Compliance ensures that businesses adhere to laws, regulations, and industry standards, minimizing risks and avoiding costly penalties. Effective compliance programs foster a culture of integrity, protect company reputation, and enhance operational efficiency. Discover how you can implement robust compliance strategies to safeguard your organization by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
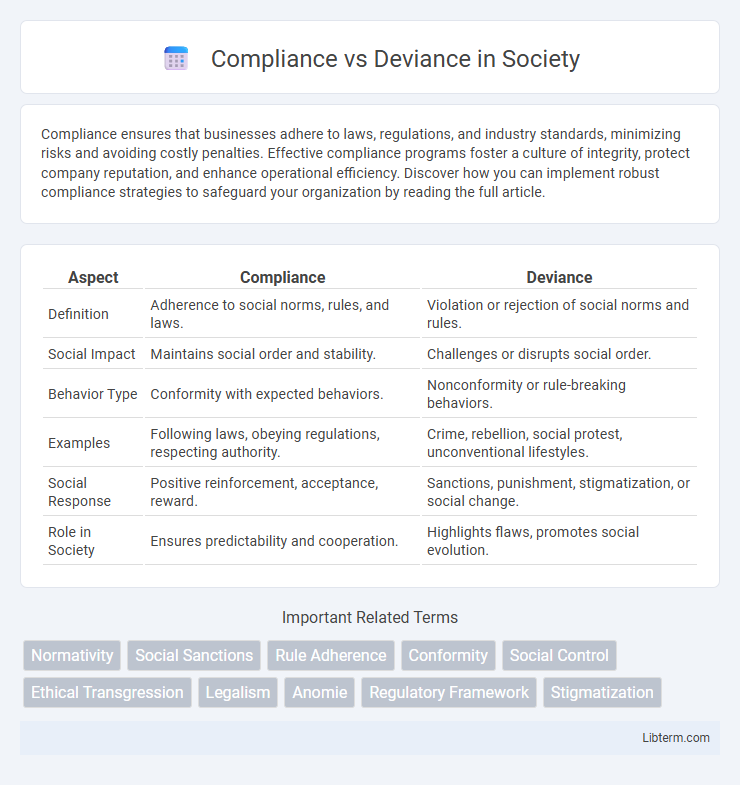
| Aspect | Compliance | Deviance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to social norms, rules, and laws. | Violation or rejection of social norms and rules. |
| Social Impact | Maintains social order and stability. | Challenges or disrupts social order. |
| Behavior Type | Conformity with expected behaviors. | Nonconformity or rule-breaking behaviors. |
| Examples | Following laws, obeying regulations, respecting authority. | Crime, rebellion, social protest, unconventional lifestyles. |
| Social Response | Positive reinforcement, acceptance, reward. | Sanctions, punishment, stigmatization, or social change. |
| Role in Society | Ensures predictability and cooperation. | Highlights flaws, promotes social evolution. |
Understanding Compliance and Deviance
Compliance involves adhering to established social norms, laws, or rules, reflecting conformity within a societal framework. Deviance represents actions or behaviors that violate these norms, often prompting social sanctions or corrective measures. Understanding compliance and deviance requires analyzing the motivations behind conformity and rule-breaking, their impacts on social order, and the mechanisms that regulate behavior in various cultural contexts.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Deviance
Compliance involves adhering to established rules, social norms, or laws, often motivated by external sanctions or the desire for social acceptance. Deviance refers to behaviors or actions that violate societal expectations or norms, eliciting negative reactions or punishments from the community. The key difference lies in compliance's alignment with social standards, while deviance signifies deviation from accepted norms, impacting social order and cohesion.
Theoretical Perspectives on Social Behavior
Compliance and deviance are fundamental concepts in sociological theories analyzing social behavior. Structural functionalism views compliance as essential for social order and deviance as a mechanism that challenges norms, prompting social change. Symbolic interactionism explores how individuals internalize norms through socialization, with deviance arising from differential labeling and interpretation within social contexts.
Factors Influencing Compliance
Factors influencing compliance include social norms, authority presence, and perceived consequences of actions. Psychological elements such as motivation, peer pressure, and individual belief systems also significantly affect adherence to rules. Environmental contexts and cultural values further shape the likelihood of conforming to established guidelines or engaging in deviant behavior.
Causes and Motivations of Deviance
Deviance arises from complex social, psychological, and economic factors including strain theory, which links deviance to the pressure individuals feel to achieve socially accepted goals without access to legitimate means. Motivations for deviance often stem from the desire for social acceptance, rebellion against norms, or coping with marginalization and inequality. These causes highlight the dynamic interaction between individual choices and structural constraints influencing non-conforming behavior.
The Role of Social Norms
Social norms serve as unwritten rules that guide individual behavior within a society, promoting compliance by establishing expectations for acceptable conduct. Deviance occurs when individuals violate these norms, challenging the social order and often triggering sanctions or corrective measures. The dynamic interplay between compliance and deviance highlights the influence of social norms in maintaining group cohesion and defining the boundaries of acceptable behavior.
Consequences of Compliance and Deviance
Compliance with organizational policies results in positive outcomes such as reward recognition, career advancement, and enhanced workplace harmony. Deviance, including rule-breaking or unethical behavior, leads to consequences like disciplinary action, loss of trust, and potential legal repercussions. The contrasting outcomes emphasize the importance of adherence to norms for maintaining both individual and organizational integrity.
Compliance, Deviance, and Organizational Culture
Compliance involves adherence to established rules, policies, and standards within an organization, ensuring consistent behavior aligned with organizational goals. Deviance represents actions that violate these norms, potentially disrupting organizational culture and undermining performance. A strong organizational culture fosters compliance by promoting shared values, clear communication, and accountability, which collectively reduce the likelihood of deviant behaviors.
Managing Deviant Behavior in Society
Managing deviant behavior in society involves establishing clear norms and enforcing consistent consequences to deter actions that violate social standards. Effective strategies include community-based interventions, rehabilitative programs, and restorative justice practices designed to realign individuals with societal expectations. Continuous monitoring and adaptive policy frameworks help balance social order while addressing the root causes of deviance.
Striking a Balance: Encouraging Compliance, Addressing Deviance
Striking a balance between compliance and deviance requires fostering a culture that motivates adherence to rules while effectively identifying and addressing deviations through clear policies and consistent enforcement. Encouraging compliance involves transparent communication of expectations and positive reinforcement, which reduces resistance and promotes ethical behavior. Addressing deviance promptly minimizes risks, deters future misconduct, and maintains organizational integrity.
Compliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com