. Income disparity, employment opportunities, and wealth distribution shape these dynamics, underscoring economic factors as crucial determinants in mate selection patterns.
Gender Roles and Their Evolution
Hypergamy and hypogamy represent social phenomena where individuals marry into a partner with higher or lower socioeconomic status, respectively, reflecting traditional gender roles rooted in economic provision and caretaking. Shifts in gender roles, propelled by increased female education and workforce participation, have transformed these marriage patterns, challenging the classic hypergamous norm with more egalitarian and hypogamous unions. Contemporary research highlights how evolving gender norms reduce the emphasis on economic status in mate selection, promoting partnerships based on emotional compatibility and shared values rather than strict socioeconomic hierarchies.
Hypergamy vs Hypogamy in Modern Dating
Hypergamy and hypogamy influence partner selection in modern dating, where hypergamy refers to individuals seeking partners with higher socioeconomic status, while hypogamy involves choosing partners with lower status. In contemporary dating dynamics, hypergamy often shapes preferences influenced by career ambition, education, and financial stability, impacting match outcomes on dating apps and social media. Understanding these patterns helps explain shifts in relationship expectations, gender roles, and dating market behavior in today's interconnected digital landscape.
Impacts on Marriage Stability and Satisfaction
Hypergamy, the practice of marrying someone of higher socioeconomic status, often correlates with increased financial stability and improved marital satisfaction due to enhanced resource availability. Conversely, hypogamy, marrying a partner of lower socioeconomic status, may face challenges in social acceptance and resource allocation, potentially impacting marriage stability negatively. Research indicates that disparities in socioeconomic status within marriages can influence communication patterns and conflict resolution, directly affecting overall relationship satisfaction and longevity.
Future Trends in Partner Selection
Hypergamy and hypogamy, reflecting tendencies to select partners from higher or lower social or economic statuses respectively, are evolving amid shifting societal norms and economic pressures. Future trends indicate increased fluidity in partner selection criteria, driven by digital platforms that expand social networks and emphasize compatibility over traditional status factors. Economic uncertainty and cultural globalization further contribute to diverse mating patterns, reducing rigid adherence to hypergamous or hypogamous preferences.
Hypergamy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com