Border enforcement plays a crucial role in national security by regulating and monitoring the movement of people and goods across borders. Effective strategies include advanced surveillance technologies, well-trained personnel, and comprehensive policies to prevent illegal activities while facilitating legitimate travel and trade. Explore this article to understand how border enforcement impacts your safety and economic well-being.
Table of Comparison
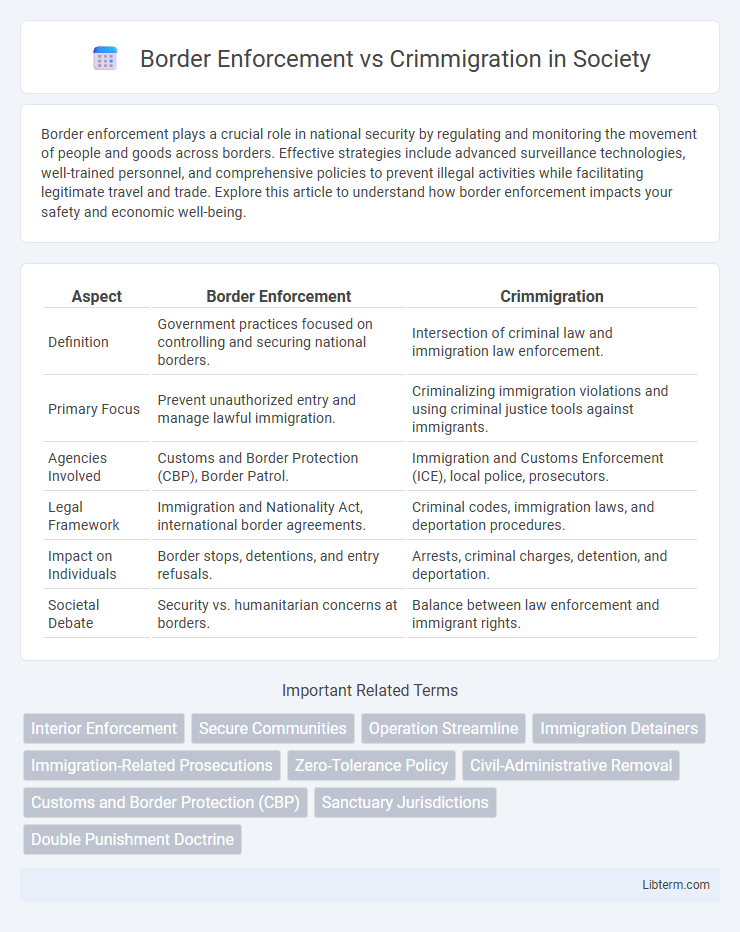
| Aspect | Border Enforcement | Crimmigration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government practices focused on controlling and securing national borders. | Intersection of criminal law and immigration law enforcement. |
| Primary Focus | Prevent unauthorized entry and manage lawful immigration. | Criminalizing immigration violations and using criminal justice tools against immigrants. |
| Agencies Involved | Customs and Border Protection (CBP), Border Patrol. | Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), local police, prosecutors. |
| Legal Framework | Immigration and Nationality Act, international border agreements. | Criminal codes, immigration laws, and deportation procedures. |
| Impact on Individuals | Border stops, detentions, and entry refusals. | Arrests, criminal charges, detention, and deportation. |
| Societal Debate | Security vs. humanitarian concerns at borders. | Balance between law enforcement and immigrant rights. |
Understanding Border Enforcement: Definitions and Objectives
Border enforcement refers to the range of strategies and operations employed by government agencies to regulate and control the movement of people and goods across national borders. Its primary objectives include preventing illegal entry, enhancing national security, and facilitating lawful trade and travel. Understanding border enforcement requires examining policies such as surveillance technologies, border patrol deployment, and international cooperation efforts designed to maintain sovereign territorial integrity.
Crimmigration: The Merging of Criminal and Immigration Law
Crimmigration refers to the convergence of criminal law and immigration enforcement, resulting in increased criminalization of immigration violations. This fusion has led to stricter border enforcement policies and harsher penalties for migrants, often treating immigration offenses as criminal acts rather than civil infractions. The growing overlap challenges traditional legal distinctions, raising concerns about due process, human rights, and the disproportionate impact on marginalized communities.
