Social conformity influences individual behavior by aligning actions and beliefs with group norms, often enhancing social cohesion and acceptance. This phenomenon affects decision-making, attitudes, and perceptions, shaping how you interact within various social contexts. Explore the rest of this article to understand the mechanisms behind conformity and its impact on your daily life.
Table of Comparison
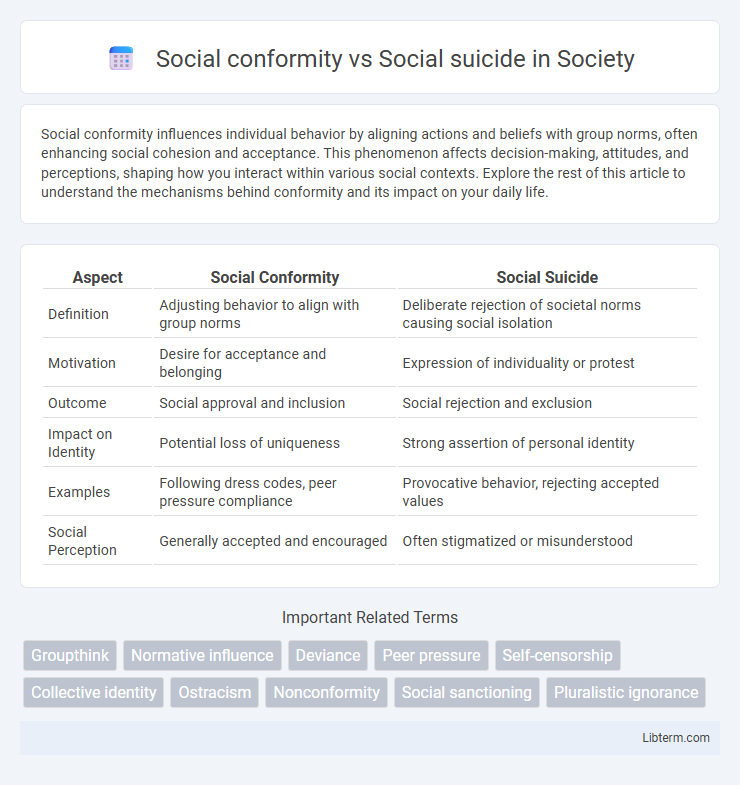
| Aspect | Social Conformity | Social Suicide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting behavior to align with group norms | Deliberate rejection of societal norms causing social isolation |
| Motivation | Desire for acceptance and belonging | Expression of individuality or protest |
| Outcome | Social approval and inclusion | Social rejection and exclusion |
| Impact on Identity | Potential loss of uniqueness | Strong assertion of personal identity |
| Examples | Following dress codes, peer pressure compliance | Provocative behavior, rejecting accepted values |
| Social Perception | Generally accepted and encouraged | Often stigmatized or misunderstood |
Understanding Social Conformity
Social conformity refers to the act of aligning one's attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors to match those of a group, driven by the desire for social acceptance or fear of rejection. Understanding social conformity involves examining psychological mechanisms such as normative influence and informational influence, which guide individuals to adapt to perceived social norms. While conformity promotes social harmony and cohesion, excessive conformity can suppress individuality and lead to negative outcomes akin to social suicide, where one sacrifices personal identity for group approval.
Defining Social Suicide
Social suicide refers to the deliberate act of rejecting social norms, expectations, and relationships to preserve personal identity, even at the cost of social isolation or ostracism. Unlike social conformity, which entails aligning behavior to group standards to gain acceptance, social suicide involves consciously choosing authenticity over social approval. This concept highlights the tension between individuality and belonging, emphasizing the psychological and social risks associated with nonconformity.
The Psychology Behind Social Conformity
Social conformity involves aligning behaviors and beliefs with group norms to gain acceptance and avoid rejection, driven by the human need for social belonging and fear of isolation. Psychological mechanisms such as normative influence and informational influence explain why individuals adopt group behaviors even when they conflict with personal values. In contrast, social suicide occurs when a person deliberately rejects societal expectations to maintain authenticity, often risking social exclusion and psychological stress.
Causes and Motivations of Social Suicide
Social suicide occurs when individuals consciously reject prevailing societal norms and expectations, motivated by a desire to assert personal identity or express dissent against perceived injustices. Causes often include deep dissatisfaction with social conformity, psychological needs for authenticity, or the pursuit of values conflicting with mainstream culture. The motivation behind social suicide reflects a strategic sacrifice of social acceptance to uphold integrity, promote change, or resist oppressive structures.
Social Pressures and Group Dynamics
Social conformity involves adapting behaviors and beliefs to align with group norms due to social pressures, often driven by the desire for acceptance and fear of rejection. Group dynamics intensify this effect as individuals navigate complex interactions, influence patterns, and hierarchical structures that reinforce conformity. In contrast, social suicide occurs when individuals resist normative expectations so drastically that they face ostracism, highlighting the powerful role of social sanctions in maintaining group cohesion.
Consequences of Conforming vs. Non-Conforming
Conforming to social norms often leads to acceptance, stability, and reduced social friction, but may suppress individuality and critical thinking. Non-conforming behaviors can result in social isolation, stigmatization, or "social suicide," where individuals risk losing relationships and status. The consequences of conforming versus non-conforming hinge on the balance between social cohesion and personal authenticity.
Benefits and Risks of Social Conformity
Social conformity promotes group cohesion and facilitates smooth social interactions by encouraging individuals to adopt shared norms and behaviors, enhancing cooperation and social acceptance. However, excessive conformity risks suppression of individuality, critical thinking, and innovation, potentially leading to social stagnation and psychological distress. Balancing conformity benefits with personal authenticity is crucial for maintaining healthy social dynamics and individual well-being.
Recognizing Signs of Social Suicide
Recognizing signs of social suicide involves identifying behaviors where individuals consistently reject social norms, isolate themselves from support networks, and engage in self-sabotaging actions that harm their relationships and reputations. Patterns such as abrupt withdrawal from social activities, persistent rejection of advice from trusted peers, and public defiance of culturally accepted values signal a shift from healthy social conformity toward social self-destruction. Awareness of these indicators is crucial for timely intervention to restore social bonds and prevent long-term isolation.
Strategies to Navigate Social Expectations
Navigating social expectations requires strategic balance between social conformity and social suicide. Employing adaptive conformity involves selectively aligning with group norms to foster acceptance while preserving personal values to avoid alienation. Critical self-awareness and setting clear boundaries empower individuals to maintain authentic identity without sacrificing social integration.
Building Authenticity Amidst Social Pressure
Building authenticity amidst social pressure requires resisting social conformity that demands abandoning personal values to fit in, which can lead to social suicide by eroding self-identity and mental well-being. Embracing genuine beliefs and expressing unique perspectives fosters resilience and meaningful connections, countering the negative effects of societal expectations. Prioritizing authenticity enhances psychological health and empowers individuals to thrive despite external pressures.
Social conformity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com