Plurality refers to a voting system where the candidate with the most votes wins, even if they do not achieve an absolute majority. This method is commonly used in various elections but can sometimes lead to outcomes where the winner lacks broad support. Discover how plurality impacts democratic processes and elections in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
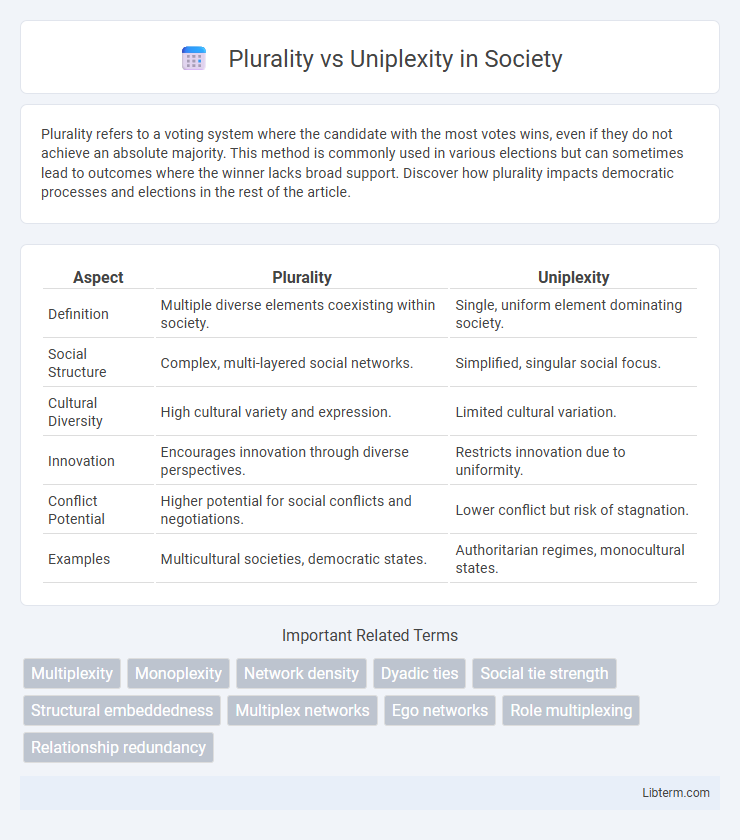
| Aspect | Plurality | Uniplexity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple diverse elements coexisting within society. | Single, uniform element dominating society. |
| Social Structure | Complex, multi-layered social networks. | Simplified, singular social focus. |
| Cultural Diversity | High cultural variety and expression. | Limited cultural variation. |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation through diverse perspectives. | Restricts innovation due to uniformity. |
| Conflict Potential | Higher potential for social conflicts and negotiations. | Lower conflict but risk of stagnation. |
| Examples | Multicultural societies, democratic states. | Authoritarian regimes, monocultural states. |
Understanding Plurality and Uniplexity
Understanding plurality involves recognizing multiple independent relationships or connections between entities within a network or system, highlighting complex and diverse interactions. Uniplexity refers to a simpler structure where entities are connected by a single type of relationship, emphasizing clarity and specificity in connections. Analyzing these concepts aids in mapping social networks, organizational structures, and communication patterns with varying degrees of complexity and diversity.
Historical Origins of Plurality and Uniplexity
The historical origins of plurality and uniplexity trace back to early sociological and network theory studies, where plurality emerged as a concept describing multiple, overlapping social ties or affiliations within communities. Uniplexity, contrastingly, originated from the analysis of single, exclusive types of relationships, often studied in traditional family or close-knit group contexts. These foundational distinctions laid the groundwork for understanding complex social networks and the multifaceted nature of human interactions.
Key Differences Between Plurality and Uniplexity
Plurality involves multiple entities or factors interacting simultaneously, creating complex relationships, whereas uniplexity centers on a single entity or factor operating independently. In social network analysis, plurality reflects multiplex ties where individuals share various types of connections, while uniplexity pertains to single-type ties within a network. Understanding these key differences is essential for analyzing multilayered social interactions versus simpler, singular relationships.
Plurality in Social Networks
Plurality in social networks refers to the presence of multiple, diverse connections and interactions across various social groups, enhancing network resilience and information flow. It fosters complex relational structures where individuals belong to overlapping social circles, promoting access to broader resources and perspectives compared to uniplex networks with single-type ties. Research shows plurality increases social capital by enabling multiplex ties and stronger community integration within platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
Uniplexity in Relationship Structures
Uniplexity in relationship structures refers to the presence of a single type of social tie linking individuals, such as only friendship or only work connections, which simplifies the analysis of social networks. This concept contrasts with plurality, where multiple relationship types coexist, creating complex, multiplex networks that require multifaceted examination. Understanding uniplex ties helps clarify influence patterns, resource flows, and social support dynamics within specific relational contexts, providing a foundation for studying more intricate social systems.
Advantages of Plurality Systems
Plurality systems offer the advantage of simplicity, making voting easy to understand and quick to execute, which encourages higher voter participation. They tend to produce decisive outcomes and often lead to stable governments by favoring the dominance of major parties. This system also reduces the likelihood of political fragmentation, supporting clear accountability and governance.
Challenges of Uniplexity in Modern Contexts
Uniplexity, characterized by single-layered social connections, presents significant challenges in modern contexts due to its limited diversity and resilience compared to plurality networks. The lack of multiplex ties can hinder effective communication, reduce access to varied resources, and weaken social support systems, making individuals and organizations more vulnerable to disruptions. Modern complex environments demand adaptive and multifaceted interactions that uniplex structures often fail to provide, leading to inefficiencies in collaboration and innovation.
Plurality vs Uniplexity in Organizational Settings
Plurality in organizational settings refers to the presence of multiple perspectives, values, and identities within a single entity, fostering diversity and dynamic interaction among stakeholders. Uniplexity, by contrast, emphasizes hierarchical, single-identity structures prioritizing uniformity and centralized decision-making. Organizations embracing plurality often demonstrate enhanced adaptability and innovation due to their inclusive approach to problem-solving and stakeholder engagement.
Impact of Plurality and Uniplexity on Communication
Plurality enhances communication by introducing diverse perspectives and multiple channels, fostering innovation and broader understanding across networks. Uniplexity, often characterized by single-tie relationships, tends to limit information flow and restricts the depth of communication to specific contexts or topics. The impact of plurality versus uniplexity significantly influences the robustness and adaptability of communication networks, affecting collaboration and knowledge sharing outcomes.
Future Trends: Evolving Dynamics of Plurality and Uniplexity
Future trends in plurality and uniplexity indicate a shift towards more integrated and hybrid communication networks, driven by advancements in digital technologies and social media platforms. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning enhances the ability to manage multiple simultaneous social interactions while maintaining uniplex connections for specialized, context-specific communication. Emerging dynamics suggest that evolving societal structures and technological innovations will increasingly blend plurality's diverse interactions with uniplexity's focused relational ties, optimizing both reach and depth in social exchanges.
Plurality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com