Mainstream culture shapes societal norms, values, and trends that influence everyday life and collective behavior. It impacts entertainment, fashion, language, and social interactions, reflecting the dominant ideas embraced by the majority. Explore how mainstream culture affects your world and discover its nuances in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
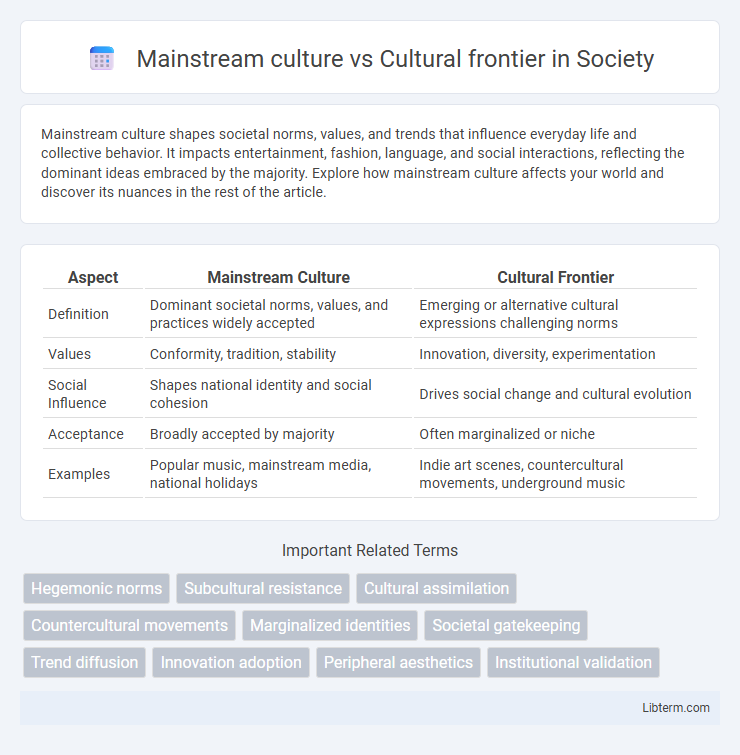
| Aspect | Mainstream Culture | Cultural Frontier |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dominant societal norms, values, and practices widely accepted | Emerging or alternative cultural expressions challenging norms |
| Values | Conformity, tradition, stability | Innovation, diversity, experimentation |
| Social Influence | Shapes national identity and social cohesion | Drives social change and cultural evolution |
| Acceptance | Broadly accepted by majority | Often marginalized or niche |
| Examples | Popular music, mainstream media, national holidays | Indie art scenes, countercultural movements, underground music |
Defining Mainstream Culture and Cultural Frontier
Mainstream culture represents the dominant set of values, norms, and practices widely accepted and practiced by the majority within a society. Cultural frontier refers to the dynamic boundary where mainstream culture interacts with, adapts, or resists alternative lifestyles, subcultures, or emerging social movements. Defining these concepts highlights the tension between conformity and innovation, shaping societal evolution and identity formation.
Historical Evolution of Mainstream and Frontier Cultures
Mainstream culture has historically evolved through dominant societal norms, political institutions, and widespread economic practices that shape collective identity and values. Cultural frontiers emerge at the margins or contact zones, often involving indigenous, immigrant, or subaltern groups whose practices challenge or diversify mainstream narratives. Over time, interaction between mainstream and frontier cultures drives cultural innovation, hybridization, and social change, reflecting dynamics of power, resistance, and adaptation.
Key Characteristics: Mainstream vs. Cultural Frontier
Mainstream culture is characterized by widely accepted norms, values, and practices that dominate a society, promoting uniformity and social cohesion. Cultural frontier represents boundary areas where differing cultural groups interact, often marked by hybrid identities, innovation, and tension between preservation and change. Key differences include mainstream culture's emphasis on conformity versus the cultural frontier's role as a space for cultural negotiation and transformation.
How Mainstream Culture Shapes Societal Norms
Mainstream culture plays a pivotal role in shaping societal norms by establishing widely accepted values, behaviors, and traditions that influence public opinion and social expectations. This dominant cultural framework acts as a reference point for acceptable conduct, often marginalizing or challenging alternative perspectives found at the cultural frontier. Through mass media, education systems, and popular institutions, mainstream culture perpetuates norms that guide interpersonal interactions and community practices.
The Role of Cultural Frontiers in Social Innovation
Cultural frontiers serve as crucial incubators for social innovation by challenging mainstream culture's norms and introducing novel ideas, values, and practices that drive societal progress. These frontiers often emerge from marginalized or hybrid communities where diverse perspectives foster creativity and transformative solutions. The dynamic interaction between mainstream culture and cultural frontiers enables the diffusion of innovative social models, reshaping cultural landscapes and promoting inclusive development.
Challenges Faced by Cultural Pioneers
Cultural pioneers face significant challenges such as social resistance, marginalization, and limited access to resources while pushing the boundaries of mainstream culture. Their innovative ideas and practices often clash with established norms, leading to misunderstandings and slow acceptance. Overcoming these obstacles requires resilience and strategic adaptation to gradually influence broader societal values and trends.
Media Influence: Mainstream Adoption vs. Fringe Resistance
Media influence plays a pivotal role in shaping mainstream culture by amplifying widely accepted norms, values, and trends through dominant platforms like television, social media, and major news outlets. In contrast, cultural frontiers often resist this homogenization by maintaining alternative narratives, using niche channels, independent media, and grassroots movements to preserve distinct identities and challenge mainstream perspectives. The dynamic tension between mainstream adoption and fringe resistance influences cultural evolution, driving both widespread social cohesion and diverse subcultural innovation.
Cultural Appropriation and Authenticity Debates
Mainstream culture often absorbs elements from cultural frontiers, sparking heated debates on cultural appropriation and authenticity as marginalized groups seek to protect their heritage from commodification. Cultural appropriation occurs when dominant groups adopt symbols or practices without understanding or respecting their original context, leading to accusations of exploitation and misrepresentation. Authenticity debates center on who has the right to represent or adapt cultural expressions, highlighting tensions between preserving tradition and allowing cultural evolution.
The Future of Mainstream Culture and Emerging Frontiers
The future of mainstream culture is increasingly shaped by digital innovation, global connectivity, and evolving social values that drive widespread adoption of diverse ideas and trends. Emerging cultural frontiers, characterized by niche subcultures and avant-garde movements, challenge traditional norms and push the boundaries of creativity and identity. The dynamic interaction between mainstream culture and these cultural frontiers fosters a continuous cycle of transformation and integration in societal norms and collective experiences.
Bridging the Gap: Dialogue Between Mainstream and Margins
Bridging the gap between mainstream culture and cultural frontiers involves fostering open dialogue that respects and integrates marginalized voices, enhancing mutual understanding and cultural enrichment. Effective communication strategies emphasize inclusivity and cultural exchange, allowing mainstream narratives to evolve while empowering peripheral communities. This dynamic interplay promotes social cohesion and challenges dominant cultural paradigms by acknowledging diverse identities and experiences.
Mainstream culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com