Ethnicity encompasses shared cultural traits, language, ancestry, and social experiences that connect individuals to distinct groups. Understanding ethnicity enhances appreciation of diversity and promotes inclusion within communities and workplaces. Explore the rest of this article to gain deeper insights into how ethnicity shapes identity and society.
Table of Comparison
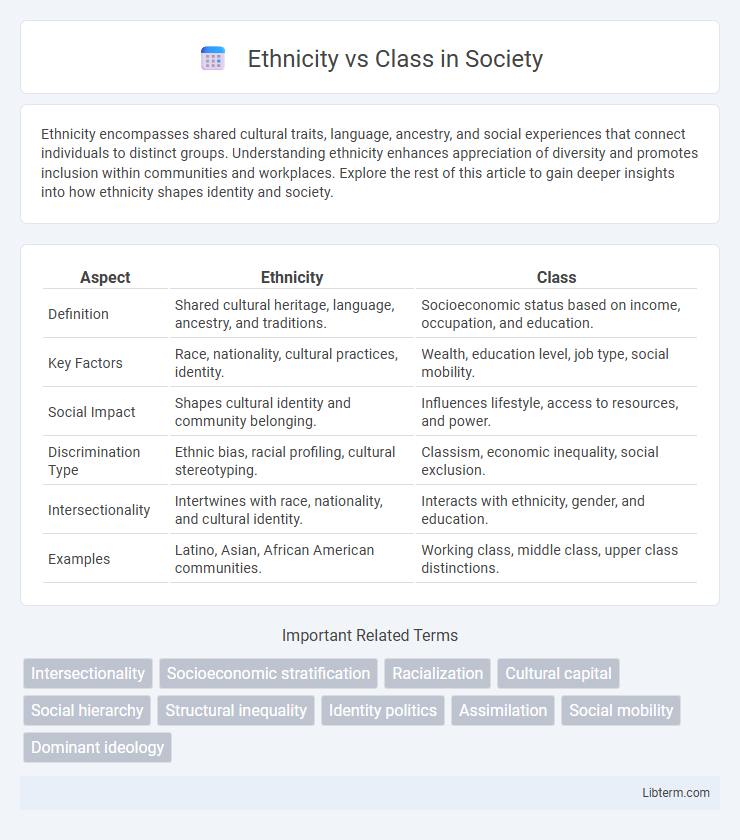
| Aspect | Ethnicity | Class |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared cultural heritage, language, ancestry, and traditions. | Socioeconomic status based on income, occupation, and education. |
| Key Factors | Race, nationality, cultural practices, identity. | Wealth, education level, job type, social mobility. |
| Social Impact | Shapes cultural identity and community belonging. | Influences lifestyle, access to resources, and power. |
| Discrimination Type | Ethnic bias, racial profiling, cultural stereotyping. | Classism, economic inequality, social exclusion. |
| Intersectionality | Intertwines with race, nationality, and cultural identity. | Interacts with ethnicity, gender, and education. |
| Examples | Latino, Asian, African American communities. | Working class, middle class, upper class distinctions. |
Introduction to Ethnicity and Class
Ethnicity refers to shared cultural traits, language, ancestry, and historical experience that distinguish groups within a society, shaping identity and social interactions. Class primarily involves socio-economic status determined by income, occupation, and education, influencing access to resources and power. Understanding the distinction and interplay between ethnicity and class is essential for analyzing social stratification and inequality in diverse societies.
Defining Ethnicity: Origins and Characteristics
Ethnicity refers to a group of people who share common cultural traits, language, ancestry, and historical experiences, distinct from race and class categorizations. Ethnic origins are often traced through shared heritage, traditions, and a collective sense of identity that shapes social interactions and community bonds. Key characteristics of ethnicity include common origin myths, distinct customs and rituals, and a shared sense of belonging within the group.
Understanding Social Class: Key Concepts
Social class is a hierarchical system that categorizes individuals based on economic status, occupation, education, and cultural capital, influencing access to resources and opportunities. Unlike ethnicity, which relates to shared cultural heritage and identity, social class primarily shapes individuals' life experiences and social mobility through wealth distribution and social networks. Key concepts in understanding social class include socioeconomic status, class stratification, and social reproduction, highlighting the persistent inequalities embedded within societal structures.
Historical Intersections of Ethnicity and Class
Historical intersections of ethnicity and class reveal how marginalized ethnic groups often faced both racial discrimination and economic exploitation, reinforcing social hierarchies. In many societies, ethnic minorities were relegated to lower socioeconomic statuses through institutionalized practices such as segregation, discriminatory labor policies, and exclusion from wealth accumulation opportunities. These intertwined dynamics shaped systemic inequalities, influencing access to education, employment, and political power across generations.
Socioeconomic Inequalities Across Ethnic Groups
Socioeconomic inequalities across ethnic groups persist due to intersecting factors such as disparities in income, education, and employment opportunities. Ethnic minorities often experience systemic barriers that limit social mobility, resulting in higher poverty rates and reduced access to quality healthcare compared to majority populations. Addressing these inequities requires targeted policies that consider both ethnic and class-based dimensions to promote inclusive economic growth and social justice.
Cultural Identity vs Economic Status
Cultural identity shapes individuals' sense of belonging through shared traditions, language, and heritage, influencing social interactions and self-perception. Economic status determines access to resources, education, and opportunities, often impacting social mobility and quality of life. Differences in ethnicity emphasize collective cultural experiences, while class highlights material conditions and economic power within society.
The Role of Policy in Shaping Ethnic and Class Dynamics
Policy decisions significantly influence ethnic and class dynamics by determining resource allocation, access to education, and employment opportunities. Affirmative action programs and housing regulations can either reduce or exacerbate disparities between ethnic groups and social classes. Institutional policies shape social mobility, reinforcing or challenging existing inequalities through their impact on socioeconomic status and ethnic identity.
Ethnicity and Class in Education and Employment
Ethnicity significantly influences educational achievement and employment opportunities, often intersecting with socioeconomic class to exacerbate disparities. Minority ethnic groups frequently face systemic barriers in access to quality education and high-paying jobs due to discrimination and limited social capital. Class further compounds these challenges, as lower-income families from ethnic minorities are less likely to afford resources that enhance academic success and career advancement, perpetuating cycles of inequality.
Case Studies: Global Perspectives on Ethnicity and Class
Case studies on ethnicity and class reveal how socio-economic disparities intersect with racial and cultural identities across different societies. Research from countries like the United States, Brazil, and South Africa highlights systemic inequalities rooted in historical contexts and institutional policies. These global perspectives emphasize the complex dynamics between ethnic marginalization and class stratification influencing access to education, employment, and social mobility.
Moving Forward: Addressing Ethnic and Class Disparities
Addressing ethnic and class disparities requires targeted policies that promote equitable access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities across diverse communities. Research indicates that systemic barriers disproportionately affect marginalized ethnic groups and lower socioeconomic classes, necessitating comprehensive reforms in social welfare, housing, and criminal justice sectors. Effective interventions include community-driven initiatives and data-driven strategies that prioritize inclusivity and economic mobility to bridge gaps in social equity.
Ethnicity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com