Legal sanctions impose penalties or restrictions to enforce laws and ensure compliance with regulations. They serve as deterrents against unlawful behavior, ranging from fines and community service to imprisonment and license revocations. Explore the rest of the article to understand the types of sanctions and how they might affect your rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
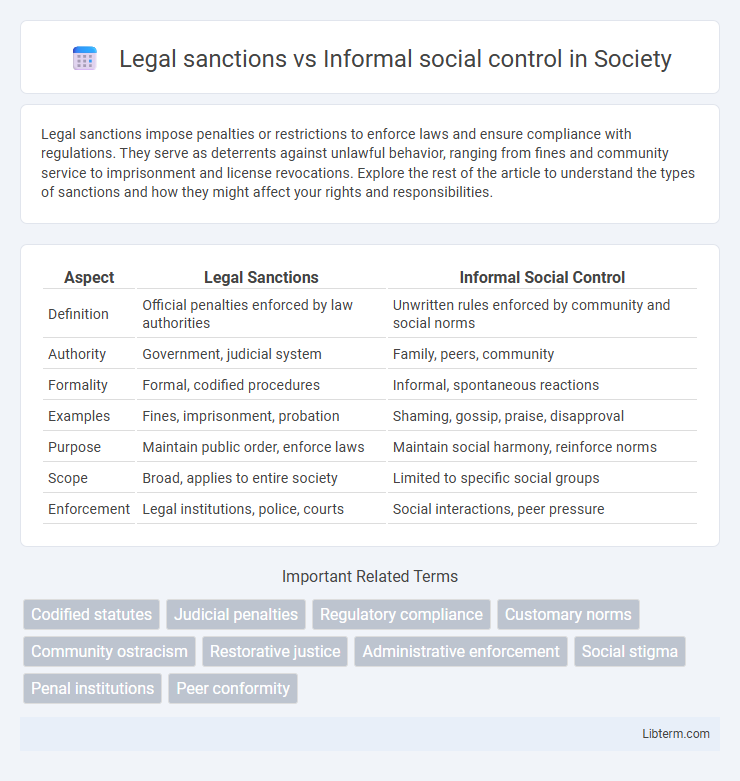
| Aspect | Legal Sanctions | Informal Social Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official penalties enforced by law authorities | Unwritten rules enforced by community and social norms |
| Authority | Government, judicial system | Family, peers, community |
| Formality | Formal, codified procedures | Informal, spontaneous reactions |
| Examples | Fines, imprisonment, probation | Shaming, gossip, praise, disapproval |
| Purpose | Maintain public order, enforce laws | Maintain social harmony, reinforce norms |
| Scope | Broad, applies to entire society | Limited to specific social groups |
| Enforcement | Legal institutions, police, courts | Social interactions, peer pressure |
Understanding Legal Sanctions: Definition and Purpose
Legal sanctions are formal penalties imposed by authorized institutions to enforce laws and ensure compliance, often including fines, imprisonment, or community service. Their primary purpose is to maintain social order by deterring unlawful behavior and punishing offenders through a structured judicial process. Unlike informal social control, which relies on societal norms and peer pressure, legal sanctions provide clear, codified consequences sanctioned by the state.
Informal Social Control: Meaning and Mechanisms
Informal social control refers to the unwritten, socially shared norms and expectations that regulate individual behavior within a community without relying on formal legal systems. Mechanisms include peer pressure, family influence, community sanctions like gossip or ostracism, and cultural traditions that reinforce conformity. These controls operate through socialization processes, promoting social order and discouraging deviance by leveraging social relationships and collective values.
Key Differences Between Legal Sanctions and Informal Control
Legal sanctions are formal penalties imposed by authorized entities such as courts or law enforcement agencies to enforce laws and maintain social order, often involving fines, imprisonment, or other legal punishments. Informal social control operates through unwritten rules and social norms maintained by family, peers, and community members, relying on mechanisms like social approval, ridicule, or ostracism to influence behavior. The key differences lie in the formal authority, codification of rules, and official enforcement methods in legal sanctions versus the socially driven, culturally embedded, and interpersonal nature of informal social control.
The Role of Law Enforcement in Legal Sanctions
Law enforcement agencies play a critical role in implementing legal sanctions by investigating crimes, apprehending offenders, and ensuring compliance with legal standards. Their authority to impose penalties such as fines, arrests, and prosecutions distinguishes legal sanctions from informal social control mechanisms like peer pressure or community disapproval. Effective law enforcement reinforces societal norms by providing formal consequences that deter criminal behavior and promote public safety.
Social Norms and Community Influence in Informal Control
Legal sanctions are formal mechanisms enforced by judicial systems to regulate behavior through penalties, whereas informal social control relies on social norms and community influence to guide individuals' conduct without official intervention. Social norms, deeply embedded within communities, shape informal control by promoting conformity through expectations, peer pressure, and communal approval or disapproval. Community influence reinforces these norms, creating a dynamic environment where social cohesion and collective values govern behavior more effectively than punitive legal measures in many social contexts.
Effectiveness of Legal Sanctions vs Informal Social Norms
Legal sanctions impose formal penalties enforced by institutions, effectively deterring violations through clear consequences such as fines or imprisonment. Informal social norms regulate behavior via community pressure and social approvals, often shaping conduct more subtly but persistently. Studies indicate that combining both approaches enhances compliance, with legal sanctions providing structure while social norms encourage internalized adherence.
Impact on Individual and Group Behavior
Legal sanctions impose formal penalties such as fines, imprisonment, or community service, directly influencing individual and group behavior through deterrence and enforcement of societal norms. Informal social control operates via social pressures, including approval, ridicule, or ostracism, shaping behavior by reinforcing cultural values and expectations within communities. Both mechanisms play crucial roles in maintaining social order, with legal sanctions targeting compliance through codified laws and informal control fostering conformity via interpersonal relationships.
Case Studies: Legal vs Informal Control in Practice
Case studies comparing legal sanctions and informal social control reveal distinct effectiveness based on social context and community cohesion. In tightly knit communities, informal social control such as peer pressure and social norms often prevent deviant behavior more efficiently than formal legal sanctions. Conversely, in urban settings with weaker social bonds, legal sanctions administered by law enforcement and judicial systems provide necessary deterrence and resolution for criminal acts.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Legal sanctions face challenges such as rigid enforcement, high costs, and potential inequities in judicial processes that may undermine public trust. Informal social control often struggles with inconsistency, cultural bias, and limited reach, making it less effective in diverse or anonymous societies. Both approaches can encounter limitations in addressing complex social behaviors due to their distinct scopes and mechanisms of influence.
Integrating Legal Sanctions and Informal Control for Social Order
Legal sanctions, enforced by formal institutions such as courts and law enforcement agencies, provide clear rules and penalties that maintain social order through deterrence and punishment. Informal social control operates through community norms, peer pressure, and socialization processes that encourage conformity without legal enforcement. Integrating legal sanctions with informal social control enhances social cohesion by combining formal authority with community values, creating a comprehensive framework that promotes compliance and reduces deviance effectively.
Legal sanctions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com