Legal kinship establishes recognized family relationships through laws governing marriage, adoption, and guardianship, which grant individuals specific rights and responsibilities. These connections affect inheritance, custody, and decision-making authority in various legal contexts. Explore the article to understand how legal kinship impacts your rights and familial bonds.
Table of Comparison
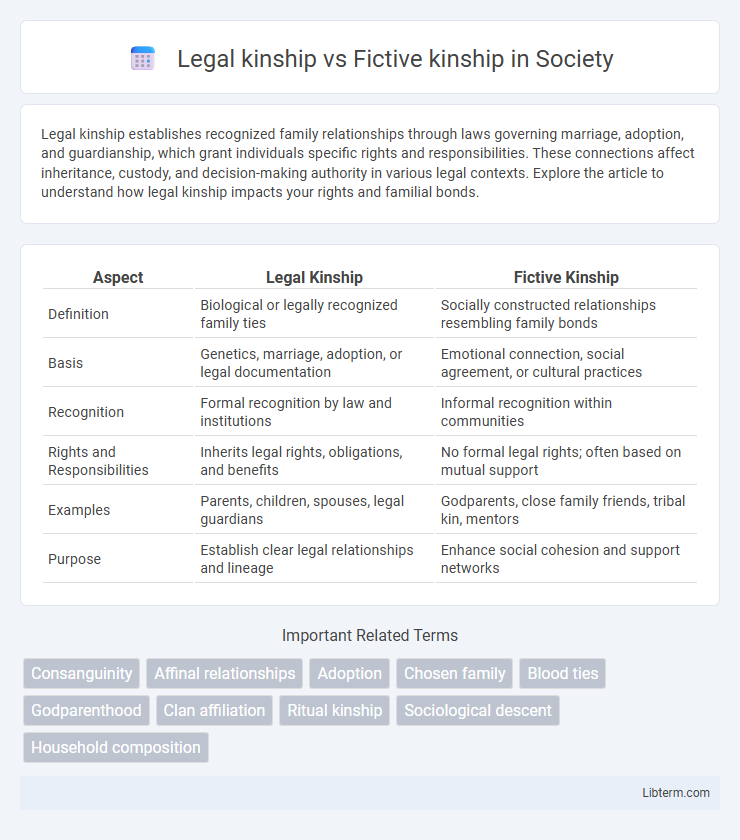
| Aspect | Legal Kinship | Fictive Kinship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological or legally recognized family ties | Socially constructed relationships resembling family bonds |
| Basis | Genetics, marriage, adoption, or legal documentation | Emotional connection, social agreement, or cultural practices |
| Recognition | Formal recognition by law and institutions | Informal recognition within communities |
| Rights and Responsibilities | Inherits legal rights, obligations, and benefits | No formal legal rights; often based on mutual support |
| Examples | Parents, children, spouses, legal guardians | Godparents, close family friends, tribal kin, mentors |
| Purpose | Establish clear legal relationships and lineage | Enhance social cohesion and support networks |
Understanding Legal Kinship: Definition and Foundations
Legal kinship refers to familial relationships recognized and established by law, including blood relations, marriage, and adoption, which determine rights and responsibilities such as inheritance, custody, and support. These relationships are grounded in legal statutes and formal documentation like birth certificates, marriage licenses, and adoption records, providing a clear framework for social and legal obligations. Understanding legal kinship is essential for navigating the family law system, ensuring rightful claims and protections within society.
Exploring Fictive Kinship: Meaning and Cultural Significance
Fictive kinship refers to social bonds that imitate family relationships but lack biological or legal ties, often found in communities where chosen families provide emotional support and cultural continuity. This type of kinship is significant in cultures that value extended support networks beyond traditional bloodlines, helping individuals navigate social, economic, and emotional challenges. Unlike legal kinship, which is established through formal recognition like marriage or adoption, fictive kinship emphasizes voluntary, culturally meaningful connections that shape identity and belonging.
Historical Origins of Legal and Fictive Kinship
Legal kinship traces its origins to ancient codified laws and formal social contracts that defined family relationships for inheritance, property rights, and social order, rooted in civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Roman law. Fictive kinship, by contrast, emerges from cultural and social practices where bonds resemble family ties but lack legal recognition, historically prevalent in indigenous societies and communal groups that emphasize social obligations and mutual support. These dual systems reflect diverse approaches to kinship: one institutionalized through law, the other embedded in social customs and collective identity.
Key Differences Between Legal and Fictive Kinship
Legal kinship refers to relationships recognized by law, such as those established through birth, marriage, or adoption, granting specific rights and responsibilities. Fictive kinship encompasses socially constructed bonds that mimic family ties without legal sanction, often formed through friendship, mentorship, or community connections. The key difference lies in legal kinship's formal status with enforceable obligations, while fictive kinship depends on emotional and social recognition without legal authority.
Examples of Legal Kinship Across Cultures
Legal kinship is formally recognized by laws and institutions, such as marriage, adoption, and blood relations exemplified by civil marriage in the United States, adoption laws in Japan, and inheritance rights in India. Fictive kinship refers to social ties and bonds formed through friendship, mentorship, or community roles without biological or legal connections, commonly observed in African American communities with godparent relationships and among Indigenous Australian kinship systems. These distinctions highlight how legal kinship governs family rights and obligations, whereas fictive kinship enhances social support and cultural identity.
Forms and Functions of Fictive Kinship Globally
Fictive kinship encompasses socially recognized relationships that are not based on blood or legal ties, such as godparents, close family friends, or community elders acting as surrogate family members, fulfilling essential social and emotional support roles globally. These forms often serve functions like resource sharing, childcare, socialization, and strengthening community bonds, especially in cultures with extended family systems or those affected by migration and displacement. Unlike legal kinship, which is defined by formal laws and documentation regarding inheritance, custody, and marriage, fictive kinship operates through cultural practices and mutual recognition, influencing social structure and individual identity worldwide.
The Role of Law in Establishing Kinship Ties
Legal kinship is established through formal laws and regulations that define family relationships for purposes such as inheritance, custody, and rights. Fictive kinship, by contrast, involves social bonds and roles recognized culturally or personally without legal sanction. The role of law in establishing kinship ties solidifies biological or legally recognized relationships, ensuring rights and responsibilities are enforceable in society.
Social Implications of Fictive Kinship Relationships
Fictive kinship relationships, unlike legal kinship based on blood or marriage, are socially constructed bonds that provide emotional support, resource sharing, and community integration. These relationships often fill gaps left by traditional kinship systems, strengthening social networks and resilience in marginalized or displaced groups. The social implications include enhanced collective identity, mutual caregiving responsibilities, and expanded social capital beyond biological ties.
Legal Kinship vs Fictive Kinship in Modern Society
Legal kinship establishes relationships recognized by law through blood, marriage, or adoption, ensuring rights and responsibilities such as inheritance, custody, and healthcare decisions. Fictive kinship involves emotionally significant bonds resembling family ties without legal recognition, often serving as essential support networks in modern society, especially for marginalized or non-traditional families. In contemporary social structures, both legal and fictive kinships play vital roles in shaping identity, social support, and community belonging.
Impact on Identity and Inheritance Rights
Legal kinship establishes identity and inheritance rights through formal recognition by law, defining clear familial relationships such as parent-child or spouse, which directly impact legal claims to property and social status. Fictive kinship, based on social bonds and chosen affiliations rather than biology or legal ties, influences personal identity and support networks but generally lacks formal inheritance rights unless specifically granted through legal mechanisms like wills or trusts. The distinction shapes individuals' access to resources and social belonging, affecting the dynamics of family identity and the distribution of wealth.
Legal kinship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com