Historical Context: Evolution of U.S. Border Policies
U.S. border enforcement policies have evolved significantly since the early 20th century, initially emphasizing immigration control through the Immigration Act of 1924, which established national origin quotas restricting certain groups. The 1986 Immigration Reform and Control Act marked a turning point by introducing employer sanctions and increasing border patrol efforts amid rising unauthorized migration. In recent decades, the intersection of border enforcement and crimmigration--where criminal law enforcement overlaps with immigration control--has expanded through policies like the 1996 Illegal Immigration Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act, intensifying deportations and linking immigration violations with criminal offenses.
Key Legal Frameworks: Comparing Border Enforcement and Crimmigration
Key legal frameworks in border enforcement primarily involve the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) and customs regulations that govern the physical control and inspection of borders. Crimmigration merges criminal law with immigration law, relying heavily on statutes such as the INA's removal grounds, the Illegal Immigration Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act (IIRIRA), and criminal codes that define offenses leading to deportation. The contrasting frameworks highlight border enforcement's preventive focus versus crimmigration's post-entry enforcement through criminal prosecution and removal processes.
Impact on Migrants: Rights, Detention, and Due Process
Border enforcement policies often result in heightened migrant detention rates, frequently limiting access to fundamental rights such as legal representation and fair hearings. Crimmigration, the intersection of criminal law and immigration enforcement, exacerbates these challenges by criminalizing immigration violations, leading to prolonged detention and increased risk of deportation without due process. Migrants face significant barriers to judicial protections, resulting in violations of constitutional rights and undermining access to humanitarian protections and asylum claims.
The Role of Law Enforcement Agencies in Border Control
Law enforcement agencies play a central role in border enforcement by implementing immigration laws, conducting surveillance, and intercepting unauthorized crossings. Agencies such as U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) coordinate efforts to secure borders and manage immigration-related criminal activities. The growing overlap between immigration enforcement and traditional criminal law, known as crimmigration, highlights the expanded responsibilities of these agencies in maintaining national security and public safety.
Policy Shifts: From Border Security to Crimmigration Practices
Policy shifts in U.S. immigration enforcement have evolved from traditional border security measures to encompassing crimmigration practices that merge immigration control with criminal justice systems. This transition emphasizes the detention and deportation of noncitizens through punitive measures, increasing collaboration between immigration authorities and local law enforcement under programs like Secure Communities. The paradigm reflects a strategic focus on interior enforcement, prioritizing the removal of individuals based on criminal convictions and expanding the scope of immigration violations as criminal offenses.
Societal Implications: Communities, Profiling, and Public Perception
Border enforcement policies deeply impact communities by often targeting marginalized groups, leading to increased racial profiling and strained public trust in law enforcement. The intersection of criminal law and immigration (crimmigration) amplifies social stigmatization, causing fear and alienation within immigrant populations. Public perception is shaped by media portrayal and government rhetoric, which can either exacerbate xenophobia or foster understanding and inclusive policy reform.
Comparing Outcomes: Effectiveness and Consequences
Border enforcement strategies prioritize preventing unauthorized entry through physical barriers, surveillance technology, and patrol deployments, resulting in immediate but often temporary deterrence. Crimmigration policies integrate immigration control with criminal law enforcement, leading to increased detention and deportation rates but raising concerns about civil rights violations and long-term social consequences. Effectiveness in border enforcement tends to reduce crossings temporarily, while crimmigration's broader scope impacts immigrant communities through heightened legal risks and systemic inequalities.
Future Directions: Reform, Advocacy, and Policy Recommendations
Future directions in border enforcement and crimmigration emphasize comprehensive reform aimed at balancing security with human rights protections. Policy recommendations advocate for eliminating mandatory detention, expanding legal pathways for migration, and increasing oversight to prevent racial profiling and abuses of power. Advocacy efforts focus on community-based alternatives to enforcement, promoting transparency and accountability in immigration agencies to foster more equitable and just immigration systems.
Border Enforcement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com