Government plays a crucial role in shaping public policy, regulating economies, and providing essential services to communities. Effective governance ensures transparency, accountability, and the protection of citizens' rights while promoting social and economic development. Explore the rest of this article to understand how different government systems impact your daily life and society as a whole.
Table of Comparison
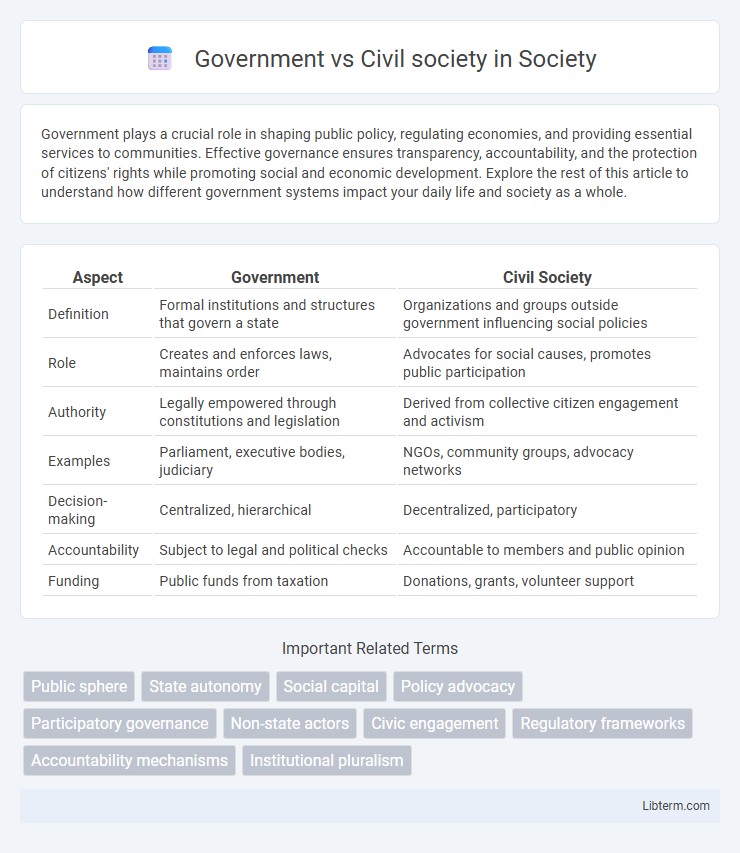
| Aspect | Government | Civil Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal institutions and structures that govern a state | Organizations and groups outside government influencing social policies |
| Role | Creates and enforces laws, maintains order | Advocates for social causes, promotes public participation |
| Authority | Legally empowered through constitutions and legislation | Derived from collective citizen engagement and activism |
| Examples | Parliament, executive bodies, judiciary | NGOs, community groups, advocacy networks |
| Decision-making | Centralized, hierarchical | Decentralized, participatory |
| Accountability | Subject to legal and political checks | Accountable to members and public opinion |
| Funding | Public funds from taxation | Donations, grants, volunteer support |
Understanding Government and Civil Society
Government refers to formal institutions and structures responsible for creating and enforcing laws, managing public resources, and providing essential services to citizens. Civil society encompasses non-governmental organizations, community groups, and individuals that advocate for social interests, promote transparency, and hold governments accountable. Understanding the distinct roles and interactions between government and civil society is crucial for fostering democratic governance and ensuring effective public participation.
Historical Evolution of Government and Civil Society
The historical evolution of government traces back to ancient civilizations where centralized authority emerged to maintain order, enforce laws, and manage resources, evolving from tribal chiefs to monarchies and eventually modern nation-states. Civil society developed alongside governments as autonomous groups, including religious organizations, guilds, and later NGOs, that represented citizens' interests and acted as a counterbalance to state power. Over time, the dynamic interaction between government institutions and civil society has shaped political systems by promoting accountability, civic participation, and social reforms.
Distinct Roles and Functions
Government operates as the formal authority responsible for creating laws, implementing policies, and maintaining public order, functioning through structured institutions such as legislatures, courts, and law enforcement agencies. Civil society comprises non-governmental organizations, community groups, advocacy organizations, and other entities that represent citizens' interests, promote social welfare, and hold governments accountable through activism and public engagement. The distinct roles involve the government providing governance and regulatory frameworks, while civil society fosters participation, ensures transparency, and drives social change from the grassroots level.
Sources of Power and Legitimacy
Governments derive power primarily from constitutional authority and legal frameworks, enabling them to enforce laws and policies through official institutions such as the judiciary and law enforcement. Civil society gains legitimacy through grassroots participation, social norms, and collective action, relying on public trust and moral influence rather than formal legal mandates. The interplay between government authority and civil society's social capital shapes the balance of power and legitimacy within a political system.
Collaboration and Conflict Dynamics
Government and civil society often engage in complex collaboration and conflict dynamics, where governments provide policy frameworks and resources while civil society drives grassroots advocacy and accountability. Collaborative efforts enhance public service delivery and democratic governance, though conflicts arise over differing priorities, power imbalances, and accountability issues. Effective interaction depends on transparent communication, mutual respect, and institutional mechanisms that balance authority and citizen participation.
Civil Society’s Role in Policy Advocacy
Civil society plays a crucial role in policy advocacy by representing diverse community interests and holding governments accountable through public participation and dialogue. Non-governmental organizations, advocacy groups, and grassroots movements mobilize citizens, influence legislation, and promote transparency and human rights. Their engagement helps shape inclusive policies that address social justice, environmental sustainability, and economic equity.
Government Regulation of Civil Society
Government regulation of civil society involves establishing legal frameworks and policies to monitor, control, or support non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community groups, and other civic entities. These regulations can include registration requirements, financial reporting, and operational restrictions aimed at ensuring transparency, accountability, and conformity with national interests. Such regulatory measures impact civil society's autonomy, influencing its capacity to advocate, mobilize resources, and participate in public policy processes effectively.
Impact on Democracy and Governance
Government and civil society both play crucial roles in shaping democracy and governance by providing checks and balances and fostering citizen participation. Governments establish laws and policies that create the institutional framework for democratic governance, while civil society organizations mobilize public opinion, promote transparency, and hold officials accountable. Strong interaction between government institutions and active civil society enhances democratic consolidation, improves policy outcomes, and deepens political legitimacy.
Challenges in Government–Civil Society Relations
Government-civil society relations often face challenges such as mistrust, lack of transparency, and limited communication channels, which hinder collaborative efforts. Power imbalances and differing priorities create tensions that delay policy implementation and reduce public participation. Addressing institutional barriers and building mutual accountability are critical for fostering effective partnerships between state actors and civil organizations.
Future Prospects for Interaction
Government and civil society increasingly leverage digital platforms to enhance collaboration, enabling more transparent and participatory governance models. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain offer potential for real-time policy feedback and decentralized decision-making processes between public institutions and citizen groups. Strengthening partnerships will depend on legal frameworks that support civic innovation while ensuring accountability and data privacy.
Government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com